Abstract
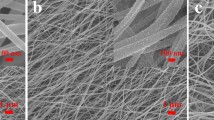
Electromagnetic (EM) wave absorbing materials with superhydrophobic property and enhanced microwave absorbing ability are very important for the application of stealth technologies, especially in humid conditions. In the present work, the electrospinning technique was employed to fabricate NiAc/PVA nanofibers (NFs) from nickel acetate tetrahydrate (NiAc) and poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) solution as precursors, while the PVA component was further pyrolyzed and carbonized to obtain Ni/NiO/C NFs. Microwave absorption performance and EM parameters of the prepared NFs were then investigated from 2.0 to 18.0 GHz. Comparative studies between different samples elucidated not only the possible causes for lose mechanisms, but also impedance matching. According to the experimental results, when NiAc/PVA NFs contained 8% NiAc, the calcinated Ni/NiO/C NFs could achieve an optimum reflection loss of − 33.9 dB at 10.4 GHz under a thickness of 2.5 mm and exhibit an effective frequency bandwidth of 5.7 GHz. Furthermore, the membrane of Ni/NiO/C NFs with the best absorption property exhibited robust hydrophobicity and the contact angle was 144.9°, It shows that the obtained Ni/NiO/C NFs have a broad application prospect in waterproof stealth materials.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
X. Wang, B. Zhang, W. Zhang, M. Yu, L. Cui, X. Cao, J. Liu, Super-light Cu@Ni nanowires/graphene oxide composites for significantly enhanced microwave absorption performance. Sci. Rep. 7(1), 1584 (2017)
W. She, H. Bi, Z. Wen, Q. Liu, X. Zhao, J. Zhang, R. Che, Tunable microwave absorption frequency by aspect ratio of hollow polydopamine@alpha-MnO2 microspindles studied by electron holography. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8(15), 9782–9789 (2016)
Q. Liu, Q. Cao, H. Bi, C. Liang, K. Yuan, W. She, Y. Yang, R. Che, CoNi@SiO2@TiO2 and CoNi@Air@TiO2 microspheres with strong wideband microwave absorption. Adv. Mater. 28(3), 486–490 (2016)
B. Wang, J. Zhang, T. Wang, L. Qiao, F. Li, Synthesis and enhanced microwave absorption properties of Ni@Ni2O3 core–shell particles. J. Alloys Compd. 567, 21–25 (2013)
T. Wang, H. Wang, X. Chi, R. Li, J. Wang, Synthesis and microwave absorption properties of Fe–C nanofibers by electrospinning with disperse Fe nanoparticles parceled by carbon. Carbon 74, 312–318 (2014)
Y. Shen, Y. Wei, J. Li, Q. Li, J. Ma, P. Wang, B. Li, W. He, X. Du, Preparation of microwave absorbing Co–C nanofibers with robust superhydrophobic properties by electrospinning. J. Mater. Sci. 30, 3365–3377 (2019)
H. Xu, W. Sun, X. Qiu, L. Wang, M. Yu, Q. Zhang, Structural, magnetic and microwave absorption properties of Ni-doped ZnO nanofibers. J. Mater. Sci. 28(3), 2803–2811 (2016)
X. Jian, B. Wu, Y. Wei, S.X. Dou, X. Wang, W. He, N. Mahmood, Facile synthesis of Fe3O4/GCs composites and their enhanced microwave absorption properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8(9), 6101–6109 (2016)
J. Deng, X. Zhang, B. Zhao, Z. Bai, S. Wen, S. Li, S. Li, J. Yang, R. Zhang, Fluffy microrods to heighten the microwave absorption properties through tuning the electronic state of Co/CoO. J. Mater. Chem. C 6(26), 7128–7140 (2018)
C. Tian, Y. Du, P. Xu, R. Qiang, Y. Wang, D. Ding, J. Xue, J. Ma, H. Zhao, X. Han, Constructing uniform core–shell PPy@PANI composites with tunable shell thickness toward enhancement in microwave absorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7(36), 20090–20099 (2015)
W. Liu, Q. Shao, G. Ji, X. Liang, Y. Cheng, B. Quan, Y. Du, Metal–organic-frameworks derived porous carbon-wrapped Ni composites with optimized impedance matching as excellent lightweight electromagnetic wave absorber. Chem. Eng. J. 313, 734–744 (2017)
Y. Cheng, M. Tan, P. Hu, X. Zhang, B. Sun, L. Yan, S. Zhou, W. Han, Strong and thermostable SiC nanowires/graphene aerogel with enhanced hydrophobicity and electromagnetic wave absorption property. Appl. Surf. Sci. 448, 138–144 (2018)
X. Zhang, G. Ji, W. Liu, X. Zhang, Q. Gao, Y. Li, Y. Du, A novel Co/TiO2 nanocomposite derived from a metal-organic framework: synthesis and efficient microwave absorption. J. Mater. Chem. C 4(9), 1860–1870 (2016)
S. Dai, B. Quan, X. Liang, J. Lv, Z. Yang, G. Ji, Y. Du, Excellent microwave response derived from the construction of dielectric-loss 1D nanostructure. Nanotechnology 29(19), 195603 (2018)
P. Liu, Y. Huang, J. Yan, Y. Yang, Y. Zhao, Construction of CuS nanoflakes vertically aligned on magnetically decorated graphene and their enhanced microwave absorption properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8(8), 5536–5546 (2016)
C. Song, X. Yin, M. Han, X. Li, Z. Hou, L. Zhang, L. Cheng, Three-dimensional reduced graphene oxide foam modified with ZnO nanowires for enhanced microwave absorption properties. Carbon 116, 50–58 (2017)
Y. Shen, Y. Wei, J. Ma, Q. Li, J. Li, W. Shao, P. Yan, G. Huang, X. Du, Tunable microwave absorption properties of nickel-carbon nanofibers prepared by electrospinning. Ceram. Int. 45(3), 3313–3324 (2019)
Z. Yang, H. Lv, R. Wu, Rational construction of graphene oxide with MOF-derived porous NiFe@C nanocubes for high-performance microwave attenuation. Nano Res. 9(12), 3671–3682 (2016)
Y. Lan, X. Li, Y. Zong, Z. Li, Y. Sun, G. Tan, J. Feng, Z. Ren, X. Zheng, In-situ synthesis of carbon nanotubes decorated by magnetite nanoclusters and their applications as highly efficient and enhanced microwave absorber. Ceram. Int. 42(16), 19110–19118 (2016)
G. Wang, Z. Gao, S. Tang, C. Chen, F. Duan, S. Zhao, S. Lin, Y. Feng, L. Zhou, Y. Qin, Microwave absorption properties of carbon nanocoils coated with highly controlled magnetic materials by atomic layer deposition. ACS Nano 6(12), 11009–11017 (2012)
B. Quan, X. Liang, G. Ji, J. Lv, S. Dai, G. Xu, Y. Du, Laminated graphene oxide-supported high-efficiency microwave absorber fabricated by an in situ growth approach. Carbon 129, 310–320 (2018)
X.F. Zhang, X.L. Dong, H. Huang, Y.Y. Liu, W.N. Wang, X.G. Zhu, B. Lv, J.P. Lei, C.G. Lee, Microwave absorption properties of the carbon-coated nickel nanocapsules. Appl. Phys. Lett. 89(5), 053115 (2006)
Y. Sun, X. Liu, C. Feng, J. Fan, Y. Lv, Y. Wang, C. Li, A facile synthesis of FeNi3@C nanowires for electromagnetic wave absorber. J. Alloys Compd. 586, 688–692 (2014)
Y. Zhang, X. Zhang, B. Quan, G. Ji, X. Liang, W. Liu, Y. Du, A facile self-template strategy for synthesizing 1D porous Ni@C nanorods towards efficient microwave absorption. Nanotechnology 28(11), 115704 (2017)
Y. Liu, N. Zhang, C. Yu, L. Jiao, J. Chen, MnFe2O4@C nanofibers as high-performance anode for sodium-ion batteries. Nano Lett. 16(5), 3321–3328 (2016)
Y. Liu, H. Teng, H. Hou, T. You, Nonenzymatic glucose sensor based on renewable electrospun Ni nanoparticle-loaded carbon nanofiber paste electrode. Biosens. Bioelectron. 24(11), 3329–3334 (2009)
S. Wang, L. Jiang, Definition of superhydrophobic states. Adv. Mater. 19(21), 3423–3424 (2007)
Y. Li, Y. Zhao, X. Lu, Y. Zhu, L. Jiang, Self-healing superhydrophobic polyvinylidene fluoride/Fe3O4@polypyrrole fiber with core–sheath structures for superior microwave absorption. Nano Res. 9(7), 2034–2045 (2016)
Y. Zhu, J. Zhang, J. Zhai, Y. Zheng, L. Feng, L. Jiang, Multifunctional carbon nanofibers with conductive, magnetic and superhydrophobic properties. Chemphyschem 7, 336–341 (2006)
S. Zhang, Q. Shi, C. Christodoulatos, X. Meng, Lead and cadmium adsorption by electrospun PVA/PAA nanofibers: batch, spectroscopic, and modeling study. Chemosphere 233, 405–413 (2019)
Z. Liu, R. Liu, Y. Yi, W. Han, F. Kong, S. Wang, Photocatalytic degradation of dyes over a xylan/PVA/TiO2 composite under visible light irradiation. Carbohydr. Polym. 223, 115081 (2019)
K. Kaviyarasu, E. Manikandan, J. Kennedy, M. Jayachandran, R. Ladchumananandasiivam, U. De Gomes, M. Maaza, Synthesis and characterization studies of NiO nanorods for enhancing solar cell efficiency using photon upconversion materials. Ceram. Int. 42(7), 8385–8394 (2016)
Y. Zhang, T. Gao, S. Xie, B. Dai, L. Fu, Y. Gao, Y. Chen, M. Liu, Z. Liu, Different growth behaviors of ambient pressure chemical vapor deposition graphene on Ni(111) and Ni films: a scanning tunneling microscopy study. Nano Res. 5(6), 402–411 (2012)
T. Liu, X.B. Xie, Y. Pang, S. Kobayashi, Co/C nanoparticles with low graphitization degree: a high performance microwave-absorbing material. J. Mater. Chem. C 4(8), 1727–1735 (2016)
N. Liu, L. Fu, B. Dai, K. Yan, X. Liu, R. Zhao, Y. Zhang, Z. Liu, Universal segregation growth approach to wafer-size graphene from non-noble metals. Nano Lett. 11(1), 297–303 (2011)
L.L. Patera, F. Bianchini, C. Africh, C. Dri, G. Soldano, M.M. Mariscal, M. Peressi, G. Comelli, Real-time imaging of adatom-promoted graphene growth on nickel. Science 359(6381), 1243–1246 (2018)
N.A.M. Barakat, B. Kim, H.Y. Kim, Production of smooth and pure nickel metal nanofibers by the electrospinning technique: nanofibers possess splendid magnetic properties. J. Phys. Chem. C 113(2), 531–536 (2009)
J.F. Löffler, J.P. Meier, B. Doudin, J.-P. Ansermet, W. Wagner, Random and exchange anisotropy in consolidated nanostructured Fe and Ni: role of grain size and trace oxides on the magnetic properties. Phys. Rev. B 57(5), 2915–2924 (1998)
J. Gong, L.L. Wang, Y. Liu, J.H. Yang, Z.G. Zong, Structural and magnetic properties of hcp and fcc Ni nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 457(1–2), 6–9 (2008)
T. Chen, F. Deng, J. Zhu, C. Chen, G. Sun, S. Ma, X. Yang, Hexagonal and cubic Ni nanocrystals grown on graphene: phase-controlled synthesis, characterization and their enhanced microwave absorption properties. J. Mater. Chem. 22(30), 15190 (2012)
Y. Du, W. Liu, R. Qiang, Y. Wang, X. Han, J. Ma, P. Xu, Shell thickness-dependent microwave absorption of core-shell Fe3O4@C composites. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 6(15), 12997–13006 (2014)
V.A. Markel, Can the imaginary part of permeability be negative? Phys. Rev. E 78(2), 026608 (2008)
M. Maglione, M.A. Subramanian, Dielectric and polarization experiments in high loss dielectrics: a word of caution. Appl. Phys. Lett. 93(3), 032902 (2008)
F. Wang, Y. Sun, D. Li, B. Zhong, Z. Wu, S. Zuo, D. Yan, R. Zhuo, J. Feng, P. Yan, Microwave absorption properties of 3D cross-linked Fe/C porous nanofibers prepared by electrospinning. Carbon 134, 264–273 (2018)
Z.L. Hou, M. Zhang, L.B. Kong, H.M. Fang, Z.J. Li, H.F. Zhou, H.B. Jin, M.S. Cao, Microwave permittivity and permeability experiments in high-loss dielectrics: caution with implicit Fabry–Perot resonance for negative imaginary permeability. Appl. Phys. Lett. 103(16), 162905 (2013)
T. Wu, Y. Liu, X. Zeng, T. Cui, Y. Zhao, Y. Li, G. Tong, Facile hydrothermal synthesis of Fe3O4/C core–shell nanorings for efficient low-frequency microwave absorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8(11), 7370–7380 (2016)
H. Wang, L. Xiang, W. Wei, J. An, J. He, C. Gong, Y. Hou, Efficient and lightweight electromagnetic wave absorber derived from metal organic framework-encapsulated cobalt nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9(48), 42102–42110 (2017)
M. Qiao, X. Lei, Y. Ma, L. Tian, W. Wang, K. Su, Q. Zhang, Facile synthesis and enhanced electromagnetic microwave absorption performance for porous core–shell Fe3O4@MnO2 composite microspheres with lightweight feature. J. Alloys Compd. 693, 432–439 (2017)
A. Aharoni, Exchange resonance modes in a ferromagnetic sphere. J. Appl. Phys. 69(11), 7762–7764 (1991)
H. Xu, X. Yin, M. Zhu, M. Han, Z. Hou, X. Li, L. Zhang, L. Cheng, Carbon hollow microspheres with a designable mesoporous shell for high-performance electromagnetic wave absorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9(7), 6332–6341 (2017)
J. Kuang, P. Jiang, F. Ran, W. Cao, Conductivity-dependent dielectric properties and microwave absorption of Al-doped SiC whiskers. J. Alloys Compd. 687, 227–231 (2016)
X. Zheng, J. Feng, Y. Zong, H. Miao, X. Hu, J. Bai, X. Li, Hydrophobic graphene nanosheets decorated by monodispersed superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanocrystals as synergistic electromagnetic wave absorbers. J. Mater. Chem. C 3(17), 4452–4463 (2015)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51363015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, Y., Wei, Y., Li, J. et al. Fabrication of microwave absorbing Ni/NiO/C nanofibers with robust superhydrophobic properties by electrospinning. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 31, 226–238 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-02462-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-02462-y