Abstract
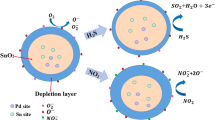
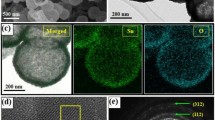
The raspberry-like hollow SnO2-based (bare SnO2 and Pd-doped SnO2) nanostructures with different dominant crystal facets were prepared facilely using carbon nanospheres as templates via solvothermal method. Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and ammonia (NH3) gas sensing performances of the hollow SnO2-based structures were studied systematically. The gas sensing performances were investigated in a temperature range of 150–315 °C. It was found that 285 °C was the optimum operating temperature for both the sensors. The SnO2 sensor showed excellent VOCs (1–100 ppm) sensing performances, with a fast response/recovery behavior (around 4 s/30 s) at 285 °C. While the Pd-SnO2 sensor displayed selective NH3 sensing characteristics at low concentrations of 1.5–12 ppm, interestingly, with a response/recovery time of about 4 s/80 s at 285 °C. Both the SnO2 and Pd-SnO2 sensors showed great repeatability for 8 response/recovery cycles, and very slight response recession for a long period. It was found that not only the morphology, the synergistic effect from the heterojunctions of doped Pd and SnO2, and the Pd catalysis, but also the crystal facets could modulate the sensing performance of metal oxides.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
T.T. Lin, X. Lv, Z.N. Hu, A.S. Xu, C.H. Feng, Sensors (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/s19020233
I.P. Liu, C.H. Chang, T.C. Chou, K.W. Lin, Sens. Actuator B 291, 148 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.04.046
V.B. Raj, A.T. Nimal, Y. Parmar, M.U. Sharma, K. Sreenivas, V. Gupta, Sens. Actuator B 147, 517 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2010.03.079
D.D. Nguyen, D.V. Dang, D.C. Nguyen, Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci Nanotechnol 6, 035006 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1088/2043-6262/6/3/035006
J. Zhang, S.R. Wang, Y.M. Wang et al., Sens. Actuator B 135, 610 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2008.09.026
P.M. Bulemo, H.J. Cho, D.H. Kim, I.D. Kim, ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10, 18183 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b00901
J.Y. Liu, T.S. Wang, B.Q. Wang et al., Sens. Actuator B 245, 551 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.01.148
B.-Y. Kim, J.S. Cho, J.-W. Yoon et al., Sens. Actuators B 234, 353 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.05.002
Z. Li, J.X. Yi, Sens. Actuator B 243, 96 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.11.136
S.L. Bai, W.G. Tong, Y. Tian et al., J. Mater. Sci. 54, 2025 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-1588-2
K. Suematsu, H. Uchino, T. Mizukami, K. Watanabe, K. Shimanoe, J. Mater. Sci. 54, 3135 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-3020-y
L. Xiao, S.M. Shu, S.T. Liu, Sens. Actuator B 221, 120 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2015.06.099
J. Rebholz, K. Grossmann, D. Pham et al., Sensors 16, 1437 (2016)
K. Großmann, K.E. Kovács, D.K. Pham, L. Mädler, N. Barsan, U. Weimar, Sens. Actuators B 158, 388 (2011)
L.P. Yang, X.Y. Zhou, L.F. Song et al., ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 1, 6327 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.8b01529
F. Gyger, A. Sackmann, M. Hübner et al., Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 31, 591 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1002/ppsc.201300241
J.M. Walker, S.A. Akbar, P.A. Morris, Sens. Actuator B 286, 624 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.01.049
D. Degler, U. Weimar, N. Barsan, ACS Sens. 4, 2228 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.9b00975
F. Shao, M.W.G. Hoffmann, J.D. Prades, J.R. Morante, N. Lopez, F. Hernandez-Ramirez, J. Phys. Chem. C 117, 3520 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp3085342
B. Cho, J. Yoon, M.G. Hahm et al., J. Mater. Chem. C 2, 5280 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/c4tc00510d
X. Han, M. Jin, S. Xie, Q. Kuang, L. Zheng, Angew Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 48, 9180 (2009)
X. Sun, Y. Li, Angew Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 43, 597 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200352386
T. Takeguchi, O. Takeoh, S. Aoyama, J. Ueda, R. Kikuchi, K. Eguchi, Appl. Catal. A 252, 205 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0926-860x(03)00418-6
Y. Masayoshi, T. Masaki et al., Sens. Actuators B 136, 99 (2009)
T.S. Wang, S.F. Zhang, Q. Yu et al., Sens. Actuator B 276, 262 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.07.020
B.Y. Huang, Z.X. Zhang, C.H. Zhao et al., Sens. Actuator B 255, 2248 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.09.022
L.L. Guo, F. Chen, N. Xie et al., Sens. Actuator B 272, 185 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.05.161
P. Sun, W. Wang, Y. Liu, Y. Sun, J. Ma, G. Lu, Sens. Actuators B 173, 52 (2012)
G.H. Mhlongo, D.E. Motaung, F.R. Cummings, H.C. Swart, S.S. Ray, Sci. Rep. 9, 9881 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-46247-z
P.G. Su, L.Y. Yang, Sens. Actuator B 223, 202 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2015.09.091
M. Shahabuddin, A. Sharma, J. Kumar, M. Tomar, A. Umar, V. Gupta, Sens. Actuator B 194, 410 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2013.12.097
N. Van Toan, C.M. Hung, N. Van Duy, N.D. Hoa, D.T.T. Le, N. Van Hieu, Mater. Sci. Eng. B 224, 163 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2017.08.004
Y. Li, H.T. Ban, M.J. Yang, Sens. Actuator B 224, 449 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2015.10.078
S.G. Leonardi, W. Wlodarski, Y.X. Li, N. Donato, A. Bonavita, G. Neri, J. Alloy Compd. 781, 440 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.12.110
A.M. Al-Enizi, M. Naushad, A.H. Al-Muhtaseb et al., Chem. Eng. J. 345, 58 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.03.138
A. Rothschild, Y. Komem, Sens. Actuator B 93, 362 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-4005(03)00212-0
D. Koziej, M. Hubner, N. Barsan, U. Weimar, M. Sikora, J.D. Grunwaldt, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 11, 8620 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1039/b906829e
Y.H. Zhang, Y.L. Li, F.L. Gong, K.F. Xie, H.L. Zhang, S.M. Fang, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 21, 22039 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/c9cp04242c
D.P. Xue, P.T. Wang, Z.Y. Zhang, Y. Wang, Sens. Actuator B 296, 126710 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.126710
P. Bechthold, M.E. Pronsato, C. Pistonesi, Appl. Surf. Sci. 347, 291 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.03.149
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge M. L. for help with the TEM, XRD, and XPS characterizations. The authors W. Y., H. Z, and C. G. acknowledge the 2011 Zhejiang Regional Collaborative Innovation Center for Smart City.
Funding
This research was supported by the Zhejiang Science and Technology Foundation (LQ20F040006), 2011 Zhejiang Regional Collaborative Innovation Center for Smart City, and Research Foundation of Hangzhou Dianzi University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, W., Zeng, X., Wu, G. et al. Raspberry-like hollow SnO2-based nanostructures for sensing VOCs and ammonia. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 31, 14165–14173 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-03971-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-03971-x