Abstract
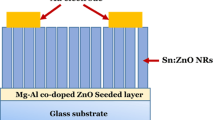
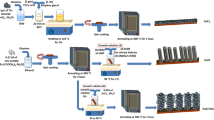
Tin-doped zinc oxide/tin oxide nanorod (Sn:ZnO/SnO2 NR) films were successfully synthesized using a solution immersion method by manipulating the pH concentration of the solutions to fabricate an ethanol gas sensor. Sn:ZnO/SnO2 NR films were prepared at constant Sn:ZnO solution pH (5.5), while the pH of the SnO2 solutions was varied between 4.5 and 6.5. In this study, the structural, morphological, and optical properties of Sn:ZnO/SnO2 NR films were investigated. The diameter and thickness of Sn:ZnO/SnO2 NR films were found to increase with the SnO2 pH. Interestingly, the Sn:ZnO/SnO2 NR sample that was prepared at SnO2 solution pH 5.5 showed the highest relative peak intensity along the c-axis plane orientation, which enhanced the sensor performance due to the shorter carrier pathway. In addition, this sample indicated a higher level of surface donor-related defects, which are favorable for sensing device performance. The samples were exposed to ethanol gas to measure their gas-sensing properties. Sn:ZnO/SnO2 NR films prepared at SnO2 solution pH 5.5 showed the highest sensing performance with short response/recovery times.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Zhang, J. Zhao, H. Lu, L. Li, J. Zheng, J. Zhang, H. Li, Z. Zhu, Highly sensitive and selective dimethylamine sensors based on hierarchical ZnO architectures composed of nanorods and nanosheet-assembled microspheres. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 171–172, 1101–1109 (2012)
C. Oros, M. Horprathum, A. Wisitsoraat, T. Srichaiyaperk, B. Samransuksamer, S. Limwichean, P. Eiamchai, D. Phokharatkul, N. Nuntawong, C. Chananonnawathorn, V. Patthanasettakul, A. Klamchuen, J. Kaewkhao, A. Tuantranont, P. Chindaudom, Ultra-sensitive NO2 sensor based on vertically aligned SnO2 nanorods deposited by DC reactive magnetron sputtering with glancing angle deposition technique. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 223, 936–945 (2016)
P. Cao, Z. Yang, S.T. Navale, S. Han, X. Liu, W. Liu, Y. Lu, F.J. Stadler, D. Zhu, Ethanol sensing behavior of Pd-nanoparticles decorated ZnO-nanorod based chemiresistive gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 298, 126850 (2019)
X. Jia, H. Fan, Preparation and ethanol sensing properties of the superstructure SnO2/ZnO composite via alcohol-assisted hydrothermal route. Mater. Res. Bull. 45, 1496–1500 (2010)
Y. Liu, J. Huang, J. Yang, S. Wang, Pt nanoparticles functionalized 3D SnO2 nanoflowers for gas sensor application. Solid-State Electron. 130, 20–27 (2017)
Q. Ge, S.Y. Ma, Y.B. Xu, X.L. Xu, H. Chen, Z. Qiang, H.M. Yang, L. Ma, Q.Z. Zeng, Preparation, characterization and gas sensing properties of Pr-doped ZnO/SnO2 nanoflowers. Mater. Lett. 191, 5–9 (2017)
S. Liu, B. Yu, F. Li, Y. Ji, T. Zhang, Coaxial electrospinning route to prepare Au-loading SnO2 hollow microtubes for non-enzymatic detection of H2O2. Electrochim. Acta 141, 161–166 (2014)
R. Mohamed, M.H. Mamat, A.S. Ismail, M.F. Malek, A.S. Zoolfakar, Z. Khusaimi, A.B. Suriani, A. Mohamed, M.K. Ahmad, M. Rusop, Hierarchically assembled tin-doped zinc oxide nanorods using low-temperature immersion route for low temperature ethanol sensing. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 28, 16292–16305 (2017)
Z. Zhang, M. Xu, L. Liu, X. Ruan, J. Yan, W. Zhao, J. Yun, Y. Wang, S. Qin, T. Zhang, Novel SnO2@ZnO hierarchical nanostructures for highly sensitive and selective NO2 gas sensing. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 257, 714–727 (2018)
J. Deng, B. Yu, Z. Lou, L. Wang, R. Wang, T. Zhang, Facile synthesis and enhanced ethanol sensing properties of the brush-like ZnO–TiO2 heterojunctions nanofibers. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 184, 21–26 (2013)
B. Zhang, W. Fu, H. Li, X. Fu, Y. Wang, H. Bala, G. Sun, X. Wang, Y. Wang, J. Cao, Z. Zhang, Actinomorphic ZnO/SnO2 core–shell nanorods: two-step synthesis and enhanced ethanol sensing propertied. Mater. Lett. 160, 227–230 (2015)
N.D. Khoang, D.D. Trung, N. Van Duy, N.D. Hoa, N. Van Hieu, Design of SnO2/ZnO hierarchical nanostructures for enhanced ethanol gas-sensing performance. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 174, 594–601 (2012)
S.H. Yan, S.Y. Ma, W.Q. Li, X.L. Xu, L. Cheng, H.S. Song, X.Y. Liang, Synthesis of SnO2–ZnO heterostructured nanofibers for enhanced ethanol gas-sensing performance. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 221, 88–95 (2015)
W. Li, S. Ma, Y. Li, G. Yang, Y. Mao, J. Luo, D. Gengzang, X. Xu, S. Yan, Enhanced ethanol sensing performance of hollow ZnO–SnO2 core–shell nanofibers. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 211, 392–402 (2015)
Y. Ling-min, L. Sheng, Y. Bing, H. Miao-miao, K. Meng-di, F. Xinhui, A highly sensitive ethanol gas sensor based on mesoporous SnO2 fabricated from a facile double-surfactant template method. Mater. Lett. 158, 409–412 (2015)
S. Hussain, T. Liu, B. Miao, M. Kashif, N. Aslam, M. Rashad, W. Zeng, X. Peng, Embedded ZnO nanorods and gas-sensing properties. Ceram. Int. 41, 4861–4866 (2015)
C.M. Shin, J.H. Heo, J.H. Park, T.M. Lee, H. Ryu, B.C. Shin, W.J. Lee, H.K. Kim, The effect of pH on ZnO hydrothermal growth on PES flexible substrates. Physica E 43, 54–57 (2010)
J. Wang, L. Gao, Synthesis of uniform rod-like, multi-pod-like ZnO whiskers and their photoluminescence properties. J. Cryst. Growth 262, 290–294 (2004)
Y. Liu, W. Gao, Growth process, crystal size and alignment of ZnO nanorods synthesized under neutral and acid conditions. J. Alloys Compd. 629, 84–91 (2015)
M.F. Malek, M.H. Mamat, Z. Khusaimi, M.Z. Sahdan, M.Z. Musa, A.R. Zainun, A.B. Suriani, N.D. Md Sin, S.B. Abd Hamid, M. Rusop, Sonicated sol–gel preparation of nanoparticulate ZnO thin films with various deposition speeds: the highly preferred c-axis (002) orientation enhances the final properties. J. Alloys Compd. 582, 12–21 (2014)
M.J. Alam, D.C. Cameron, Preparation and properties of transparent conductive aluminum-doped zinc oxide thin films by sol–gel process. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 19, 1642–1646 (2001)
D. Lu, Q. Gao, X. Wu, Y. Fan, ZnO nanostructures decorated hollow glass microspheres as near infrared reflective pigment. Ceram. Int. 43, 9164–9170 (2017)
F. Tsin, A. Venerosy, J. Vidal, S. Collin, J. Clatot, L. Lombez, M. Paire, S. Borensztajn, C. Broussillou, P.P. Grand, S. Jaime, D. Lincot, J. Rousset, Electrodeposition of ZnO window layer for an all-atmospheric fabrication process of chalcogenide solar cell. Sci. Rep. 5, 8961 (2015)
C.-H. Hsu, D.-H. Chen, Synthesis and conductivity enhancement of Al-doped ZnO nanorod array thin films. Nanotechnology 21, 285603 (2010)
G. Kwak, S. Jung, K. Yong, Multifunctional transparent ZnO nanorod films. Nanotechnology 22, 115705 (2011)
J. Zhang, W. Que, Preparation and characterization of sol–gel Al-doped ZnO thin films and ZnO nanowire arrays grown on Al-doped ZnO seed layer by hydrothermal method. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 94, 2181–2186 (2010)
H.K. Lee, M.S. Kim, J.S. Yu, Effect of AZO seed layer on electrochemical growth and optical properties of ZnO nanorod arrays on ITO glass. Nanotechnology 22, 445602 (2011)
J.H. Lee, C.-Y. Chou, Z. Bi, C.-F. Tsai, H. Wang, Growth-controlled surface roughness in Al-doped ZnO as transparent conducting oxide. Nanotechnology 20, 395704 (2009)
M.F. Malek, M.H. Mamat, M.Z. Musa, T. Soga, S.A. Rahman, S.A.H. Alrokayan, H.A. Khan, M. Rusop, Metamorphosis of strain/stress on optical band gap energy of ZAO thin films via manipulation of thermal annealing process. J. Lumin. 160, 165–175 (2015)
M.H. Mamat, Z. Khusaimi, M.Z. Musa, M.F. Malek, M. Rusop, Fabrication of ultraviolet photoconductive sensor using a novel aluminium-doped zinc oxide nanorod–nanoflake network thin film prepared via ultrasonic-assisted sol–gel and immersion methods. Sens. Actuators A 171, 241–247 (2011)
M.H. Mamat, M.Z. Sahdan, Z. Khusaimi, A.Z. Ahmed, S. Abdullah, M. Rusop, Influence of doping concentrations on the aluminum doped zinc oxide thin films properties for ultraviolet photoconductive sensor applications. Opt. Mater. 32, 696–699 (2010)
R. Ghosh, D. Basak, S. Fujihara, Effect of substrate-induced strain on the structural, electrical, and optical properties of polycrystalline ZnO thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 96, 2689–2692 (2004)
C.J. Brinker, G.W. Scherer, Sol–Gel Science: The Physics and Chemistry of Sol–Gel Processing (Academic Press, New York, 2013)
J.-H. Yim, Y.-Y. Lyu, H.-D. Jeong, S.A. Song, I.-S. Hwang, J. Hyeon-Lee, S.K. Mah, S. Chang, J.-G. Park, Y.F. Hu, J.N. Sun, D.W. Gidley, The preparation and characterization of small mesopores in siloxane-based materials that use cyclodextrins as templates. Adv. Funct. Mater. 13, 382–386 (2003)
G. Wypych, Handbook of Fillers (ChemTec, Norwich, 1999)
V. Pandey, N. Mehta, S.K. Tripathi, D.A. Kumar, Optical band gap and optical constants in Se85Te15-xPbx thin films. J. Optoelectron. Adv. Mater. 7, 39 (2005)
S. Mridha, D. Basak, Effect of thickness on the structural, electrical and optical properties of ZnO films. Mater. Res. Bull. 42, 875–882 (2007)
J.K. Liang, H.L. Su, C.L. Kuo, S.P. Kao, J.W. Cui, Y.C. Wu, J.C.A. Huang, Structural, optical and electrical properties of electrodeposited Sb-doped ZnO nanorod arrays. Electrochim. Acta 125, 124–132 (2014)
S.K. Mishra, S. Bayan, R. Shankar, P. Chakraborty, R.K. Srivastava, Efficient UV photosensitive and photoluminescence properties of sol–gel derived Sn doped ZnO nanostructures. Sens. Actuators A 211, 8–14 (2014)
D.-T. Phan, G.-S. Chung, Effects of defects in Ga-doped ZnO nanorods formed by a hydrothermal method on CO sensing properties. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 187, 191–197 (2013)
S. Wei, J. Lian, H. Wu, Annealing effect on the photoluminescence properties of ZnO nanorod array prepared by a PLD-assistant wet chemical method. Mater. Charact. 61, 1239–1244 (2010)
N.S. Norberg, D.R. Gamelin, Influence of surface modification on the luminescence of colloidal ZnO nanocrystals. J. Phys. Chem. B 109, 20810–20816 (2005)
H. Zhou, H. Alves, D.M. Hofmann, W. Kriegseis, B.K. Meyer, G. Kaczmarczyk, A. Hoffmann, Behind the weak excitonic emission of ZnO quantum dots: ZnO/Zn(OH)2 core-shell structure. Appl. Phys. Lett. 80, 210–212 (2002)
P. Jiang, J.-J. Zhou, H.-F. Fang, C.-Y. Wang, Z.L. Wang, S.-S. Xie, Hierarchical shelled ZnO structures made of bunched nanowire arrays. Adv. Funct. Mater. 17, 1303–1310 (2007)
M. JayChithra, M. Sathya, K. Pushpanathan, Effect of pH on crystal size and photoluminescence property of ZnO nanoparticles prepared by chemical precipitation method. Acta Metall. Sin. (Engl. Lett.) 28, 394–404 (2015)
R. Xie, T. Sekiguchi, T. Ishigaki, N. Ohashi, D. Li, D. Yang, B. Liu, Y. Bando, Enhancement and patterning of ultraviolet emission in ZnO with an electron beam. Appl. Phys. Lett. 88, 134103 (2006)
M.-W. Ahn, K.-S. Park, J.-H. Heo, J.-G. Park, D.-W. Kim, K.J. Choi, J.-H. Lee, S.-H. Hong, Gas sensing properties of defect-controlled ZnO-nanowire gas sensor. Appl. Phys. Lett. 93, 263103 (2008)
S. Luo, J. Fan, W. Liu, M. Zhang, Z. Song, C. Lin, X. Wu, P.K. Chu, Synthesis and low-temperature photoluminescence properties of SnO2 nanowires and nanobelts. Nanotechnology 17, 1695–1699 (2006)
L.M. Li, Z.F. Du, T.H. Wang, Enhanced sensing properties of defect-controlled ZnO nanotetrapods arising from aluminum doping. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 147, 165–169 (2010)
N. Han, L. Chai, Q. Wang, Y. Tian, P. Deng, Y. Chen, Evaluating the doping effect of Fe, Ti and Sn on gas sensing property of ZnO. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 147, 525–530 (2010)
C.-L. Hsu, Y.-D. Gao, Y.-S. Chen, T.-J. Hsueh, Vertical Ti doped ZnO nanorods based on ethanol gas sensor prepared on glass by furnace system with hotwire assistance. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 192, 550–557 (2014)
M.Z. Ahmad, A.Z. Sadek, K. Latham, J. Kita, R. Moos, W. Wlodarski, Chemically synthesized one-dimensional zinc oxide nanorods for ethanol sensing. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 187, 295–300 (2013)
S. Roy, N. Banerjee, C.K. Sarkar, P. Bhattacharyya, Development of an ethanol sensor based on CBD grown ZnO nanorods. Solid-State Electron. 87, 43–50 (2013)
X. Li, Y. Chang, Y. Long, Influence of Sn doping on ZnO sensing properties for ethanol and acetone. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 32, 817–821 (2012)
S. Hemmati, A. AnarakiFirooz, A.A. Khodadadi, Y. Mortazavi, Nanostructured SnO2–ZnO sensors: highly sensitive and selective to ethanol. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 160, 1298–1303 (2011)
W.-H. Zhang, W.-D. Zhang, Fabrication of SnO2–ZnO nanocomposite sensor for selective sensing of trimethylamine and the freshness of fishes. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 134, 403–408 (2008)
J.Y. Park, K. Asokan, S.-W. Choi, S.S. Kim, Growth kinetics of nanograins in SnO2 fibers and size dependent sensing properties. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 152, 254–260 (2011)
S.H. Yan, S.Y. Ma, X.L. Xu, W.Q. Li, J. Luo, W.X. Jin, T.T. Wang, X.H. Jiang, Y. Lu, H.S. Song, Preparation of SnO2–ZnO hetero-nanofibers and their application in acetone sensing performance. Mater. Lett. 159, 447–450 (2015)
W. Tang, J. Wang, P. Yao, X. Li, Hollow hierarchical SnO2-ZnO composite nanofibers with heterostructure based on electrospinning method for detecting methanol. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 192, 543–549 (2014)
Z. Zhang, C. Shao, X. Li, L. Zhang, H. Xue, C. Wang, Y. Liu, Electrospun nanofibers of ZnO−SnO2 heterojunction with high photocatalytic activity. J. Phys. Chem. C 114, 7920–7925 (2010)
J.Y. Park, S.-W. Choi, S.S. Kim, A model for the enhancement of gas sensing properties in SnO2–ZnO core–shell nanofibres. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 44, 205403 (2011)
S.-W. Choi, A. Katoch, J. Zhang, S.S. Kim, Electrospun nanofibers of CuOSnO2 nanocomposite as semiconductor gas sensors for H2S detection. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 176, 585–591 (2013)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Grant No. FRGS/600-IRMI/FRGS 5/3 (264/2019). The authors would like to thank the Research Management Institute (RMI), Universiti Teknologi MARA (UiTM), and Ministry of Higher Education Ministry (MoHE), Malaysia, for the financial support. The authors thank Mrs. Ts. Irmaizatussyehdany Buniyamin (Senior Research Officer), Mr. Ts. Salifairus Mohammad Jafar (UiTM Senior Science Officer), Mr. Mohd Azlan Jaafar (UiTM assistant engineer), Mr. Suhaimi Ahmad (UiTM assistant engineer), and Mr. Muhamad Faizal Abd Halim (Assistant Research Officer) for their kind support on this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohamed, R., Mamat, M.H., Malek, M.F. et al. Controllable synthesis of Sn:ZnO/SnO2 nanorods: pH-dependent growth for an ethanol gas sensor. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 31, 15394–15406 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-04103-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-04103-1