Abstract
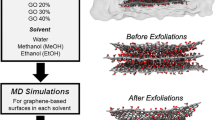
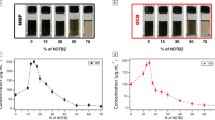
The electrochemical exfoliation of graphene is a very useful technique to prepare highly conductive graphene with a low defect level. However, low dispersion stability is a barrier to this process being used to prepare graphene directly in a wide range of applications. Even though the dispersion stability and concentration of graphene are important, the reasons for the lower dispersion stability and lower concentration of electrochemically exfoliated graphene have not yet been clarified. In this study, we identified that the strong electrostatic attractive interaction between charged ions from electrolytes at the interfaces of graphene layers substantially deteriorated the dispersion stability. Both the stability and the concentration of graphene dispersions were substantially enhanced upon removal of the residual electrolytes from the organic solvents used in this study.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
B.-H. Wee, W.-H. Khoh, A.K. Sarker, C.-H. Lee, J.-D. Hong, A high-performance moisture sensor based on ultralarge graphene oxide. Nanoscale 7, 17805–17811 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/C5NR05726D
V. León, A.M. Rodriguez, P. Prieto, M. Prato, E. Vázquez, Exfoliation of graphite with triazine derivatives under ball-milling conditions: preparation of few-layer graphene via selective noncovalent interactions. ACS Nano 8, 563–571 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/nn405148t
R.S. Edwards, K.S. Coleman, Graphene synthesis: relationship to applications. Nanoscale 5, 38–51 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1039/C2NR32629A
Z.-S. Wu, S. Pei, W. Ren, D. Tang, L. Gao, B. Liu, F. Li, C. Liu, H.-M. Cheng, Field emission of single-layer graphene films prepared by electrophoretic deposition. Adv. Mater. 21, 1756–1760 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200802560
J.I. Paredes, J.M. Munuera, Recent advances and energy-related applications of high quality/chemically doped graphenes obtained by electrochemical exfoliation methods. J. Mater. Chem. A 5, 7228–7242 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1039/C7TA01711A
L.G. Cançado, K. Takai, T. Enoki, M. Endo, Y.A. Kim, H. Mizusaki, N.L. Speziali, A. Jorio, M.A. Pimenta, Measuring the degree of stacking order in graphite by Raman spectroscopy. Carbon N. Y. 46, 272–275 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CARBON.2007.11.015
S. Park, J. An, I. Jung, R.D. Piner, S.J. An, X. Li, A. Velamakanni, R.S. Ruoff, Colloidal suspensions of highly reduced graphene oxide in a wide variety of organic solvents. Nano Lett. 9, 1593–1597 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1021/nl803798y
H.K. Jeong, Y.P. Lee, R.J.W.E. Lahaye, M.H. Park, K.H. An, I.J. Kim, C.W. Yang, C.Y. Park, R.S. Ruoff, Y.H. Lee, Evidence of graphitic AB stacking order of graphite oxides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. (2008). https://doi.org/10.1021/JA076473O
G. Eda, M. Chhowalla, Chemically derived graphene oxide: towards large-area thin-film electronics and optoelectronics. Adv. Mater. 22, 2392–2415 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200903689
H.-X. Wang, Q. Wang, K.-G. Zhou, H.-L. Zhang, Graphene in light: design, synthesis and applications of photo-active graphene and graphene-like materials. Small 9, 1266–1283 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201203040
V.C. Tung, M.J. Allen, Y. Yang, R.B. Kaner, High-throughput solution processing of large-scale graphene. Nat. Nanotechnol. 4, 25–29 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2008.329
A. Bagri, C. Mattevi, M. Acik, Y.J. Chabal, M. Chhowalla, V.B. Shenoy, Structural evolution during the reduction of chemically derived graphene oxide. Nat. Chem. 2, 581–587 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/nchem.686
A. Ciesielski, P. Samorì, Grapheneviasonication assisted liquid-phase exfoliation. Chem. Soc. Rev. 43, 381–398 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CS60217F
M. Yi, Z. Shen, A review on mechanical exfoliation for the scalable production of graphene. J. Mater. Chem. A 3, 11700–11715 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/C5TA00252D
H. Shima, M.M. Hossain, J.R. Hahn, Highly dispersed graphene ribbons produced from ZnO–C core–shell nanorods and their use as a filler in polyimide composites. RSC Adv. 4, 41204–41211 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA06782G
S. Liang, Z. Shen, M. Yi, L. Liu, X. Zhang, S. Ma, In-situ exfoliated graphene for high-performance water-based lubricants. Carbon N. Y. 96, 1181–1190 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CARBON.2015.10.077
S. Wang, M. Yi, Z. Shen, The effect of surfactants and their concentration on the liquid exfoliation of graphene. RSC Adv. 6, 56705–56710 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA10933K
M. Yi, Z. Shen, Kitchen blender for producing high-quality few-layer graphene. Carbon N. Y. 78, 622–626 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CARBON.2014.07.035
M. Yi, Z. Shen, S. Liang, L. Liu, X. Zhang, S. Ma, Water can stably disperse liquid-exfoliated graphene. Chem. Commun. 49, 11059 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1039/c3cc46457a
L. Liu, Z. Shen, M. Yi, X. Zhang, S. Ma, A green, rapid and size-controlled production of high-quality graphene sheets by hydrodynamic forces. RSC Adv. 4, 36464–36470 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA05635C
M. Yi, Z. Shen, J. Zhu, A fluid dynamics route for producing graphene and its analogues. Chin. Sci. Bull. 59, 1794–1799 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-014-0303-9
M. Yi, Z. Shen, X. Zhang, S. Ma, Achieving concentrated graphene dispersions in water/acetone mixtures by the strategy of tailoring Hansen solubility parameters. J. Phys. D 46, 025301 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/46/2/025301
M.M. Hossain, H. Shima, I. Lee, J.R. Hahn, In situ preparation of graphene-ZnO composites for enhanced graphite exfoliation and graphene-nylon-6 composite films. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 134, 45034 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/app.45034
M.M. Hossain, J.R. Hahn, B.C. Ku, Synthesis of highly dispersed and conductive graphene sheets by exfoliation of preheated graphite in a sealed bath and its applications to polyimide nanocomposites. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. (2014). https://doi.org/10.5012/bkcs.2014.35.7.2049
M.M. Hossain, O.-K. Park, J.R. Hahn, B.-C. Ku, High yield and high concentration few-layer graphene sheets using solvent exfoliation of graphite with pre-thermal treatment in a sealed bath. Mater. Lett. 123, 90–92 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MATLET.2014.03.024
J.N. Coleman, Liquid exfoliation of defect-free graphene. Acc. Chem. Res. 46, 14–22 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1021/ar300009f
Y. Hernandez, V. Nicolosi, M. Lotya, F.M. Blighe, Z. Sun, S. De, I.T. McGovern, B. Holland, M. Byrne, Y.K. Gun’Ko, J.J. Boland, P. Niraj, G. Duesberg, S. Krishnamurthy, R. Goodhue, J. Hutchison, V. Scardaci, A.C. Ferrari, J.N. Coleman, High-yield production of graphene by liquid-phase exfoliation of graphite. Nat. Nanotechnol. 3, 563–568 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2008.215
C.-J. Shih, S. Lin, M.S. Strano, D. Blankschtein, Understanding the stabilization of liquid-phase-exfoliated graphene in polar solvents: molecular dynamics simulations and kinetic theory of colloid aggregation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132, 14638–14648 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja1064284
A.A. Green, M.C. Hersam, Solution phase production of graphene with controlled thickness via density differentiation. Nano Lett. 9, 4031–4036 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1021/nl902200b
M. Lotya, P.J. King, U. Khan, S. De, J.N. Coleman, High-concentration, surfactant-stabilized graphene dispersions. ACS Nano 4, 3155–3162 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1021/nn1005304
D. Ager, V. Arjunan Vasantha, R. Crombez, J. Texter, Aqueous graphene dispersions–optical properties and stimuli-responsive phase transfer. ACS Nano 8, 11191–11205 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/nn502946f
A.S. Wajid, S. Das, F. Irin, H.S.T. Ahmed, J.L. Shelburne, D. Parviz, R.J. Fullerton, A.F. Jankowski, R.C. Hedden, M.J. Green, Polymer-stabilized graphene dispersions at high concentrations in organic solvents for composite production. Carbon N. Y. 50, 526–534 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CARBON.2011.09.008
P. May, U. Khan, J.M. Hughes, J.N. Coleman, Role of solubility parameters in understanding the steric stabilization of exfoliated two-dimensional nanosheets by adsorbed polymers. J. Phys. Chem. C 116, 11393–11400 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp302365w
V. Chabot, B. Kim, B. Sloper, C. Tzoganakis, A. Yu, High yield production and purification of few layer graphene by Gum Arabic assisted physical sonication. Sci. Rep. 3, 1378 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep01378
S. Das, F. Irin, H.S. Tanvir Ahmed, A.B. Cortinas, A.S. Wajid, D. Parviz, A.F. Jankowski, M. Kato, M.J. Green, Non-covalent functionalization of pristine few-layer graphene using triphenylene derivatives for conductive poly (vinyl alcohol) composites. Polym. (Guildf) 53, 2485–2494 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.POLYMER.2012.03.012
L. Guardia, M.J. Fernández-Merino, J.I. Paredes, P. Solís-Fernández, S. Villar-Rodil, A. Martínez-Alonso, J.M.D. Tascón, High-throughput production of pristine graphene in an aqueous dispersion assisted by non-ionic surfactants. Carbon N. Y. 49, 1653–1662 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CARBON.2010.12.049
S. Pei, J. Zhao, J. Du, W. Ren, H.-M. Cheng, Direct reduction of graphene oxide films into highly conductive and flexible graphene films by hydrohalic acids. Carbon N. Y. 48, 4466–4474 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CARBON.2010.08.006
P. He, J. Sun, S. Tian, S. Yang, S. Ding, G. Ding, X. Xie, M. Jiang, Processable aqueous dispersions of graphene stabilized by graphene quantum dots. Chem. Mater. 27, 218–226 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/cm503782p
T.C. Achee, W. Sun, J.T. Hope, S.G. Quitzau, C.B. Sweeney, S.A. Shah, T. Habib, M.J. Green, High-yield scalable graphene nanosheet production from compressed graphite using electrochemical exfoliation. Sci. Rep. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-32741-3
A. Ejigu, L.W. Le Fevre, K. Fujisawa, M. Terrones, A.J. Forsyth, R.A.W. Dryfe, Electrochemically exfoliated graphene electrode for high-performance rechargeable chloroaluminate and dual-ion batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b06528
K. Parvez, Z.-S. Wu, R. Li, X. Liu, R. Graf, X. Feng, K. Müllen, Exfoliation of graphite into graphene in aqueous solutions of inorganic salts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136, 6083–6091 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja5017156
C.Y. Lee, D.R.G. Mitchell, P. Molino, A. Fahy, G.G. Wallace, Tunable solution-processable anodic exfoliated graphene. Appl. Mater. Today 15, 290–296 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmt.2019.02.008
Y.Z.N. Htwe, W.S. Chow, Y. Suda, A.A. Thant, M. Mariatti, Effect of electrolytes and sonication times on the formation of graphene using an electrochemical exfoliation process. Appl. Surf. Sci. 469, 951–961 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.11.029
A. Ejigu, I.A. Kinloch, R.A.W. Dryfe, Single stage simultaneous electrochemical exfoliation and functionalization of graphene. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9, 710–721 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b12868
K. Parvez, R.A. Rincón, N.-E. Weber, K.C. Cha, S.S. Venkataraman, One-step electrochemical synthesis of nitrogen and sulfur co-doped, high-quality graphene oxide. Chem. Commun. 52, 5714–5717 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC01250G
Z. Liu, Z.-S. Wu, S. Yang, R. Dong, X. Feng, K. Müllen, Ultraflexible in-plane micro-supercapacitors by direct printing of solution-processable electrochemically exfoliated graphene. Adv. Mater. 28, 2217–2222 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201505304
A. Ambrosi, M. Pumera, Electrochemically exfoliated graphene and graphene oxide for energy storage and electrochemistry applications. Chem. A 22, 153–159 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.201503110
H.M. Yadav, J.-S. Kim, Solvothermal synthesis of anatase TiO2-graphene oxide nanocomposites and their photocatalytic performance, J. Alloys Compd. 688, 123–129 (2016). https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0925838816321697. Accessed 8 Sept 2016
R. Muzyka, S. Drewniak, T. Pustelny, M. Chrubasik, G. Gryglewicz, Characterization of graphite oxide and reduced graphene oxide obtained from different graphite precursors and oxidized by different methods using raman spectroscopy. Materials (Basel, Switzerland) (2018). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11071050
A. Ilnicka, M. Skorupska, P. Kamedulski, J.P. Lukaszewicz, Electro-exfoliation of graphite to graphene in an aqueous solution of inorganic salt and the stabilization of its sponge structure with poly(furfuryl alcohol). Nanomaterials (Basel, Switzerland) (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9070971
K. Chen, D. Xue, Preparation of colloidal graphene in quantity by electrochemical exfoliation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 436, 41–46 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2014.08.057
C.E. Hamilton, J.R. Lomeda, Z. Sun, J.M. Tour, A.R. Barron, High-yield organic dispersions of unfunctionalized graphene. Nano Lett. 9, 3460–3462 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1021/nl9016623
L. Xu, J.-W. McGraw, F. Gao, M. Grundy, Z. Ye, Z. Gu, J.L. Shepherd, Production of high-concentration graphene dispersions in low-boiling-point organic solvents by liquid-phase noncovalent exfoliation of graphite with a hyperbranched polyethylene and formation of graphene/ethylene copolymer composites. J. Phys. Chem. C 117, 10730–10742 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp4008009
M. Lotya, Y. Hernandez, P.J. King, R.J. Smith, V. Nicolosi, L.S. Karlsson, F.M. Blighe, S. De, Z. Wang, I.T. McGovern, G.S. Duesberg, J.N. Coleman, Liquid phase production of graphene by exfoliation of graphite in surfactant/water solutions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131, 3611–3620 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja807449u
S. Barwich, U. Khan, J.N. Coleman, A technique to pretreat graphite which allows the rapid dispersion of defect-free graphene in solvents at high concentration. J. Phys. Chem. C 117, 19212–19218 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp4047006
D. Li, M.B. Müller, S. Gilje, R.B. Kaner, G.G. Wallace, Processable aqueous dispersions of graphene nanosheets. Nat. Nanotechnol. 3, 101–105 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2007.451
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes of the National Research Foundation, funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning (Grant NRF-2016M1A2A2940912 and NRF-2015M1A2A2054996). This work was also supported by the Dongguk University Research Fund of 2017 and 2019 (S-2019-G0001-00030).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hossain, M.M., Lee, S.Y., Yadav, H.M. et al. Role of electrolyte at the interface and in the dispersion of graphene in organic solvents. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 31, 404–413 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-02542-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-02542-z