Abstract
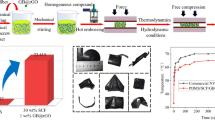
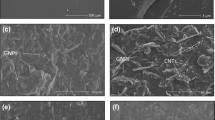
The performance of an electronic product depends on how efficiently it can dissipate the heat of its parts. As a result, intensive ongoing research seeks to improve the thermal conductivity of polymeric materials. In this study, we investigate magnesia nanofibers as thermal conductive filler in the resin and compared them to conventional spherical filler. Magnesia nanofiber mats were fabricated by electrospinning a solution of polyvinyl alcohol and magnesium ethoxide mixtures; they were then impregnated with resins to obtain a composite sheet. We assessed the thermal conductivity of the composite sheet. The resin sheet with aligned magnesia nanofibers content (49 vol%) had high thermal conductivity (12.9 W/mK) in the direction parallel to the aligned magnesia nanofibers. The conductivity increased in proportion to magnesia nanofiber content. In addition, the magnesia nanofiber composite sheet showed anisotropic thermal conductivity derived from the fiber direction and had electrical insulation (7.7 × 1012 Ω/□), and flexibility. These electrically insulating sheets with anisotropy in thermal conductivity would be useful in designing effective heat removal paths in electronic devices.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Tanaka, S. Ogata, R. Kobayashi, T. Tamura, M. Kitsunezuka, A. Shinma, J. Appl. Phys. 114, 193512 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4831946
E.N. Galashov, A.A. Yusuf, E.M. Mandrik, V.V. Atuchun, Int. J. Manuf. Technol. 86, 475–478 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-015-8186-8
Y. Agari, A. Ueda, M. Tanaka, S. Nagai, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 40(56), 929–941 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1002/app.1990.070400526
S. Yu, P. Hing, X. Hu, Composites A 33(2), 289–292 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-835X(01)00107-5
Y. Agari, A. Ueda, S. Nagai, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 49(9), 1625–1634 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1002/app.1993.070490914
W. Zhou, S. Qi, Q. An, H. Zhao, N. Liu, Mater. Res. Bull. 42(10), 1863–1873 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2006.11.047
M. Harada, N. Hamaura, M. Ochi, Y. Agari, Composites B 55, 306–313 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2013.06.031
D.S. Muratov, D.V. Kuznetsov, I.A. Ilinykh, I.N. Mazov, A.A. Stepashkin, V.V. Tcherdyntsev, J. Alloys Compd. 586, S451–S454 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2012.11.142
K. Kim, M. Kim, Y. Hwang, J. Kim, Ceram. Int. 40(1), 2047–2056 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2013.07.117
S. Choi, J. Kim, Composites B 51, 140–147 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2013.03.002
C. Shao, H. Guan, Y. Liu, R. Mu, J. Mater. Sci. 4, 3821–3824 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-005-5623-3
C. Xu, K. Yuan, X. Jin, Z. Yu, L. Zheng, Y. Lü, X. Wang, L. Zhu, G. Zhang, D. Xu, Ceram. Int. 43, 16210–16216 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.08.199
K. Nakane, S. Ichikawa, S. Gao, M. Seto, S. Irie, S. Yonezawa, N. Ogata, Sen’i Gakkaishi 71(1), 67–71 (2015). https://doi.org/10.2115/fiber.71.1
A. Ohgoshi, S. Gao, K. Takahashi, K. Nakane, J. Text. Eng. 65(4), 67–72 (2019)
T. Lopez, I. Garcia-Cruz, R. Gomez, J. Catal. 127, 75–85 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1016/0021-9517(91)90210-U
D.A.G. Bruggeman, Annal. der Phys. 416, 636–664 (1935). https://doi.org/10.1002/andp.19354160705
Acknowledgements
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public or not-for-profit sectors, and is supported financially by Nissan Chemical Corporation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ohgoshi, A., Takahashi, K. & Nakane, K. Polymer/magnesia nanofiber composite sheets with anisotropic high thermal conductivity. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 30, 20566–20573 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-02421-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-02421-7