Abstract
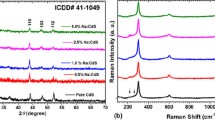
Cd–ZnO–Na alloy nanostructured thin films were synthesized via sol–gel spin coating method on glass substrates and the effect of Na (1, 2 and 3 wt%) doping variation on linear, nonlinear optical, opto-dielectric, and emission properties of the films was investigated. The variations in physical properties with different Na doping concentrations were analyzed using X-ray diffraction (XRD), atomic force microscope (AFM), scanning electron microscope (SEM), FT-Raman, UV–Vis, and photoluminescence spectroscopy. From XRD patterns, it was observed that the growth of the films occurs along (002) plane with hexagonal wurtzite structure. High percentage of transmittance (viz. 85 to 90%) was recorded for all as grown films. However, the estimated bandgap energy of the films was found to decrease from 3.37 to 3.30 eV with increasing Na doping concentration from 1 to 3 wt%. Emission spectra of the films show an intense and sharp peak near band emission (NBE) at 389 nm whereas a low intense peak was observed at 475 nm. The intensity of NBE peak specifies the significant enhancement in photoluminescence properties of the grown films with increasing Na doping concentrations. Nonlinear optical parameters of the Cd–ZnO–Na films such as χ3 and n2 showed substantial improvements, which were deduced and obtained in the range 1.11 × 10–14–1.91 × 10–12 esu and 5.20 × 10–13–3.19 × 10–11 esu, respectively. The achieved improvement in the grown ZnO films via co-doping with Cd and Na makes them highly suitable candidates for optoelectronics devices applications.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.-P. Kim, S.-A. Lee, J.S. Bae, S.-K. Park, U.-C. Choi, C.-R. Cho, Electric properties and surface characterization of transparent Al-doped ZnO thin films prepared by pulsed laser deposition. Thin Solid Films 516, 5223–5226 (2008)
L. Jiang, K. Huang, J. Li, S. Li, Y. Gao, W. Tang, X. Guo, J. Wang, T. Mei, X. Wang, High carrier mobility low-voltage ZnO thin film transistors fabricated at a low temperature via solution processing. Ceram. Int. 44, 11751–11756 (2018)
F. Ghomrani, A. Aissat, H. Arbouz, A. Benkouider, Al concentration effect on ZnO based thin films: for photovoltaic applications. Energy Procedia 74, 491–498 (2015)
A. Myzaferi, A.J. Mughal, D.A. Cohen, R.M. Farrell, S. Nakamura, J.S. Speck, S.P. DenBaars, Zinc oxide clad limited area epitaxy semipolar III-nitride laser diodes. Opt. Express 26, 12490–12498 (2018)
A. Zawadzka, P. Płóciennik, Y. El Kouari, H. Bougharraf, B. Sahraoui, Linear and nonlinear optical properties of ZnO thin films deposited by pulsed laser deposition. J. Lumin. 169, 483–491 (2016)
X. Si, S. Xiong-Rui, L. Chun, H. Yi-Bo, F. Guo-Jia, W. Qu-Quan, Linear and nonlinear optical properties of ZnO nanorod arrays. Chin. Phys. B 17, 1291 (2008)
B.G. Shohany, L. Motevalizadeh, M.E. Abrishami, Investigation of ZnO thin-film sensing properties for CO2 detection: effect of Mn doping. J. Theor. Appl. Phys. 12, 219–225 (2018)
V.L. Patil, S.A. Vanalakar, P.S. Patil, J.H. Kim, Fabrication of nanostructured ZnO thin films based NO2 gas sensor via SILAR technique. Sensors Actuators B 239, 1185–1193 (2017)
C.S. Prajapati, N. Bhat, Highly sensitive CO sensor based on thickness-selective ZnO thin film: device fabrication and packaging. Cryst. Res. Technol. 54, 1800241 (2019)
M. Shkir, M. Arif, V. Ganesh, M.A. Manthrammel, A. Singh, I.S. Yahia, S.R. Maidur, P.S. Patil, S. AlFaify, Investigation on structural, linear, nonlinear and optical limiting properties of sol-gel derived nanocrystalline Mg doped ZnO thin films for optoelectronic applications. J. Mol. Struct. 1173, 375–384 (2018)
R. Bairy, P.S. Patil, S.R. Maidur, U. Bhat, The role of cobalt doping in tuning the band gap, surface morphology and third-order optical nonlinearities of ZnO nanostructures for NLO device applications. RSC Adv. 9, 22302–22312 (2019)
A. Agrawal, T. Ahmad Dar, R. Solanki, D.M. Phase, P. Sen, Study of nonlinear optical properties of pure and Mg-doped ZnO films. Physica Status Solidi (b) 252, 1848–1853 (2015)
R. Hollinger, D. Gupta, M. Zapf, M. Karst, R. Röder, I. Uschmann, U. Reislöhner, D. Kartashov, C. Ronning, C. Spielmann, Polarization dependent multiphoton absorption in ZnO thin films. J. Phys. D 53, 055102 (2019)
K. Sandeep, S. Bhat, S. Dharmaprakash, Nonlinear absorption properties of ZnO and Al doped ZnO thin films under continuous and pulsed modes of operations. Opt. Laser Technol. 102, 147–152 (2018)
M.R. Islam, M. Rahman, S.F.U. Farhad, J. Podder, Structural, optical and photocatalysis properties of sol–gel deposited Al-doped ZnO thin films. Surf. Interfaces 16, 120–126 (2019)
N. Talebian, M.R. Nilforoushan, R. Ramazan Ghasem, Enhanced photocatalytic activities of ZnO thin films: a comparative study of hybrid semiconductor nanomaterials. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 64, 36–46 (2012)
M. Shkir, B.M. Al-Shehri, M. Pachamuthu, A. Khan, K.V. Chandekar, S. AlFaify, M.S. Hamdy, A remarkable improvement in photocatalytic activity of ZnO nanoparticles through Sr doping synthesized by one pot flash combustion technique for water treatments. Colloids Surf. A 587, 124340 (2020)
K.V. Chandekar, M. Shkir, A. Khan, B.M. Al-Shehri, M.S. Hamdy, S. AlFaify, M.A. El-Toni, A. Aldalbahi, A.A. Ansari, H. Ghaithan, A facile one-pot flash combustion synthesis of La@ZnO nanoparticles and their characterizations for optoelectronic and photocatalysis applications. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 395, 112465 (2020)
M. Shkir, K.V. Chandekar, B.M. Alshehri, A. Khan, S. AlFaify, M.S. Hamdy, A remarkable enhancement in photocatalytic activity of facilely synthesized Terbium@Zinc oxide nanoparticles by flash combustion route for optoelectronic applications. Appl. Nanosci. 10, 1811 (2019)
M.-L. Lin, J.-M. Huang, C.-S. Ku, C.-M. Lin, H.-Y. Lee, J.-Y. Juang, High mobility transparent conductive Al-doped ZnO thin films by atomic layer deposition. J. Alloy. Compd. 727, 565–571 (2017)
M. Rouchdi, E. Salmani, B. Fares, N. Hassanain, A. Mzerd, Synthesis and characteristics of Mg doped ZnO thin films: experimental and ab-initio study. Results Phys. 7, 620–627 (2017)
S. Vijayalakshmi, S. Venkataraj, R. Jayavel, Characterization of cadmium doped zinc oxide (Cd:ZnO) thin films prepared by spray pyrolysis method. J. Phys. D 41, 245403 (2008)
D. Akcan, A. Gungor, L. Arda, Structural and optical properties of Na-doped ZnO films. J. Mol. Struct. 1161, 299–305 (2018)
M. Hjiri, M.S. Aida, O.M. Lemine, L. El Mir, Study of defects in Li-doped ZnO thin films. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 89, 149–153 (2019)
K.D.A. Kumar, R. Thomas, S. Valanarasu, V. Ganesh, M. Shkir, S. AlFaify, J. Thirumalai, Analysis of Pr co-doped Al:ZnO thin films using feasible nebulizer spray technique for optoelectronic technology. Appl. Phys. A 125, 712 (2019)
D. Spemann, E.M. Kaidashev, M. Lorenz, J. Vogt, T. Butz, Ion beam analysis of epitaxial (Mg, Cd)xZn1−xO and ZnO:(Li, Al, Ga, Sb) thin films grown on c-plane sapphire. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B 219–220, 891–896 (2004)
M.R. AlfaroCruz, O. Ceballos-Sanchez, E. Luévano-Hipólito, L.M. Torres-Martínez, ZnO thin films deposited by RF magnetron sputtering: Effects of the annealing and atmosphere conditions on the photocatalytic hydrogen production. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 43, 10301–10310 (2018)
K. Kandpal, J. Singh, N. Gupta, C. Shekhar, Effect of thickness on the properties of ZnO thin films prepared by reactive RF sputtering. J. Mater. Sci. 29, 14501–14507 (2018)
S. Chen, R.M. Wilson, R. Binions, Synthesis of highly surface-textured ZnO thin films by aerosol assisted chemical vapour deposition. J. Mater. Chem. A 3, 5794–5797 (2015)
G. Kaur, A. Mitra, K.L. Yadav, Pulsed laser deposited Al-doped ZnO thin films for optical applications. Prog. Nat. Sci. 25, 12–21 (2015)
D. Dastan, Effect of preparation methods on the properties of titania nanoparticles: solvothermal versus sol–gel. Appl. Phys. A 123, 699 (2017)
W.-D. Zhou, D. Dastan, J. Li, X.-T. Yin, Q. Wang, Discriminable sensing response behavior to homogeneous gases based on n-ZnO/p-NiO composites. Nanomaterials 10, 785 (2020)
X. Zhu, J. Yang, D. Dastan, H. Garmestani, R. Fan, Z. Shi, Fabrication of core-shell structured Ni@BaTiO3 scaffolds for polymer composites with ultrahigh dielectric constant and low loss. Compos. A 125, 105521 (2019)
M. Shkir, M. Anis, S.S. Shaikh, S. AlFaify, An investigation on structural, morphological, optical and third order nonlinear properties of facilely spray pyrolysis fabricated In:CdS thin films. Superlatt. Microstruct. 133, 106202 (2019)
M. Novotný, M. Vondráček, E. Marešová, P. Fitl, J. Bulíř, P. Pokorný, Š. Havlová, N. Abdellaoui, A. Pereira, P. Hubík, J. More-Chevalier, J. Lančok, Optical and structural properties of ZnO:Eu thin films grown by pulsed laser deposition. Appl. Surf. Sci. 476, 271–275 (2019)
N. Kumari, S.R. Patel, J.V. Gohel, Optical and structural properties of ZnO thin films prepared by spray pyrolysis for enhanced efficiency perovskite solar cell application. Opt. Quant. Electron. 50, 180 (2018)
A. Kepceoğlu, S. Yiğit Gezgin, Y. Gündoğdu, H. Küçükçelebi, H.Ş. Kılıç, Nonlinear optical properties of zinc oxide thin films produced by pulsed laser deposition. Mater. Today 18, 1819–1825 (2019)
K.N. Tonny, R. Rafique, A. Sharmin, M.S. Bashar, Z.H. Mahmood, Electrical, optical and structural properties of transparent conducting Al doped ZnO (AZO) deposited by sol–gel spin coating. AIP Adv. 8, 065307 (2018)
A. Jafari, K. Tahani, D. Dastan, S. Asgary, Z. Shi, X.-T. Yin, W.-D. Zhou, H. Garmestani, Ş. Ţălu, Ion implantation of copper oxide thin films; statistical and experimental results. Surf. Interfaces 18, 100463 (2020)
Y. Song, S. Zhang, C. Zhang, Y. Yang, K. Lv, Raman spectra and microstructure of zinc oxide irradiated with swift heavy ion. Crystals 9, 395 (2019)
R. Zhang, P.-G. Yin, N. Wang, L. Guo, Photoluminescence and Raman scattering of ZnO nanorods. Solid State Sci. 11, 865–869 (2009)
V.A. Nikitenko, V.G. Plekhanov, S.V. Mukhin, M.V. Tkachev, Raman spectra of oxide zinc powders and single crystals. J. Appl. Spectrosc. 63, 290–292 (1996)
H.-M. Cheng, Hsu, Y.-K. Tseng, L.-J. Lin, W.-F. Hsieh, Raman scattering and efficient UV photoluminescence from well-aligned ZnO nanowires epitaxially grown on GaN buffer layer. J. Phys. Chem. B 109, 8749–8754 (2005)
Z. Wang, H. Zhang, L. Zhang, J. Yuan, S. Yan, C. Wang, Low-temperature synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles by solid-state pyrolytic reaction. Nanotechnology 14, 11–15 (2002)
Y. Lv, Z. Zhang, J. Yan, W. Zhao, C. Zhai, J. Liu, Growth mechanism and photoluminescence property of hydrothermal oriented ZnO nanostructures evolving from nanorods to nanoplates. J. Alloy. Compd. 718, 161–169 (2017)
J. Lü, K. Huang, J. Zhu, X. Chen, X. Song, Z. Sun, Preparation and characterization of Na-doped ZnO thin films by sol–gel method. Phys. B 405, 3167–3171 (2010)
A.H. Hammad, M.S. Abdel-wahab, S. Vattamkandathil, A.R. Ansari, Structural and optical properties of ZnO thin films prepared by RF sputtering at different thicknesses. Phys. B 540, 1–8 (2018)
J.M. Khoshman, A.A. Manda, M.E. Kordesch, Near-infrared optical constants and optical polarization properties of ZnO thin films. Thin Solid Films 578, 139–147 (2015)
A. El-Denglawey, Characterization of As–Se–Tl films near infrared region. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 357, 1757–1763 (2011)
I.Y.Y. Bu, Sol-gel production of p-type ZnO thin film by using sodium doping. Superlattices Microstruct. 96, 59–66 (2016)
J. Tauc, Amorphous and Liquid Semiconductors (Plenum, London, 1974)
M. Shakir, S. Kushwaha, K. Maurya, G. Bhagavannarayana, M. Wahab, Characterization of ZnSe nanoparticles synthesized by microwave heating process. Solid State Commun. 149, 2047–2049 (2009)
Z.R. Khan, M. Zulfequar, M.S. Khan, Optical and structural properties of thermally evaporated cadmium sulphide thin films on silicon (100) wafers. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 174, 145–149 (2010)
R. Shakoury, A. Arman, Ş. Ţălu, D. Dastan, C. Luna, S. Rezaee, Stereometric analysis of TiO2 thin films deposited by electron beam ion assisted. Opt. Quant. Electron. 52, 1–12 (2020)
D. Dastan, Nanostructured anatase titania thin films prepared by sol–gel dip coating technique. J. Atomic Mol. Condensate Nano Phys. 2, 109–114 (2015)
M. Shkir, Z.R. Khan, M. Anis, S.S. Shaikh, S. AlFaify, A comprehensive study of opto-electrical and nonlinear properties of Cu@CdS thin films for optoelectronics. Chin. J. Phys. 63, 51–62 (2020)
M. Arif, M. Shkir, S. AlFaify, A. Sanger, P.M. Vilarinho, A. Singh, Linear and nonlinear optical investigations of N:ZnO/ITO thin films system for opto-electronic functions. Opt. Laser Technol. 112, 539–547 (2019)
M. Shkir, M. Anis, S. Shafik, M.A. Manthrammel, M.A. Sayeed, M.S. Hamdy, S. AlFaify, An effect of Zn content doping on opto-third order nonlinear characteristics of nanostructured CdS thin films fabricated through spray pyrolysis for optoelectronics. Physica E 118, 113955 (2020)
Z. Khan, M. Shkir, V. Ganesh, S. AlFaify, I. Yahia, H. Zahran, Linear and nonlinear optics of CBD grown nanocrystalline F doped CdS thin films for optoelectronic applications: an effect of thickness. J. Electron. Mater. 47, 5386–5395 (2018)
V. Ganesh, I.S. Yahia, S. AlFaify, M. Shkir, Sn-doped ZnO nanocrystalline thin films with enhanced linear and nonlinear optical properties for optoelectronic applications. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 100, 115–125 (2017)
J. Yang, X. Zhu, H. Wang, X. Wang, C. Hao, R. Fan, D. Dastan, Z. Shi, Achieving excellent dielectric performance in polymer composites with ultralow filler loadings via constructing hollow-structured filler frameworks. Compos. A 131, 105814 (2020)
L. Sun, Z. Shi, H. Wang, K. Zhang, D. Dastan, K. Sun, R. Fan, Ultrahigh discharge efficiency and improved energy density in rationally designed bilayer polyetherimide–BaTiO3/P (VDF-HFP) composites. J. Mater. Chem. A 8, 5750–5757 (2020)
D. Dastan, A. Banpurkar, Solution processable sol–gel derived titania gate dielectric for organic field effect transistors. J. Mater. Sci. 28, 3851–3859 (2017)
D. Dastan, S. W. Gosavi, and N. B. Chaure, Studies on electrical properties of hybrid polymeric gate dielectrics for field effect transistors. in MacromolecularSymposia (Wiley Online Library, 2015), pp. 81–86.
W. Hu, T. Li, X. Liu, D. Dastan, K. Ji, P. Zhao, 1550 nm pumped upconversion chromaticity modulation in Er3+ doped double perovskite LiYMgWO6 for anti-counterfeiting. J. Alloy. Compd. 818, 152933 (2020)
C.-F. Fu, L.-F. Han, C. Liu, T. Sun, X.-B. Liu, Influence of annealing on microstructure and properties of Cr-doped ZnO thin films deposited on glass surface. J. Mater. Sci. 28, 3812–3818 (2017)
L.W. Wang, F. Wu, D.X. Tian, W.J. Li, L. Fang, C.Y. Kong, M. Zhou, Effects of Na content on structural and optical properties of Na-doped ZnO thin films prepared by sol–gel method. J. Alloy. Compd. 623, 367–373 (2015)
R. Adair, L. Chase, S.A. Payne, Nonlinear refractive index of optical crystals. Phys. Rev. B 39, 3337 (1989)
L. Guo, S. Yang, C. Yang, P. Yu, J. Wang, W. Ge, G.K. Wong, Highly monodisperse polymer-capped ZnO nanoparticles: preparation and optical properties. Appl. Phys. Lett. 76, 2901–2903 (2000)
H. Ticha, L. Tichy, Semiempirical relation between non-linear susceptibility (refractive index), linear refractive index and optical gap and its application to amorphous chalcogenides. J. Optoelectron. Adv. Mater. 4, 381–386 (2002)
Z.R. Khan, M. Shkir, A.S. Alshammari, V. Ganesh, S. AlFaify, M. Gandouzi, Structural, linear and third order nonlinear optical properties of sol–gel grown Ag-CdS nanocrystalline thin films. J. Electr. Mater. 48(2), 1122–1132 (2019)
Z.R. Khan, A.S. Alshammari, M. Shkir, V. Ganesh, S. AlFaify, Enhancement in the photoluminescence, linear and third order nonlinear optical properties of nanostructured Na-CdS thin films for optoelectronic applications. J. Nanopart. Res. 22, 1–16 (2020)
E. Shaaban, M. El-Hagary, H.S. Hassan, Y.A. Ismail, M. Emam-Ismail, A. Ali, Structural, linear and nonlinear optical properties of co-doped ZnO thin films. Appl. Phys. A 122, 20 (2016)
Acknowledgements
This research has been supported by Scientific Research Deanship at University of Hai’l-Saudi Arabia through project number RG-191242. The authors would like to express their gratitude to Deanship of Scientific Research at King Khalid University for funding this work through Research Groups Program under Grant No. R.G.P2/95/41.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, Z.R., Alshammari, A.S., Bouzidi, M. et al. Emission and opto-dielectric nonlinearity in 2D Cd–ZnO–Na nanostructures: an effect of Na doping. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 31, 12116–12126 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-03758-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-03758-0