Abstract
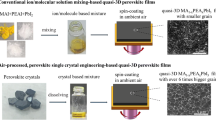
Metal hybrid halide perovskite solar cells (PSCs) are very sensitive to air, and it is challenging to obtain air-processed, air-stable, and highly crystalline perovskite films. Photovoltaic performance decays dramatically due to air humidity influence with power conversion efficiency (PCE) of most air-processed PSCs < 15%. In this work, we develop a facile method to air-processed, highly crystalline (MA0.2FA0.8PbI3)1.0(CsPbBr3)0.05 perovskite films in ambient air with large grain size and low trap density based on mix-cation single crystal engineering. This method shows 75% increase in grain size and 28% decrease in trap density than conventional molecule/ion solution mixing-processed method. The large grain, low trap density, andhigh crystalline perovskite films result in high-efficient and air-stable PSCs. Consequently, the PCE increases to 36.7% from 12.56% for conventional molecule/ion solution mixing-processed devices and to 17.17% for single crystal engineering-based ones. Furthermore, benefiting from high moisture resistance of mix-cation single crystal engineering-based films, the PSC air stability has been improved significantly and 72% of the initial performance retains after 40 days of storage in ambient environment with a relative humidity of 60% at 25 °C without any encapsulation, with a 26% slower degradation rate than conventional solution-mixing method.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Jiang, M.A. Green, R. Sheng et al., Room temperature optical properties of organic–inorganic lead halide perovskites. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 137, 253–257 (2015)
M.A. Green, A. Ho-Baillie, H.J. Snaith, The emergence of perovskite solar cells. Nat. Photon. 8, 506 (2014)
C.C. Stoumpos, C.D. Malliakas, M.G. Kanatzidis, Semiconducting tin and lead iodide perovskites with organic cations: phase transitions, high mobilities, and near-infrared photoluminescent properties. Inorg. Chem. 52, 9019–9038 (2013)
G. Xing, N. Mathews, S.Y. Sun et al., Long-range balanced electron-and hole-transport lengths in organic-inorganic CH3NH3PbI3. Science 342, 344–347 (2013)
S.D. Stranks, G.E. Eperon, G. Grancini et al., Electron-hole diffusion lengths exceeding 1 micrometer in an organometal trihalide perovskite absorber. Science 342, 341–344 (2013)
M.M. Lee, J. Teuscher, T. Miyasaka et al., Efficient hybrid solar cells basedon meso-superstructured organometal halide perovskites. Science 338, 643–647 (2012)
A. Mei, X. Li, L. Liu et al., A hole-conductor-free, fully printable mesoscopic perovskite solar cell with high stability. Science 345, 295 (2014)
Z.K. Tan, R.S. Moghaddam, M.L. Lai et al., Bright light-emitting diodes based on organometal halide perovskite. Nat. Nanotechnol. 9, 687 (2014)
G. Xing, N. Mathews, S.S. Lim et al., Low-temperature solution-processed wavelength-tunable perovskites for lasing. Nat. Mater. 13, 476–480 (2014)
R. Dong, Y. Fang, J. Chae et al., High-gain and low-driving-voltage photodetectors based on organolead triiodide perovskites. Adv. Mater. 27, 1912–1918 (2015)
M.M. Lee, J. Teuscher, T. Miyasaka et al., Efficient hybrid solar cells based on meso-superstructured organometal halide perovskites. Science 338, 643 (2012)
W.S. Yang, B.W. Park, E.H. Jung et al., Iodide management in formamidinium-lead-halide-based perovskite layers for efficient solar cells. Science 356, 1376–1379 (2017)
G.E. Eperon, V.M. Burlakov, P. Docampo et al., Solution-processed planar heterojunction perovskite solar cells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 24, 151–157 (2014)
H.J. Snaith, A. Abate, J.M. Ball et al., Anomalous hysteresis in perovskite solar cells. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 5, 1511–1515 (2014)
R.S. Sanchez, V. Gonzalez-Pedro, J.W. Lee et al., Slow dynamic processes in lead halide perovskite solar cells. Characteristic times and hysteresis. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 5, 2357–2363 (2014)
J.M. Frost, K.T. Butler, A. Walsh, Molecular ferroelectric contributions to anomalous hysteresis in hybrid perovskite solar cells. Appl. Mater 2, 081506 (2014)
N.J. Jeon, J.H. Noh, W.S. Yang et al., Compositional engineering of perovskite materials for high-performance solar cells. Nature 517, 476–480 (2015)
M. Saliba, T. Matsui, J.-Y. Seo et al., Cesium-containing triple cation perovskite solar cells: improved stability, reproducibility and high efficiency. Energy Environ. Sci. 9, 1989–1997 (2016)
D.P. McMeekin, G. Sadoughi, W. Rehman et al., A mixed-cation lead mixed-halide perovskite absorber for tandem solar cells. Science 351, 151 (2016)
B.J. Kim, D.H. Kim, Y.-Y. Lee et al., Highly efficient and bending durable perovskite solar cells: toward a wearable power source. Energy Environ. Sci. 8, 916–921 (2015)
S.N. Habisreutinger, T. Leijtens, G.E. Eperon et al., Carbon nanotube/polymer composites as a highly stable hole collection layer in perovskite solar cells. Nano Lett. 14, 5561–5568 (2014)
Z. Yang, C.-C. Chueh, F. Zuo et al., High-performance fully printable perovskite solar cells via blade-coating technique under the ambient condition. Adv. Energy Mater. 5, 1500328 (2015)
M. Xiao, F. Huang, W. Huang et al., A fast deposition-crystallization procedure for highly efficient lead iodide perovskite thin-film solar cells. Angew. Chem. 53, 9898–9903 (2014)
G. Niu, W. Li, F. Meng et al., Study on the stability of CH3NH3PbI3 films and the effect of post-modification by aluminum oxide in all-solid-state hybrid solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. A 2, 705–710 (2014)
L. Zheng, Y.-H. Chung, Y. Ma et al., A hydrophobic hole transporting oligothiophene for planar perovskite solar cells with improved stability. Chem. Commun. 50, 11196–11199 (2014)
I.C. Smith, E.T. Hoke, D. Solis-Ibarra et al., A layered hybrid perovskite solar-cell absorber with enhanced moisture stability. Angew. Chem. 126, 11232–11235 (2014)
J.H. Noh, S.H. Im, J.H. Heo et al., Chemical management for colorful, efficient, and stable inorganic–organic hybrid nanostructured solar cells. Nano Lett. 13, 1764–1769 (2013)
F. Zhang, X. Yang, H. Wang et al., Structure engineering of hole–conductor free perovskite-based solar cells with low-temperature-processed commercial carbon paste as cathode. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 6, 16140–16146 (2014)
Z. Wei, H. Chen, K. Yan et al., Inkjet printing and instant chemical transformation of a CH3NH3PbI3/nanocarbon electrode and interface for planar perovskite solar cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 53, 13239–13243 (2014)
H. Zhou, Y. Shi, Q. Dong et al., Metal-electrode-free TiO2/CH3NH3PbI3 heterojunction solar cells based on a low-temperature carbon electrode. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 5, 3241–3246 (2014)
M.J. Brites, M.A. Barreiros, V. Corregidor et al., Ultrafast low-temperature crystallization of solar cell graded formamidinium-cesium mixed-cation lead mixed-halide perovskites using a reproducible microwave-based process. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2, 1844–1853 (2019)
S. van Reenen, M. Kemerink, H.J. Snaith, Modeling anomalous hysteresis in perovskite solar cells. J. Phys. Chemi. Lett. 6, 3808–3814 (2015)
Y. Liu, Z. Yang, D. Cui et al., Two-inch-sized perovskite CH3NH3PbX3 (X = Cl, Br, I) crystals: growth and characterization. Adv. Mater. 27, 5176–5183 (2015)
D.N. Dirin, I. Cherniukh, S. Yakunin et al., Determination of defect levels in melt-grown all-inorganic perovskite CsPbBr3 crystals by thermally stimulated current spectra. Chem. Mater 28, 8470–8474 (2016)
Y. Dang, Y. Liu, Y. Sun et al., Bulk crystal growth of hybrid perovskite material CH3NH3PbI3. CrystEngComm 17, 665–670 (2015)
M.I. Saidaminov, A.L. Abdelhady, B. Murali et al., High-quality bulk hybrid perovskite single crystals within minutes by inverse temperature crystallization. Nat. Commun. 6, 7586 (2015)
Y. Liu, J. Sun, Z. Yang et al., 20-mm-large single-crystalline formamidinium-perovskite wafer for mass production of integrated photodetectors. Adv. Opt. Mater. 4, 1829–1837 (2016)
M. Zhang, Z. Zheng, Q. Fu et al., Efficient mixed-cation perovskite solar cells with Cu electrode by scalable fabrication of active layer. J. Phys. Chem. C 122, 10309–10315 (2018)
Y. Deng, Q. Dong, C. Bi et al., Determination of defect levels in melt-grown all-inorganic perovskite CsPbBr3 crystals by thermally stimulated current spectra. Adv. Energy Mater. 6, 1600372 (2016)
M. Zhang, Z. Zheng, Q. Fu et al., Solution-grown CsPbBr3 perovskite single crystals for photon detection. J. Phys. Chem. C 122, 10309–10315 (2018)
W. Nie, H. Tsai, R. Asadpour et al., High-efficiency solution-processed perovskite solar cells with millimeter-scale grains. Science 347, 522 (2015)
N.J. Jeon, J.H. Noh, W.S. Yang et al., Compositional engineering of perovskite materials for high-performance solar cells. Nature 517, 476 (2015)
M. Shirayama, M. Kato, T. Miyadera et al., Degradation mechanism of CH3NH3PbI3 perovskite materials upon exposure to humid air. J. Appl. Phys. 119, 115501 (2016)
R.H. Bube, Trap Density, Determination by Space-charge‐limited currents. J. Appl. Phys. 33, 1733 (1962)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2016YFB0700702), the Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51502101), and the National Basic Research Program of China (Grant No. 2015CB258400). We also thank the testing center of Huazhong University of Science and Technology for SEM, XRD, PL, UV, and FT-IR measurements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Y., Zhao, C., Chen, X. et al. Air-processed and mixed-cation single crystal engineering-based perovskite films for efficient and air-stable perovskite solar cells. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 31, 2167–2176 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-02742-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-02742-7