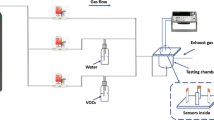
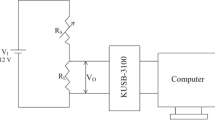
Abstract
In this study electrochemical sensors, based on undoped and doped (Cr, Mn, Cu and Zn) SnO2 as a sensing electrode material, were fabricated and used to detect acetone (10–600 ppb) and toluene (1–40 ppb). The sol–gel synthesized nanomaterial was characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), UV–Visible (UV–Vis) spectroscopy, Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy and Contact angle (CA). Electrochemical sensing characteristics were determined from the Cyclic Voltammetry (CV), Differential Pulse Voltammetry (DPV) and Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopic analysis (EIS). The electrochemical results reveal that the sensors’ response to acetone was highest with copper doping whereas in case of toluene sensing zinc dopants showed highest sensitivity. This work demonstrated that acetone and toluene sensing is selective with copper and zinc doping and these doped SnO2 nanomaterials can be used for the formation of array/electronic nose and help in simultaneous detection of acetone and toluene both.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Ansari, H. Fouad, H. Shin, Z. Ansari, Electrochemical enzyme-less urea sensor based on nano-tin oxide synthesized by hydrothermal technique. Chem. Biol. Interact. 242, 45–49 (2015)
A. Umar, K. Singh, S. Mehta, H. Fouad, O. Alothman, Highly sensitive enzyme-less glucose biosensor based on α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. Lett. 10(3), 429–434 (2018)
M. Obaid, O. Fadali, B. Lim, H. Fouad, N. Barakat, Super-hydrophilic and highly stable in oils polyamide-polysulfone composite membrane by electrospinning. Mater. Lett. 138, 196–199 (2015)
N. Parveen, S. Ansari, S. Ansari, H. Fouad, N. Abd El-Salam, M. Cho, Solid-state symmetrical supercapacitor based on hierarchical flower-like nickel sulfide with shape-controlled morphological evolution. Electrochim. Acta 268, 82–93 (2018)
R.M. Kaur, A. Umar, S. Mehta, S. Singh, S. Kansal, H. Fouad, O. Alothman, Materials 11(11), 2254 (2018)
L. Pauling, A.B. Robinson, R. Teranishi, P. Cary, Quantitative analysis of urine vapor and breath by gas-liquid partition chromatography. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 68, 2374–2376 (1971)
S.M. Gordon, J.P. Szidon, B.K. Krotoszynski, R.D. Gibbons, H.J. O'Neill, Volatile organic compounds in exhaled air from patients with lung cancer. Clin. Chem. 31, 1278–1282 (1985)
M. Phillips, K. Gleeson, J.M. Hughes, J. Greenberg, R.N. Cataneo, L. Baker, W.P. McVay, Volatile organic compounds in breath as markers of lung cancer: a cross-sectional study. Lancet 353, 1930–1933 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(98)07552-7
M. Phillips, R.N. Cataneo, A.R. Cummin, A.J. Gagliardi, K. Gleeson, J. Greenberg, R.A. Maxfield, W.N. Rom, Detection of lung cancer with volatile markers in the breath. Chest 123, 2115–2123 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.123.6.2115
Y. Saalberg, M. Wolff, VOC breath biomarkers in lung cancer. Clin. Chim. Acta 459, 5–9 (2016)
C.J. Wysocki, P. Dalton, M.J. Brody, H.J. Lawley, Acetone odor and irritation thresholds obtained from acetone-exposed factory workers and from control (occupationally unexposed) subjects. Am. Ind. Hygiene Assoc. J. 58(10), 704–712 (1997)
S. Liu, F. Zhang, H. Li, T. Chen, Y. Wang, Acetone detection properties of single crystalline tungsten oxide plates synthesized by hydrothermalmethod using cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide supermolecular template. Sens. Actuators B 162(1), 259–268 (2012)
T. Xiao, X.-Y. Wang, Z.-H. Zhao et al., Highly sensitive and selective acetone sensor based on C-doped WO3 for potential diagnosis of diabetes mellitus Dedicated to Prof Xinquan Xin on the occasion of his 80th birthday. Sens. Actuators B 199, 210–219 (2014)
T.D.C. Minh, D.R. Blake, P.R. Galassetti, The clinical potential of exhaled breath analysis for diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 97(2), 195–205 (2012)
H. Huang, J. Zhou, S. Chen, L. Zeng, Y. Huang, Sens. Actuator B-Chem. 101, 316 (2004)
M. Righettoni, A. Tricoli, S.E. Pratsinis, Si:WO3 sensors for highly selective detection of acetone for easy diagnosis of diabetes by breath analysis. Anal. Chem. 82, 3581–3587 (2010)
S. Kim, S. Park, S. Park, C. Lee, Acetone sensing of Au and Pd-decorated WO3 nanorod sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 209, 180–185 (2015)
B.L. Zhu, C.S. Xie, W.Y. Wang, K.J. Huang, J.H. Hu, Improvement in gas sensitivity of ZnO thick film to volatile organic compounds (VOCs) by adding TiO2. Mater. Lett. 58, 624–629 (2004)
L. Wang et al., Concave Cu2O octahedral nanoparticles as an advanced sensing material for benzene (C6H6) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2) detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 223, 311–317 (2016)
Y. Zeng et al., Enhanced toluene sensing characteristics of TiO2-doped flowerlike ZnO nanostructures. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 140, 73–78 (2009)
M. Nakagawa, S. Kawabata, K. Nishiyama, K. Utsunomiya, I. Yamamoto, T. Wada, Y. Yamashita, N. Yamashita, Sens. Actuator B-Chem. 34, 334 (1996)
Q.-H. Wu, J. Li, S.-G. Sun, Nano SnO2 gas sensors. Curr. Nanosci. 6(5), 525–538 (2010)
M.E. Franke, T.J. Koplin, U. Simon, Metal and metal oxide nanoparticles in chemiresistors: does the nanoscale matter? Small 2(1), 36–50 (2006)
N. Yamazoe, New approaches for improving semiconductor gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B 5(1–4), 7–19 (1991)
Y.-F. Sun et al., Metal oxide nanostructures and their gas sensing properties: a review. Sensors 12(3), 2610–2631 (2012)
S.M. Sedghi, Y. Mortazavi, A. Khodadadi, Low temperature CO and CH4 dual selective gas sensor using SnO2 quantum dots prepared by sonochemical method. Sens. Actuators B 145(1), 7–12 (2010)
D.-F. Zhang et al., Size-controllable one-dimensinal SnO2 nanocrystals: synthesis, growth mechanism, and gas sensing property. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 8(42), 4874–4880 (2006)
Q. Lipeng et al., The template-free synthesis of square-shaped SnO2 nanowires: the temperature effect and acetone gas sensors. Nanotechnology 19(18), 185705 (2008)
A. Kolmakov et al., Enhanced gas sensing by individual SnO2 nanowires and nanobelts functionalized with Pd catalyst particles. Nano Lett. 5(4), 667–673 (2005)
Y.J. Kwon et al., Selective improvement of NO2 gas sensing behavior in SnO2 nanowires by ion-beam irradiation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8(21), 13646–13658 (2016)
T. Van Dang et al., Chlorine gas sensing performance of on-chip grown ZnO, WO3, and SnO2 nanowire sensors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8(7), 4828–4837 (2016)
M. Sun, Y. Du, W. Hao, H. Xu, Y. Yu, T. Wang, Fabrication and wettability of ZnO nanorod array. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 25, 53–57 (2009)
X. Fang, Z. Yu, X. Sun, X. Liu, F. Qin, Formation of superhydrophobic boehmite film on glass substrate by Sol-gel method. Front. Chem. Eng. China 3, 97–101 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11705-009-0148-y
B.L. Caetano et al., Mechanisms of SnO2 nanoparticles formation and growth in acid ethanol solution derived from SAXS and combined Raman–XAS time-resolved studies. Chem. Mater. 26, 6777–6785 (2014)
M. Karmaoui et al., One-step synthesis, structure, and band gap properties of SnO2 nanoparticles made by a low temperature nonaqueous sol–gel technique. ACS Omega 3, 13227–13238 (2018)
M.P. Subramaniam, G. Arunachalam, R. Kandasamy, P. Veluswamy, I. Hiroya, Effect of pH and annealing temperature on the properties of tin oxide nanoparticles prepared by sol–gel method. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 29, 658–666 (2018)
D. Varshney, K. Verma, Effect of stirring time on size and dielectric properties of SnO2 nanoparticles prepared by co-precipitation method. J. Mol. Struct. 1034, 216–222 (2013)
E.P. Randviir, A cross examination of electron transfer rate constants for carbon screen-printed electrodes using Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy and cyclic voltammetry. Electrochim. Acta 286, 179–186 (2018)
Acknowledgements
Zeenat Khatoon is thankful to Indian Council of Medical Research, New Delhi for providing Senior Research Fellowship and UGC Non-NET fellowship, Government of India. H K Seo acknowledges support of the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by Government of Korea (MSIT, No. 2018R1A4A1025528). Authors acknowledge the Central Instrumentation Facility and DST-PURSE Programme of Jamia Millia Islamia, New Delhi. This work is supported by Researchers Supporting Project number (RSP-2020/117), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declare there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khatoon, Z., Fouad, H., Seo, H.K. et al. Feasibility study of doped SnO2 nanomaterial for electronic nose towards sensing biomarkers of lung cancer. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 31, 15751–15763 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-04137-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-04137-5