Abstract
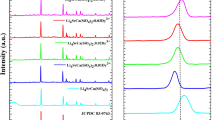
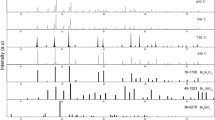
A series of Bi4Si3O12:Dy3+ phosphor have been synthesized via conventional solid-state reaction method and its luminescence properties were investigated as near cool white light emitting and long afterglow phosphor. Crystal structure and phase structure characterization is determined using X-ray diffraction (XRD), SEM and EDS. Rietveld structural refinement and XRD confirms that prepared sample exhibit pure cubic structure [space group I-43d]. Photoluminescence spectra of both doped and undoped Bi4Si3O12 phosphor were efficiently excited in the range of 200-450 nm, and prepared phosphor under 272 nm excitation exhibit three emission peaks located at 463 nm(blue), 482 nm(blue) and 576 nm (yellow) corresponding to 3P1 → 1S0, 4F9/2 → 6H15/2 and 4F9/2 → 6H13/2 transitions. Characteristic emission peaks of Dy3+ centered at 482 nm and 576 nm were assigned for white light emission. The calculated Commission Internationale de I’Eclairage (CIE) chromaticity confirms that with Dy3+ doping, the luminescence co-ordinates of Bi4Si3O12 phosphor shift to near white(x = 0.316, y = 0.358) region which is close to commercial pc-LED (Blue LED + YAG:Ce3+) (x = 0.320, y = 0.320) co-ordinates. Computation of correlated color temperature 6184 K endorses that prepared phosphor is cool in nature and can be served as white light emitting phosphor. Comparative thermoluminescence study of UV and γ-irradiated Bi4Si3O12:Dy3+ phosphor is performed for the dosimetry application. TL intensity is recorded maximum at 30 min under UV irradiation (256 nm), and for γ irradiation, it was recorded at 10 kGy dose rate. γ-irradiated Bi4Si3O12:Dy3+ phosphor TL study is reported for the first time at different dose rate and concentration for high dosimetry application. The defect characteristic is examined, Trap depths and other kinetic parameters are also evaluated by Chen’s peak shape method. Decay and fading measurement under UV/γ irradiation are performed to examine the long after glow properties of prepared samples. TL emission spectrum studies are also performed.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Tiwari, N. Brahme, R. Sharma, D.P. Bisen, S.K. Sao, S.J. Dhoble, A study on the luminescence properties of gamma-ray-irradiated white light emitting Ca2Al2SiO7:Dy3+ phosphors fabricated using a combustion-assisted method. RSC Adv. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra04913c
S. Sharma, N. Brahme, D.P. Bisen, P. Dewangan, Cool white light emission from Dy 3+ activated alkaline alumino silicate phosphors. Opt. Express (2018). https://doi.org/10.1364/oe.26.029495
Y. Zhang, J. Xu, Q. Cui, B. Yang, Eu3+ -doped Bi4 Si3 O12 red phosphor for solid state lighting: microwave synthesis, characterization, photoluminescence properties and thermal quenching mechanisms. Sci. Rep. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep42464
M.L. Wang, J.Y. Xu, Y. Zhang, Y.Q. Chu, B.B. Yang, H. Shen, T. Tian, Growth and thermo-luminescence properties. Wuji Cailiao Xuebao (2016). https://doi.org/10.15541/jim20160221
B. Yang, J. Xu, Y. Zhang, H. Zeng, T. Tian, Y. Chu, Y. Pan, Q. Cui, Improvement and luminescent mechanism of Bi4Si3O12 scintillation crystals by Dy3+ doping. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nima.2015.10.033
B. Yang, J. Xu, Y. Zhang, Y. Chu, M. Wang, Y. Wen, A yellow emitting phosphor Dy:Bi4Si3O12 crystal for LED application. Mater. Lett. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2014.07.167
T. Tian, H. Feng, Y. Zhang, D. Zhou, H. Shen, H. Wang, J. Xu, Crystal growth and luminescence properties of Dy3+ and Ge4+ Co-doped Bi4Si3O12 single crystals for high power warm white LED. Crystals (2017). https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst7080249
I. Bureau, Description Title of Invention : LUMINESCENT BISMUTH SILICATES, USE, 2016.
A.R. Kadam, R.S. Yadav, G.C. Mishra, S.J. Dhoble, Effect of singly, doubly and triply ionized ions on downconversion photoluminescence in Eu3+ doped Na2Sr2Al2PO4Cl9 phosphor: a comparative study. Ceram. Int. 46, 3264–3274 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.10.032
B.H. Toby, R factors in RIETVELD analysis: how good is good enough? Powder Diffr. 21, 67–70 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1154/1.2179804
Q. Wei, G. Liu, Z. Zhou, H. Yang, J. Zhuang, Q. Liu, Luminescence behaviors of a novel white-emitting phosphor Bi 4Si3O12: Dy prepared via sol-gel route. J. Lumin. 145, 803–807 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2013.08.069
B. Yang, J. Xu, J. Zou, Y. Zhang, T. Tian, Y. Chu, M. Wang, Bridgman growth, luminescence and energy transfer studies of Tm3+ or/and Dy3+ co-doped Bi4Si3O12 crystal phosphor. J. Ceram. Process. Res. 17, 537–542 (2016)
Y. Shen, K. Qiu, J. Wang, W. Zhang, Q. Tang, Synthesis of Dy3+ co-doped Bi4Si3O12:Sm3+ phosphors with enhanced red-emitting properties. Ceram. Int. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.08.174
F.Y. Zhang, J.J. Xie, T. Wang, D.B. Lin, W.Q. Xiao, Y. Shi, F. Lei, L. Zhang, Synthesis and luminescence properties of Bi4Si3O12:Sm3+ phosphor. Rengong Jingti Xuebao/Journal of Synthetic Crystals. 43, 15946–15951 (2017)
P. Dewangan, D.P. Bisen, N. Brahme, S. Sharma, Structural characterization and luminescence properties of Dy3+ doped Ca3MgSi2O8 phosphors. J. Alloy. Compd. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.10.390
Y. Guo, B.K. Moon, B.C. Choi, J.H. Jeong, J.H. Kim, Multi-wavelength excited white-emitting K2Gd(1–x)(PO4)(WO4): X Dy3+ phosphors with satisfactory thermal properties for UV-LEDs. RSC Adv. 7, 23083–23092 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ra02242e
C.Y. Tsai, J.W. Lin, Y.P. Huang, Y.C. Huang, Modeling and assessment of long afterglow decay curves. Sci. World J. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/102524
S.K. Sao, N. Brahme, D.P. Bisen, G. Tiwari, S.J. Dhoble, Mechanoluminescence, thermoluminescence and photoluminescence studies of UV/γ-irradiated Ba2MgSi2O7:Dy 3+ phosphors. J. Lumin. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2016.08.052
G. Tiwari, N. Brahme, R. Sharma, D.P. Bisen, S.K. Sao, S. Tigga, Luminescence properties of dysprosium doped di-calcium di-aluminium silicate phosphors. Opt. Mater. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2016.05.033
B.S. Prathibha, M.S. Chandrashekara, H. Nagabhushana, K.P. Ramesh, B.M. Naghabhushana, Thermoluminescence Studies on Sr2SiO4 nano powder. Procedia Mater. Sci. 5, 944–952 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mspro.2014.07.382
P. Dewangan, D.P. Bisen, N. Brahme, R.K. Tamrakar, K. Upadhyay, S. Sharma, I.P. Sahu, Studies on thermoluminescence properties of alkaline earth silicate phosphors. J. Alloy. Compd. 735, 1383–1388 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.11.293
M. Yüksel, T. Dogan, S. Balci-Yegen, S. Akca, Z.G. Portakal, N. Kucuk, M. Topaksu, Heating rate properties and kinetic parameters of thermoluminescence glow curves of La-doped zinc borate. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 151, 149–155 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2018.06.020
A. Deshpande, N.S. Dhoble, S.C. Gedam, S.J. Dhoble, Photo and thermoluminescence in K2Mg(SO4)2: Dy phosphor and evaluation of trapping parameters. J. Lumin. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2016.08.003
C. Ye, Ca2MgSi2O7:Ce3+/Tb3+/Eu3+ phosphors: Multicolor tunable luminescence via Ce3+ → Tb3+, Tb3+ → Eu3+ and Ce3+ → Tb3+ → Eu3+ energy transfers. J. Lumin. 213, 75–81 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2019.05.004
Acknowledgements
The author is very grateful to CSIR for CSIR-SRF fellowship, NIT Raipur for the SEM and EDS studies and Department of Physics, R.T.M University, Nagpur for Gamma radiation studies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chandrawanshi, E., Bisen, D.P., Brahme, N. et al. Photoluminescence and comparative thermoluminescence studies of UV/γ-irradiated Dy3+ doped bismuth silicate phosphor. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 31, 14454–14465 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-04005-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-04005-2