Abstract
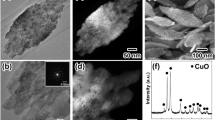
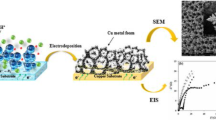
A simple annealing method was applied to prepare agglomerated copper nanoparticles on a bulk copper current collector. Copper oxide electrodes were obtained by heat treatment of bulk copper at different temperatures and for different lengths of time. The effect of annealing temperature and time on chemical and surface structure was explored. XRD, XPS, FTIR and SEM were used for characterization of the structural, compositional and morphological properties of non-annealed and annealed copper. The electrochemical performance of the electrodes was examined in different electrolytes (neutral, alkaline and ionic liquid). Copper-based electrodes were annealed at 300 °C for 30 min and their specific capacitance at a scan rate of 5 mV s−1 was calculated to be 1900 F g−1. The electrochemical performance of annealed copper was not enriched by annealing the copper electrode for long durations because the electrochemical reaction of the copper oxide film occurs between the alkali and only the outmost surface of the annealed copper. The performance of the as-prepared copper oxide electrodes was attributed to the morphology of the electrode, not its thickness. The synthesis of copper oxide by annealing in a muffle furnace could provide an easy method for the production of copper-based electrodes for supercapacitor applications.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. Apergis, J.E. Payne, Renewable and non-renewable energy consumption-growth nexus: evidence from a panel error correction model. Energy Econ. 34, 733–738 (2012)
R.J. Andres, G. Marland, I. Fung, E. Matthews, A 1 × 1 distribution of carbon dioxide emissions from fossil fuel consumption and cement manufacture, 1950–1990. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 10, 419–429 (1996)
S. Shafiee, E. Topal, When will fossil fuel reserves be diminished? Energy Policy 37, 181–189 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2008.08.016
F. Barbir, T. Molter, L. Dalton, Efficiency and weight trade-off analysis of regenerative fuel cells as energy storage for aerospace applications. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 30, 351–357 (2005)
R. Kötz, M. Carlen, Principles and applications of electrochemical capacitors. Electrochim. Acta 45, 2483–2498 (2000)
F. Béguin, V. Presser, A. Balducci, E. Frackowiak, Carbons and electrolytes for advanced supercapacitors. Adv. Mater. 26, 2219–2251 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201304137
L.L. Zhang, X.S. Zhao, Carbon-based materials as supercapacitor electrodes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 38, 2520–2531 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1039/b813846j
T. Brezesinski, J. Wang, S.H. Tolbert, B. Dunn, Ordered mesoporous α-MoO3 with iso-oriented nanocrystalline walls for thin-film pseudocapacitors. Nat. Mater. 9, 146–151 (2010)
M.F. Montemor, S. Eugénio, N. Tuyen, R.P. Silva, T.M. Silva, M.J. Carmezim, Nanostructured transition metal oxides produced by electrodeposition for application as redox electrodes for supercapacitors. Handb. Nanoelectrochem. Electrochem. Synth. Methods Prop. Charact. Tech. (2016), pp. 681–714
M. Ilhan, M.M. Koc, B. Coskun, F.Y. Lu, Optical, electrical and photoresponsive properties of Cu2NiSnS4 solar detectors. J. Electron. Mater. 49, 4457–4465 (2020)
O. Lupan, V. Postica, V. Cretu, N. Wolff, V. Duppel, L. Kienle, R. Adelung, Single and networked CuO nanowires for highly sensitive p-type semiconductor gas sensor applications. Phys. Status Solidi (RRL) Rapid Res. Lett. 10, 260–266 (2016)
C. Thangamani, M. Ponnar, P. Priyadharshini, P. Monisha, S.S. Gomathi, K. Pushpanathan, Magnetic behavior of ni-doped cuo nanoparticles synthesized by microwave irradiation method. Surf. Rev. Lett. 26, 1850184 (2019)
S.Z. Golkhatmi, M. Khalaj, A. Izadpanahi, A. Sedghi, One-step electrodeposition synthesis of high performance Graphene/Cu2O nanocomposite films on copper foils as binder-free supercapacitor electrodes. Solid State Sci. 106, 106336 (2020)
J. Chavez-Galan, R. Almanza, Solar filters based on iron oxides used as efficient windows for energy savings. Sol. Energy 81, 13–19 (2007)
L. Li, Z. Wang, T. Wang, J. Gong, B. Qi, Highly sensitive non-enzymatic MP sensor based on electrospun copper oxide-doped zirconium oxide composite microfibers. J. Electroanal. Chem. 846, 113171 (2019)
S. Deki, K. Akamatsu, T. Yano, M. Mizuhata, A. Kajinami, Preparation and characterization of copper (I) oxide nanoparticles dispersed in a polymer matrix. J. Mater. Chem. 8, 1865–1868 (1998)
M. Mirzaei, A.P. Soleymani, A. Ashrafi, M.M. Momeni, Electrochemically enhanced hydrothermal production of cupric oxide photoelectrode on copper substrate. J. Electrochem. Soc. 167, 66507 (2020)
L. Armelao, D. Barreca, M. Bertapelle, G. Bottaro, C. Sada, E. Tondello, A sol–gel approach to nanophasic copper oxide thin films. Thin Solid Films 442, 48–52 (2003)
C. Sachse, N. Weiß, N. Gaponik, L. Müller-Meskamp, A. Eychmüller, K. Leo, ITO-free, small-molecule organic solar cells on spray-coated copper-nanowire-based transparent electrodes. Adv. Energy Mater. 4, 1300737 (2014)
V. Branzoi, F. Branzoi, L. Pilan, Characterization of electrodeposited polymeric and composite modified electrodes on cobalt based alloy. Mater. Chem. Phys. 118, 197–202 (2009)
T. Cottineau, M. Toupin, T. Delahaye, T. Brousse, D. Bélanger, Nanostructured transition metal oxides for aqueous hybrid electrochemical supercapacitors. Appl. Phys. A 82, 599–606 (2006)
Y.T. Prabhu, K.V. Rao, V.S. Sai, T. Pavani, A facile biosynthesis of copper nanoparticles: a micro-structural and antibacterial activity investigation. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 21, 180–185 (2017)
M. Kouti, L. Matouri, Fabrication of nanosized cuprous oxide using fehling’s solution. Sci. Iran. 17, 73–78 (2010)
D. Collins, T. Luxton, N. Kumar, S. Shah, V.K. Walker, V. Shah, Assessing the impact of copper and zinc oxide nanoparticles on soil: a field study. PLoS ONE 7, e42663 (2012)
P.K. Raul, S. Senapati, A.K. Sahoo, I.M. Umlong, R.R. Devi, A.J. Thakur, V. Veer, CuO nanorods: a potential and efficient adsorbent in water purification. RSC Adv. 4, 40580–40587 (2014)
N.K. Yetim, N. Aslan, A. Sarıoğlu, N. Sarı, M.M. Koç, Structural, electrochemical and optical properties of hydrothermally synthesized transition metal oxide (Co3O4, NiO, CuO) nanoflowers. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. (2020), pp. 1–11
C. Carel, M. Mouallem-Bahout, J. Gaude, Re-examination of the non-stoichiometry and defect structure of copper (II) oxide or tenorite, Cu1 ± zO or CuO1 ± ϵ: a short review. Solid State Ion. 117, 47–55 (1999)
L.D.L.S. Valladares, D.H. Salinas, A.B. Dominguez, D.A. Najarro, S.I. Khondaker, T. Mitrelias, C.H.W. Barnes, J.A. Aguiar, Y. Majima, Crystallization and electrical resistivity of Cu2O and CuO obtained by thermal oxidation of Cu thin films on SiO2/Si substrates. Thin Solid Films 520, 6368–6374 (2012)
V.V.T. Padil, M. Černík, Green synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles using gum karaya as a biotemplate and their antibacterial application. Int. J. Nanomed. 8, 889 (2013). https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S40599
A. Azam, A.S. Ahmed, M. Oves, M.S. Khan, A. Memic, Size-dependent antimicrobial properties of CuO nanoparticles against Gram-positive and-negative bacterial strains. Int. J. Nanomed. 7, 3527 (2012)
M.F. Al-Kuhaili, Characterization of copper oxide thin films deposited by the thermal evaporation of cuprous oxide (Cu2O). Vacuum 82, 623–629 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2007.10.004
D. Tahir, S. Ilyas, B. Abdullah, B. Armynah, K. Kim, H.J. Kang, Modification in electronic, structural, and magnetic properties based on composition of composites copper (II) oxide (CuO) and carbonaceous material. Mater. Res. Express 6, 35705 (2018)
F.A. Akgul, G. Akgul, N. Yildirim, H.E. Unalan, R. Turan, Influence of thermal annealing on microstructural, morphological, optical properties and surface electronic structure of copper oxide thin films. Mater. Chem. Phys. 147, 987–995 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2014.06.047
P.F.B.D. Martins, P.P. Lopes, E.A. Ticianelli, V.R. Stamenkovic, N.M. Markovic, D. Strmcnik, Hydrogen evolution reaction on copper: promoting water dissociation by tuning the surface oxophilicity. Electrochem. Commun. 100, 30–33 (2019)
S. Dulal, E.A. Charles, S. Roy, Dissolution from electrodeposited copper–cobalt–copper sandwiches. J. Appl. Electrochem. 34, 151–158 (2004)
A.P. Abbott, G. Frisch, J. Hartley, W.O. Karim, K.S. Ryder, Anodic dissolution of metals in ionic liquids. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 25, 595–602 (2015)
G. Liang, F. Mo, Q. Yang, Z. Huang, X. Li, D. Wang, Z. Liu, H. Li, Q. Zhang, C. Zhi, Commencing an acidic battery based on a copper anode with ultrafast proton-regulated kinetics and superior dendrite-free property. Adv. Mater. 31, 1905873 (2019)
S.E. Moosavifard, M.F. El-Kady, M.S. Rahmanifar, R.B. Kaner, M.F. Mousavi, Designing 3D highly ordered nanoporous CuO electrodes for high-performance asymmetric supercapacitors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 7, 4851–4860 (2015)
K.P.S. Prasad, D.S. Dhawale, T. Sivakumar, S.S. Aldeyab, J.S.M. Zaidi, K. Ariga, A. Vinu, Fabrication and textural characterization of nanoporous carbon electrodes embedded with CuO nanoparticles for supercapacitors. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 12, 44602 (2011)
J.-Y. Go, S.-I. Pyun, A review of anomalous diffusion phenomena at fractal interface for diffusion-controlled and non-diffusion-controlled transfer processes. J. Solid State Electrochem. 11, 323–334 (2007)
J. Liu, J. Wang, C. Xu, H. Jiang, C. Li, L. Zhang, J. Lin, Z.X. Shen, Advanced energy storage devices: basic principles, analytical methods, and rational materials design. Adv. Sci. 5, 1700322 (2018)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Gaziantep University BAP for supplying the equipment used to carry out this research (MF.ALT.19.18).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yavuz, A., Bedir, M. & Tunç, A. Fabrication of heat-treated bulk copper for binder-free electrodes. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 31, 21168–21179 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-04629-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-04629-4