Abstract
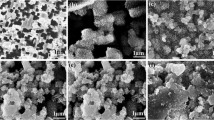
The effect of azelaic acid on microstructure evolution and electrical properties of anodic aluminum foil for electrolytic capacitor is studied quantitatively. The azelaic acid is selected as formation solution in the multi-step anodization process, and boric acid is applied for comparison. The field-emission scanning electron microscopy and X-ray diffractometer technologies are used for observation of microstructure and detection of crystallinity, respectively. The electrical properties are tested by LCR meter and T–V tester. The microstructure observation shows that the ‘corn-flake’ structures are taken place by ‘cotton-ball’ ones gradually along with the preparation process, and such phenomenon is more obvious when azelaic acid is used. The pores area of anodic aluminum foil formed in azelaic acid is larger because of the stronger acidity. The formation with azelaic acid induces smaller thickness of oxide film, promotes the formation of crystalline oxide, therefore, a barrier film with higher crystallinity and larger grain size is obtained. The barrier film formed in azelaic acid shows larger specific capacitance, lower withstand voltage and larger leakage current, which needs the multi-step anodization for performance improvement.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Z.S. Feng, J.J. Chen, C. Zhang, N. Zhao, Z. Liang, Ceram. Int. 38, 2501 (2012)
F. Chen, S.S. Park, ECS J. Solid State Sc. 4, 293 (2015)
L. Xiang, S.S. Park, Key Eng. Mater. 737, 143 (2017)
L. Liang, Y. He, H. Song, X. Yang, X. Cai, C. Xiong, Y. Li, Corros. Sci. 70, 180 (2013)
L. Liang, Y. He, H. Song, X. Yang, X. Cai, Corros. Sci. 79, 21 (2014)
G. Scaduto, M. Santamaria, P. Bocchetta, F. Di Quarto, Thin Solid Films 550, 128 (2014)
H. Uchi, T. Kanno, R.S. Alwitt, J. Electrochem. Soc. 148, 17 (2001)
J. Chang, C. Liao, C. Chen, W. Tsai, J. Power Sources 138, 301 (2004)
A.C. Geiculescu, T.F. Strange, Thin Solid Films 503, 45 (2006)
I. Vrublevsky, V. Parkoun, J. Schreckenbach, W.A. Goedel, Appl. Surf. Sci. 252, 5100 (2006)
N. Hassanzadeh, H. Omidvar, M. Poorbafrani, S.H. Tabaian, Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 38, 1305 (2013)
T. Kikuchi, T. Yamamoto, S. Natsui, R.O. Suzuki, Electrochim. Acta 123, 14 (2014)
R.A. Mirzoev, A.D. Davydov, D.K. Kurmyalevskaya, A.N. Bazylyk, S.I. Vystupov, Electrochim. Acta 184, 214 (2015)
J. Lee, J.Y. Kim, J.K. Kim, J.H. Lee, H.Y. Chung, Y.S. Tak, Corros. Sci. 51, 1501 (2009)
H. Takahashi, M. Yamaki, R. Furuichi, Corros. Sci. 31, 243 (1990)
C. Ban, Y. He, X. Shao, T. Nonferr, Metal. Soc. 21, 133 (2011)
C. Ban, Y. He, X. Shao, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. El. 24, 3442 (2013)
M. Sepúlveda, J.G. Castaño, F. Echeverría, Appl. Surf. Sci. 454, 210 (2018)
A.C. Geiculescu, T.F. Strange, Thin Solid Films 445, 105 (2003)
S. Pan, L. Liang, B. Lu, H. Li, J. Alloy. Compd. 823, 153795 (2020)
C. Ban, F. Wang, J. Chen, Z. Liu, J. Mater. Sci.-Mater. El. 29, 16166 (2018)
R.S. Alwitt, C.K. Dyer, Electrochim. Acta 23, 355 (1978)
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Project fund by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2019M663871XB), Postdoctoral Science Foundation of Guangxi Province of China, the Major scientific and technological projects of Guangxi Province of China (AA17202004), and the Innovation-driven Development Project of Hezhou City (ZX1907001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, S., Liang, L., Lu, B. et al. Effect of azelaic acid on microstructure evolution and electrical properties of anodic aluminum foil for electrolytic capacitor. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 32, 2579–2589 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-05025-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-05025-8