Abstract
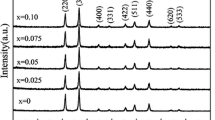
In this paper, the Pb(Zr0.52Ti0.48)1−xFexO3 (FePZT, x = 0.05) nanopowders were prepared by dry and wet sol–gel methods in the morphotropic phase boundary (MPB) region. The effect of Fe concentration on the structural, morphological, and optical properties of PZT nanopowders was investigated using X-ray diffraction (XRD), Field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM), Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR), and Ultraviolet–Visible (UV–Vis) analysis. XRD results showed that the nanopowders have a perovskite structure with the tetragonal phase. The lattice parameters and average crystallite size of samples decreased from 33 to 21 nm with increasing Fe incorporation due to the substitution of Fe atoms instead of Ti and Zr atoms. FESEM images showed that all average diameters of the nanopowders decreased with the Fe concentration. The optical properties of the pure and FePZT nanopowders such as longitudinal optical (LO) and transverse optical (TO) phonon frequencies, refractive index, extinction coefficient, and the real-imaginary parts of dielectric function were examined by the Kramers–Kronig model. As a result, the TO and refractive index of nanopowders are increased by substituting Ti and Zr with Fe atoms due to their different ionic radius. Also, while the crystallite size increases from 20.95 to 33.52 nm, the LO–TO splitting increases too. The optical band-gap values of the pure and FePZT nanopowders were estimated using UV–Vis spectroscopy and Kubelka–Munk model. The band-gap increased from 3.52 to 3.60 eV with a decrease in the crystal size of nanopowders.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. Jaffe, Piezoelectric ceramics (Elsevier, Saint Louis, 2012)
H. Lee, H. Kim, D.Y. Kim, Y. Seo, Pure piezoelectricity generation by a flexible nanogenerator based on lead zirconate titanate nanofibers. ACS Omega 4, 2610–2617 (2019)
X. Niu, W. Jia, S. Qian, J. Zhu, J. Zhang, X. Hou, J. Mu, W. Geng, J. Cho, J. He, X. Chou, High-Performance PZT-based stretchable piezoelectric nanogenerator. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 7, 979–985 (2019)
Q.-L. Zhao, G.-P. He, J.-J. Di, W.-L. Song, Z.-L. Hou, P.-P. Tan, D.-W. Wang, M.-S. Cao, Flexible semitransparent energy harvester with high pressure sensitivity and power density based on laterally aligned PZT single-crystal nanowires. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9, 24696–24703 (2017)
W. Jin, Z. Wang, H. Huang, X. Hu, Y. He, M. Li, L. Li, Y. Gao, Y. Hu, H. Gu, High-performance piezoelectric energy harvesting of vertically aligned Pb(Zr, Ti)O3 nanorod arrays. RSC Adv. 8, 7422–7427 (2018)
E. Pakizeh, M. Moradi, Effect of particle size on the optical properties of lead zirconate titanate nanopowders. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 101, 5335–5345 (2018)
L. Jian, A.S. Kumar, C.S.C. Lekha, S. Vivek, I. Salvado, A.L. Kholkin, S.S. Nair, Strong sub-resonance magnetoelectric coupling in PZT-NiFe2O4-PZT thin film composite. Nano-Structures & Nano-Objects 18, 100272 (2019)
W.-S. Jung, Y.-H. Do, M.-G. Kang, C.-Y. Kang, Energy harvester using PZT nanotubes fabricated by template-assisted method. Curr. Appl. Phys. 13, S131–S134 (2013)
S.D. Hyun, H.W. Park, Y.J. Kim, M.H. Park, Y.H. Lee, H.J. Kim, Y.J. Kwon, T. Moon, K.D. Kim, Y.B. Lee, B.S. Kim, C.S. Hwang, Dispersion in ferroelectric switching performance of polycrystalline Hf0.5Zr0.5O2 Thin Films. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 10, 35374–35384 (2018)
X.-D. Jian, B. Lu, D.-D. Li, Y.-B. Yao, T. Tao, B. Liang, X.-W. Lin, J.-H. Guo, Y.-J. Zeng, S.-G. Lu, Enhanced electrocaloric effect in Sr2+-modified lead-free BaZrxTi1–xO3 ceramics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11, 20167–20173 (2019)
S.B. Seshadri, M.M. Nolan, G. Tutuncu, J.S. Forrester, E. Sapper, G. Esteves, T. Granzow, P.A. Thomas, J.C. Nino, T. Rojac, J.L. Jones, Unexpectedly high piezoelectricity of Sm-doped lead zirconate titanate in the Curie point region. Sci. Rep. 8, 4120 (2018)
J. Tang, J. Liu, H. Huang, Dielectric, piezoelectric and ferroelectric properties of flexible 0–3 type PZT/PVDF composites doped with grapheme. J. Electron. Mater. 48, 4033–4039 (2019)
J. Zhang, Dielectric, ferroelectric and piezoelectric properties of PZT ceramics by ZnO doping. Integr. Ferroelectr. 199, 105–111 (2019)
J. Caceres, C. Passos, J. Chagas, R. Barbieri, R. Corteletti, Study of structural and electric properties of the PZT 52/48 doped with Er+3. Res. Mater. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1590/1980-5373-mr-2019-0123
S.W. Ko, W. Zhu, C. Fragkiadakis, T. Borman, K. Wang, P. Mardilovich, S. Trolier-McKinstry, Improvement of reliability and dielectric breakdown strength of Nb-doped lead zirconate titanate films via microstructure control of seed. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 102, 1211–1217 (2019)
S. Matteppanavar, B. Angadi, S. Rayaprol, Neutron diffraction studies on chemical and magnetic structure of multiferroic PbFe 0.67 W 0.33 O 3, in AIP conference proceedings, American Institute of Physics, 2014, pp. 1669–1671.
S. Matteppanavar, I. Shivaraja, S. Rayaprol, B. Angadi, B. Sahoo, Evidence for room-temperature weak ferromagnetic and ferroelectric ordering in magnetoelectric Pb (Fe0.634W0.266Nb0.1)O3 Ceramic. J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 30, 1317–1325 (2017)
S. Madolappa, A. Anupama, P. Jaschin, K. Varma, B. Sahoo, Magnetic and ferroelectric characteristics of Gd 3+ and Ti 4+ co-doped BiFeO3 ceramics. Bull. Mater. Sci. 39, 593–601 (2016)
V. Khopkar, B. Sahoo, Low temperature dielectric properties and NTCR behavior of BaFe0.5Nb0.5O3 double perovskite ceramic. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 22, 2986–2998 (2020)
H.S. Mohanty, T. Dam, H. Borkar, A. Kumar, K. Mishra, S. Sen, B. Behera, B. Sahoo, D.K. Pradhan, Studies of ferroelectric properties and leakage current behaviour of microwave sintered ferroelectric Na0.5Bi0.5TiO3 ceramic. Ferroelectrics 517, 25–33 (2017)
H.S. Mohanty, A. Kumar, B. Sahoo, P.K. Kurliya, D.K. Pradhan, Impedance spectroscopic study on microwave sintered (1–x) Na0.5Bi0.5TiO3–x BaTiO3 ceramics. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater Electron. 29, 6966–6977 (2018)
S. Matteppanavar, S. Rayaprol, B. Angadi, B. Sahoo, Composition dependent room temperature structure, electric and magnetic properties in magnetoelectric Pb (Fe1/2Nb1/2) O3Pb (Fe2/3W1/3) O3 solid-solutions. J. Alloys Compd. 677, 27–37 (2016)
S.T. Dadami, S. Matteppanavar, I. Shivaraja, S. Rayaprol, B. Angadi, B. Sahoo, Investigation on structural, Mössbauer and ferroelectric properties of (1–x) PbFe0.5Nb0.5O3–(x) BiFeO3 solid solution. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 418, 122–127 (2016)
A.S. Priya, I.S. Banu, M. Chavali, Influence of (La, Cu) doping on the room temperature multiferroic properties of BiFeO3 Ceramics. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 40, 2079–2084 (2015)
M. Prabu, I. Banu, S.T. Sundari, R. Krishnan, K.N. Prakash, Y. Chen, M. Chavali, Optical studies of pulsed laser deposited nanostructured Pb (Zr0.52Ti0.48)O3 thin film by spectroscopic ellipsometry. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 14, 5335–5341 (2014)
M. Prabu, I.S. Banu, S. Gobalakrishnan, M. Chavali, Electrical and ferroelectric properties of undoped and La-doped PZT (52/48) electroceramics synthesized by sol–gel method. J. Alloys Compd. 551, 200–207 (2013)
M. Prabu, I. Banu, S. Gobalakrishnan, M. Chavali, S. Umapathy, Synthesis and optical characterization of lead zirconate titanate (52/48) powders by sol–gel method. Adv. Sci. Eng. Med. 5, 496–499 (2013)
E. Venkata Ramana, F. Figueiras, A. Mahajan, D.M. Tobaldi, B.F.O. Costa, M.P.F. Graça, M.A. Valente, Effect of Fe-doping on the structure and magnetoelectric properties of (Ba0.85Ca0.15)(Ti0.9Zr0.1)O3 synthesized by a chemical route. J. Mater. Chem. C 4, 1066–1079 (2016)
S. Puthucheri, P.K. Pandey, N.S. Gajbhiye, A. Gupta, A. Singh, R. Chatterjee, S.K. Date, Microstructural, electrical, and magnetic properties of acceptor-doped nanostructured lead zirconate titanate. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 94, 3941–3947 (2011)
E. Perez-Delfin, J.E. García, D.A. Ochoa, R. Pérez, F. Guerrero, J.A. Eiras, Effect of Mn-acceptor dopant on dielectric and piezoelectric responses of lead lanthanum zirconate titanate piezoceramics. J. Appl. Phys. 110, 034106 (2011)
S.R. Sangawar, B. Praveenkumar, P. Divya, H.H. Kumar, Fe doped hard PZT ceramics for high power SONAR transducers. Mater. Today 2, 2789–2794 (2015)
T.-G. Lee, H.-J. Lee, S.-W. Kim, D.-H. Kim, S.H. Han, H.-W. Kang, C.-Y. Kang, S. Nahm, Piezoelectric properties of Pb(Zr, Ti)O3-Pb(Ni, Nb)O3 ceramics and their application in energy harvesters. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 37, 3935–3942 (2017)
A. Kumar, A. Goswami, K. Singh, R. McGee, T. Thundat, D. Kaur, Magnetoelectric coupling in Ni-Mn-In/PLZT artificial multiferroic heterostructure and its application in mid IR photothermal modulation by external magnetic field. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 1, 11 (2019)
Y. Lu, J. Chen, Z. Cheng, S. Zhang, The PZT/Ni unimorph magnetoelectric energy harvester for wireless sensing applications. Energy Convers. Manag. 200, 112084 (2019)
L.D. Geng, Y. Yan, S. Priya, Y.U. Wang, Computational study of cobalt-modified nickel-ferrite/PZT magnetoelectric composites for voltage tunable inductor applications. Acta Mater. 166, 493–502 (2019)
Y. Yu, J. Wu, T. Zhao, S. Dong, H. Gu, Y. Hu, MnO2 doped PSN–PZN–PZT piezoelectric ceramics for resonant actuator application. J. Alloys Compd. 615, 676–682 (2014)
H.-S. Hsu, V. Benjauthrit, F. Zheng, R. Chen, Y. Huang, Q. Zhou, K.K. Shung, PMN-PT–PZT composite films for high frequency ultrasonic transducer applications. Sens. Actuators A 179, 121–124 (2012)
N. Kumari, S. Monga, M. Arif, N. Sharma, A. Sanger, A. Singh, P.M. Vilarinho, V. Gupta, K. Sreenivas, R.S. Katiyar, J.F. Scott, Multifunctional behavior of acceptor-cation substitution at higher doping concentration in PZT ceramics. Ceram. Int. 45, 12716–12726 (2019)
S. Adel, B. Cherifa, D.D. Elhak, B. Mounira, Effect of Cr2O3 and Fe2O3 doping on the thermal activation of un-polarized PZT charge carriers. Boletín de la Sociedad Española de Cerámica y Vidrio 57, 124–131 (2018)
S. Samanta, V. Sankaranarayanan, K. Sethupathi, Effect of successive multiple doping of La, Nb and Fe on structure and lattice vibration of MPB PZT. Mater. Today 5, 27919–27927 (2018)
B. Praveen Kumar, S.R. Sangawar, H.H. Kumar, Structural and electrical properties of double doped (Fe3+ and Ba2+) PZT electroceramics. Ceram. Int. 40, 3809–3812 (2014)
M. Zhu, Z. Du, H. Li, B. Chen, L. Jing, R.Y.J. Tay, J. Lin, S.H. Tsang, E.H.T. Teo, Tuning electro-optic susceptibity via strain engineering in artificial PZT multilayer films for high-performance broadband modulator. Appl. Surf. Sci. 425, 1059–1065 (2017)
M. Zhu, H. Zhang, Z. Du, C. Liu, Structural insight into the optical and electro-optic properties of lead zirconate titanate for high-performance photonic devices. Ceram. Int. 45, 22324–22330 (2019)
H. Zhao, W. Ren, X. Liu, Design and fabrication of micromachined pyroelectric infrared detector array using lead titanate zirconate (PZT) thin film. Ceram. Int. 43, S464–S469 (2017)
M.C. Rodríguez-Aranda, F. Calderón-Piñar, M.A. Hernández-Landaverde, J. Heiras, R. Zamorano-Ulloa, D. Ramírez-Rosales, J.M. Yáñez-Limón, Photoluminescence of sol–gel synthesized PZT powders. J. Lumin. 179, 280–286 (2016)
E. Longo, A.T. de Figueiredo, M.S. Silva, V.M. Longo, V.R. Mastelaro, N.D. Vieira, M. Cilense, R.W.A. Franco, J.A. Varela, Influence of structural disorder on the photoluminescence emission of PZT powders. J. Phys. Chem. A 112, 8953–8957 (2008)
J. Cardin, D. Leduc, T. Schneider, C. Lupi, D. Averty, H.W. Gundel, Optical characterization of PZT thin films for waveguide applications. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 25, 2913–2916 (2005)
A. Patterson, The Scherrer formula for X-ray particle size determination. Phys. Rev. 56, 978 (1939)
D.-M. Smilgies, Scherrer grain-size analysis adapted to grazing-incidence scattering with area detectors. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 42, 1030–1034 (2009)
F. Wooten, Maxwell's equations and the dielectric function, in Optical properties of solids, ed. by F. Wooten (Academic Press, New York, 1972), pp. 15–41
V. Lucarini, K.-E. Peiponen, J.J. Saarinen, E.M. Vartiainen, Kramers-Kronig relations and sum rules in linear optics, in Kramers-Kronig relations in optical materials research, ed. by V. Lucarini, K.-E. Peiponen, J.J. Saarinen, E.M. Vartiainen (Springer, Berlin, 2005), pp. 27–48
E. Pakizeh, S. Hosseini, A. Kompany, M. Ghasemifard, Synthesis and optical characterization of pyroelectric nanopowders based on PZT (95/5). Int. J. Nanosci. 9, 193–199 (2010)
E. Pakizeh, M. Moradi, Kramers-Kronig method for determination of optical properties of PZT nanotubes fabricated by sol–gel method and porous anodic alumina with high aspect ratio. Int. J. Modern Phys. B 32, 1850096 (2018)
M.A. Assiri, M. Aslam Manthrammel, A.M. Aboraia, I.S. Yahia, H.Y. Zahran, V. Ganesh, M. Shkir, S. AlFaify, A.V. Soldatov, Kramers-Kronig calculations for linear and nonlinear optics of nanostructured methyl violet (CI-42535): new trend in laser power attenuation using dyes. Phys. B 552, 62–70 (2019)
M. Aslam Manthrammel, A.M. Aboraia, M. Shkir, I.S. Yahia, M.A. Assiri, H.Y. Zahran, V. Ganesh, S. AlFaify, A.V. Soldatov, Optical analysis of nanostructured rose bengal thin films using Kramers-Kronig approach: New trend in laser power attenuation. Opt. Laser Technol. 112, 207–214 (2019)
A.A.A. Darwish, A.M. Aboraia, A.V. Soldatov, I.S. Yahia, Deposition of Rhodamine B dye on flexible substrates for flexible organic electronic and optoelectronic: optical spectroscopy by Kramers-Kronig analysis. Opt. Mater. 95, 109219 (2019)
D. Roessler, Kramers-Kronig analysis of reflection data. Br. J. Appl. Phys. 16, 1119 (1965)
F. Behzadi, E. Saievar-Iranizad, E. Pakizeh, Optical study on single-layer photoluminescent graphene oxide nanosheets through a simple and green hydrothermal method. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 364, 595–601 (2018)
C. Kittel, Introduction to solid state physics (Wiley, New York, 1976)
S.S. Abdullahi, S. Güner, Y.K.I.M. Musa, B.I. Adamu, M.I. Abdulhamid, Sımple method for the determination of band gap of a nanopowdered sample using kubelka munk theory. J. Niger. Assoc. Math. Phys. 35, 241–246 (2016)
F.P. Miller, A.F. Vandome, J. McBrewster, Beer-Lambert Law (VDM Publishing, Saarbrücken, 2009)
N. Kumari, S. Monga, M. Arif, N. Sharma, A. Sanger, A. Singh, P.M. Vilarinho, V. Gupta, K. Sreenivas, R.S. Katiyar, Multifunctional behavior of acceptor-cation substitution at higher doping concentration in PZT ceramics. Ceram. Int. 45, 12716–12726 (2019)
R. Gupta, M. Tomar, A. Kumar, V. Gupta, Performance of magnetoelectric PZT/Ni multiferroic system for energy harvesting application. Smart Mater. Struct. 26, 035002 (2017)
G.H. Khorrami, A.K. Zak, A. Kompany, Optical and structural properties of X-doped (X= Mn, Mg, and Zn) PZT nanoparticles by Kramers-Kronig and size strain plot methods. Ceram. Int. 38, 5683–5690 (2012)
E. Pakizeh, M. Moradi, A. Ahmadi, Effect of sol–gel pH on XRD peak broadening, lattice strain, ferroelectric domain orientation, and optical bandgap of nanocrystalline Pb1. 1 (Zr0. 52Ti0. 48) O3. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 75, 174–181 (2014)
A.K. Zak, W.A. Majid, Effect of solvent on structure and optical properties of PZT nanoparticles prepared by sol–gel method, in infrared region. Ceram. Int. 37, 753–758 (2011)
S. Samanta, V. Sankaranarayanan, K. Sethupathi, Band gap, piezoelectricity and temperature dependence of differential permittivity and energy storage density of PZT with different Zr/Ti ratios. Vacuum 156, 456–462 (2018)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pakizeh, E. Optical response and structural properties of Fe-doped Pb(Zr0.52Ti0.48)O3 nanopowders. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 31, 4872–4881 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-03050-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-03050-1