Abstract
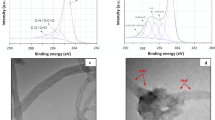
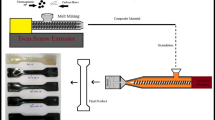
The electromagnetic shielding materials with characteristics of ultrathin, lightweight and high strength are the most advantageous materials in electromagnetic shielding. In this work, novel carbon fiber nonwoven composites with interlayer microstructure were designed and prepared. Due to their special structure, carbon fiber nonwoven composites coated with polyaniline by means of electropolymerization showed excellent electromagnetic shielding (65 dB) and mechanical properties (bending strength of 457 MPa). More intriguing, the absolute SE (Shielding Effectiveness) of the composites can be as high as 3904 dB.cm2/g. In order to explore the elementary mechanisms of electromagnetic loss, the relevant calculation of electromagnetic shielding effectiveness was carried out. The experimental and theoretical results show that the reflection is the dominant shielding performance of the carbon fiber nonwoven composites. However, with the increase of electropolymerization time, the absorption loss was enhanced and the reflection was weakened, which was caused by the conductive polyaniline network structure covered on the nonwoven fiber surface. Based on the comparison between experimental results and theoretical calculation, the effect of multiple reflection loss on the total electromagnetic shielding performance was improved, and the loss mechanism of multiple reflection was analyzed in detail. Moreover, the surface roughness of fiber and the formation of polymerization products by electropolymerization could effectively enhance the interfacial strength between carbon fiber nonwoven and epoxy, which observably increased the bending strength by 83%.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Sun, R. Che, X. You, Y. Jiang, Z. Yang, J. Deng, Cross-stacking aligned carbon-nanotube films to tune microwave absorption frequencies and increase absorption intensities. Adv. Mater. 26, 8120–8125 (2014)
B. Wen, M. Cao, M. Lu, W. Cao et al., Reduced graphene oxides: light-weight and high-efficiency electromagnetic interference shielding at elevated temperatures. Adv. Mater. 26, 3484–3489 (2014)
Y. Zhang, Y. Huang, T. Zhang, H. Chang, P. Xiao, H. Chen, Broadband and tunable high-performance microwave absorption of an ultralight and highly compressible graphene foam. Adv. Mater. 27, 2049–2053 (2015)
E. Vazquez, M. Prato, Carbon nanotubes and microwaves: interactions, responses, and applications. ACS Nano 3, 3819–3824 (2009)
M.S. Cao, W.L. Song, Z.L. Hou, B. Wen, J. Yuan, The effects of temperature and frequency on the dielectric properties, electromagnetic interference shielding and microwave-absorption of short carbon fiber/silica composites. Carbon 48, 788–796 (2010)
Z. Liu, G. Bai, Y. Huang, F. Li, Y. Ma, T. Guo, Microwave absorption of single-walled carbon nanotubes/soluble cross-linked polyurethane composites. J. Phys. Chem. C 111, 13696–13700 (2007)
F. Moglie, D. Micheli, S. Laurenzi, M. Marchetti, V.M. Primiani, Electromagnetic shielding performance of carbon foams. Carbon 50, 1972–1980 (2012)
H.B. Wang, K.Y. Teng, C. Chen, X.J. Li, Z.W. Xu et al., Conductivity and electromagnetic interference shielding of graphene-based architectures using MWCNTs as free radical scavenger in gamma irradiation. Mater. Lett. 186, 78–81 (2017)
D. Micheli, R.B. Morles, M. Marchetti, F. Moglie, V.M. Primiani, Broadband electromagnetic characterization of carbon foam to metal contact. Carbon 68, 149–158 (2014)
C. Liang, C. Liu, H. Wang, L. Wu, Z. Jiang, Y. Xu, SiCeFe3O4 dielectric magnetic hybrid nanowires: controllable fabrication, characterization and electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Mater. Chem. A 2, 16397–16402 (2014)
K.L. Wang, W. Wang, H.B. Wang, L.S. Liu, Z.W. Xu et al., 3D graphene foams/epoxy composites with double-sided binder polyaniline interlayers for maintaining excellent electrical conductivities and mechanical properties. Compos. Part A 110, 246–257 (2018)
W.L. Song, M.S. Cao, L.Z. Fan, M.M. Lu, Y. Li, C.Y. Wang, Highly ordered porous carbon/wax composites for effective electromagnetic attenuation and shielding. Carbon 77, 130–142 (2014)
H.B. Wang, W. Wang, Y.F. Zhao, Z.W. Xu, L. Chen et al., Superior adsorption of 3D nanoporous architectures for Ni(II) ions adsorption using polyvinyl alcohol as cross-linking agent and adsorption conveyor. RSC Adv. 8, 7899–7903 (2018)
Z. Wang, L. Wu, J. Zhou, Z. Jiang, B. Shen, Chemo selectivity-induced multiple interfaces in MWCNT/Fe3O4@ZnO heterotrimers for whole X-band microwave absorption. Nanoscale 6, 12298–12302 (2014)
W.X. Li, Z.W. Xu, L. Chen, M.J. Shan, X. Tian et al., A facile method to produce graphene oxide-g-poly(L-Lactic Acid)as an promising reinforcement for PLLA nanocomposites. Chem. Eng. J. 237, 291–299 (2014)
I. Arief, S. Biswas, S. Bose, FeCo-anchored reduced graphene oxide framework based soft composites containing carbon nanotubes as highly efficient microwave absorbers with excellent heat dissipation ability. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 9, 19202–19214 (2016)
B. Zhao, C. Zhao, R. Li, S.M. Hamidinejad, C.B. Park, Flexible, ultrathin, and high-efficiency electromagnetic shielding properties of poly (vinylidene fluoride)/carbon composite films. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 9, 20873–20884 (2017)
B. Wen, M.S. Cao, Z.L. Hou, W.L. Song, L. Zhang, Temperature dependent microwave attenuation behavior for carbon-nanotube/silica composites. Carbon 65, 124–139 (2013)
W.Q. Cao, X.X. Wang, J. Yuan, W.Z. Wang, M.S. Cao, Temperature dependent microwave absorption of ultrathin graphene composites. J. Mater. Chem. C 3, 10017–10022 (2015)
Z. Zeng, H. Jin, M. Chen, W. Li, L. Zhou, X. Xue, Z. Zhang, Microstructure design of lightweight, flexible, and high electromagnetic shielding porous multiwalled carbon nanotube/polymer composites. Small 13(34), 1701388 (2017)
Y.J. Wan, P.L. Zhu, S.H. Yu, R. Sun, C.P. Wong, W.H. Liao, Ultralight, superelastic and volume-preserving cellulose fiber/graphene aerogel for highperformance electromagnetic interference shielding. Carbon 115, 629–639 (2017)
X. Hong, D.D.L. Chung, Carbon nanofiber mats for electromagnetic interference shielding. Carbon 111, 529–537 (2017)
H.B. Wang, N. Li, Z.W. Xu, X. Tian, W. Mai et al., Enhanced sheet-sheet welding and interfacial wettability of 3D graphene networks as radiation protection in gamma-irradiated epoxy composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 157, 57–66 (2018)
W.W. Jiang, H.B. Wang, Z.W. Xu, N. Li, C. Chen et al., A review on manifold synthetic and reprocessing methods of 3D porous graphene-based architecture for Li-ion anode. Chem. Eng. J. 335, 954–969 (2018)
Y. Xu, Y. Li, W. Hua, A. Zhang, J. Bao, Light-weight silver plating foam and carbon nanotube hybridized epoxy composite foams with exceptional conductivity and electromagnetic shielding property. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 8, 24131–24142 (2016)
H. Wu, D. Kong, Z. Ruan, P.C. Hsu, S. Wang, Z. Yu, J. Carney Thomas, L. Hu, S. Fan, Y. Cui, A transparent electrode based on a metal nanotrough network. Nat. Nanotechnol. 8, 421–425 (2013)
S. An, H.S. Jo, D.Y. Kim, H.J. Lee, B.K. Ju, S.S. Al-Deyab, J.H. Ahn, Y. Qin, M.T. Swihart, A.L. Yarin, S.S. Yoon, Self-junctioned copper nanofiber transparent flexible conducting film via electrospinning and electroplating. Adv. Mater. 28, 7149–7154 (2016)
Y. Wang, J. Cheng, Y. Xing, M. Shahid, H. Nishijima, W. Pan, Stretchable platinum network-based transparent electrodes for highly sensitive wearable electronics. Small 13, 1604291 (2017)
J.C. Wang, C.S. Xiang, Q. Liu, Y.N. Pan, J.K. Guo, Ordered mesoporous carbon/fused silica composites. Adv. Funct. Mater. 18, 2995–3002 (2008)
J.C. Wang, H. Zhou, J.D. Zhuang, Q. Liu, Influence of spatial configurations on electromagnetic interference shielding of ordered mesoporous carbon/ordered mesoporous silica/silica composites. Sci. Rep. 3, 3252 (2013)
B. Jiang, T. Zhang, Y.D. Huang, Interfacially reinforced carbon fiber composites by grafting modified methylsilicone resin. Compos. Sci. Technol. 140, 39–45 (2017)
C. Zhang, L.S. Liu, Z.W. Xu, H.M. Lv, N. Wu et al., Improvement for interface adhesion of epoxy/carbon fibers endowed with carbon nanotubes via microwave plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition. Polym. Compos. 39, E1262–E1268 (2018)
H.M. Wu, Z.Y. Zhou, L. Chen, W.X. Li, Q.Q. Han et al., PECVD-induced growing of diverse nanomaterials on carbon nanofibers under various conditions. Mater. Lett. 216, 291–294 (2018)
J. Liu, Y.L. Tian, Y.J. Chen, J.Y. Liang, L.F. Zhang, H. Feng, A surface treatment technique of electrochemical oxidation to simultaneously improve the interfacial bonding strength and the tensile strength of PAN-based carbon fibers. Mater. Chem. Phys. 122, 548–555 (2010)
X. Qian, J.H. Zhi, L.Q. Chen, J. Huang, Y.G. Zhang, Effect of low current density electrochemical oxidation on the properties of carbon fiber-reinforced epoxy resin composites. Surf. Interface Anal. 45, 937–942 (2013)
F. Severini, L. Formaro, M. Pegoraro, L. Posca, Chemical modification of carbon fiber surfaces. Carbon 40, 735–741 (2002)
K.Z. Li, C. Wang, H.J. Li, X.T. Li, H.B. Yang, J. Wei, Effect of chemical vapor deposition treatment of carbon fibers on the reflectivity of carbon fiber-reinforced cement-based composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 68, 1105–1114 (2008)
Z.W. Xu, L.S. Liu, Y.D. Huang, Y. Sun, X.Q. Wu, J.L. Li, Graphitization of polyacrylonitrile carbon fibers and graphite irradiated by γ rays. Mater. Lett. 63, 1814–1816 (2009)
S. Tiwari, J. Bijwe, S. Panier, Gamma radiation treatment of carbon fabric to improve the fiber–matrix. Wear 271, 2184–2192 (2011)
Z.W. Xu, Y.D. Huang, C.H. Zhang, L. Liu, Y.H. Zhang, L. Wang, Effect of γ-ray irradiation grafting on the carbon fibers and interfacial adhesion of epoxy composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 67, 3261–3270 (2007)
X.H. Sui, Z.W. Xu, C.S. Hu, L. Chen, L.S. Liu, L.Y. Kuang, Microstructure evolution in γ-irradiated carbon fibers revealed by a hierarchical model and Raman spectra from fiber section. Compos. Sci. Technol. 130, 46–52 (2016)
A. Dumanl, A. Erden, Y. Yürüm, Development of supercapacitor active composites by electrochemical deposition of polypyrrole on carbon nanofibres. Polym. Bull. 68, 1395–1404 (2012)
A. Murat, A comparative study of redox parameters and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy of polycarbazole derivatives on carbon fiber microelectrode. Fiber Polym. 11, 1094–1100 (2010)
M.S. Cao, X.X. Wang, M. Zhang, J.C. Shu, W.Q. Cao et al., Electromagnetic response and energy conversion for functions and devices in low-dimensional materials. Adv. Funct. Mater. 29, 1807398 (2019)
Z.Q. Tong, L. Shikun, X.G. Li et al., Facile and controllable construction of vanadium pentoxide@conducting polymer core/shell nanostructures and their thickness-dependent synergistic energy storage properties. Electrochim. Acta 222, 194–202 (2016)
A. Attout, S. Yunus, P. Bertrand, Electroless deposition of polyaniline: synthesis and characterization. Surf. Interface Anal. 40, 657–660 (2008)
X.X. Wang, J.C. Shu, W.Q. Cao, M. Zhang, J. Yuan et al., Eco-mimetic nanoarchitecture for green EMI shielding. Chem. Eng. J. 369, 1068–1077 (2019)
M. Arjmand, M. Mahmoodi, S. Park, U. Sundararaj et al., Impact of foaming on the broadband dielectric properties of multi-walled carbon nanotube/polystyrene composites. J. Cell. Plast. 50, 551–562 (2014)
S. Geetha, K.K.S. Kumar, C.R.K. Rao, M. Vijayan et al., EMI shielding: methods and materials-a review. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 112, 2073–2086 (2009)
Y. Wang, W. Wang, D. Yu, Three-phase heterostructures f-NiFe2O4/PANI/PI EMI shielding fabric with high Microwave Absorption Performance. Appl. Surf. Sci. 425, 518–525 (2017)
J.Q. Ling, W.T. Zhai, W.W. Feng, B. Shen, J.F. Zhang, W.G. Zheng, Facile preparation of lightweight microcellular polyetherimide/graphene composite foams for electromagnetic interference shielding. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 5, 2677–2684 (2013)
G.S. Kumar, T.U. Patro, Efficient electromagnetic interference shielding and radar absorbing properties of ultrathin and flexible polymer-carbon nanotube composite films. Mater. Res. Express 5(11), 115304 (2018)
S. Teotia, B.P. Singh, I. Elizabeth, V.N. Singh, R. Ravikumar, A.P. Singh, S. Gopukumar et al., Multifunctional, robust, light-weight, free-standing MWCNT/phenolic composite paper as anodes for lithium ion batteries and EMI shielding material. RSC Adv. 4, 33168 (2014)
Z.P. Chen, C. Xu, C.Q. Ma, W.C. Ren, H.M. Cheng, Lightweight and flexible graphene foam composites for high-performance electromagnetic interference shielding. Adv. Mater. 25, 1296–1300 (2013)
Z.H. Zeng, M.J. Chen, H. Jin, W.W. Li, X. Xue, L.C. Zhou et al., Thin and flexible multi-walled carbon nanotube/waterborne polyurethane composites with high-performance electromagnetic interference shielding. Carbon 96, 768–777 (2015)
P. Saini, V. Choudhary, V.B. Singh, R.B. Mathur, S.K. Dhawan, Polyaniline–MWCNT nanocomposites for microwave absorption and EMI shielding. Mater. Chem. Phys. 113, 919–926 (2009)
X.Y. Sun, X. Liu, X. Shen, Y. Wu, Z.Y. Wang, J.K. Kim, Reprint of Graphene foam/carbon nanotube/poly(dimethyl siloxane)composites for exceptional microwave shielding. Compos. Part. A 92, 190–197 (2016)
H. Mohammed, U. Sundararaj, Electromagnetic interference shielding mechanisms of CNT/polymer composites. Carbon 47, 1738–1746 (2009)
A. Ameli, P.U. Jung, C.B. Park, Electrical properties and electromagnetic interference shielding effectiveness of polypropylene/carbon fiber composite foams. Carbon 60, 379–391 (2013)
D.X. Yan, P.G. Ren, H. Pang, Q. Fu, M.B. Yang, Z.M. Li, Efficient electromagnetic interference shielding of lightweight graphene/polystyrene composite. J. Mater. Chem. 22, 18772–18774 (2012)
T. Bansala, M. Joshi, S. Mukhopadhyay, R. Doong, M. Chaudhary, Electrically conducting graphene-based polyurethane nanocomposites for microwave shielding applications in the Ku band. J. Mater. Sci. 52, 1546–1560 (2017)
H. Mohammed, A. Saleh, U. Sundararaj, Electromagnetic interference shielding mechanisms of CNT/polymer composites. Carbon 47, 738–746 (2009)
Y. Wu, Z.Y. Wang, X. Liu, X. Shen, Q.B. Zheng, Q. Xue, Ultralight graphene foam/conductive polymer composites for exceptional electromagnetic interference shielding. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 9, 9059–9069 (2017)
W.L. Song, M.S. Cao, M.M. Lu, S. Bi, C.Y. Wang, J. Liu, Flexible graphene/polymer composite films in sandwich structures for effective electromagnetic interference shielding. Carbon 66, 67–76 (2014)
J. Lee, Y.N. Liu, Y. Liu, S. Park, M. Parkc, H.Y. Kim, Ultrahigh electromagnetic interference shielding performance of lightweight, flexible, and highly conductive copper-clad carbon fiber nonwoven fabrics. J. Mater. Chem. C 5, 7853–7861 (2017)
H. Wang, K. Zheng, X. Zhang, X. Ding, Z.X. Zhang et al., 3D network porous polymeric composites with outstanding electromagnetic interference shielding. Compos. Sci. Technol. 125, 22–29 (2016)
M.S. Cao, X.X. Wang, W.Q. Cao, X.Y. Fang, B. Wen et al., Thermally driven transport and relaxation switching self-powered electromagnetic energy conversion. Small 14, 1800987 (2018)
Y.H. Zhang, S.J. Park, Enhanced interfacial interaction by grafting carboxylated-macromolecular chains on nanodiamond surfaces for epoxy-based thermosets. J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Phys. 55(24), 1890–1898 (2017)
Z.B. Zhao, K.Y. Teng, N. Li, X.J. Li, Z.W. Xu et al., Mechanical, thermal and interfacial performances of carbon fiber reinforced composites flavored by carbon nanotube in matrix/interface. Compos. Struct. 159, 761–772 (2017)
M.J. Shan, H.B. Wang, Z.W. Xu, N. Li, C. Chen et al., Synergetic improvement of mechanical properties and surface activities in g-irradiated carbon fibers revealed by radial positioning spectroscopy and mechanical model. Anal. Methods 10, 496–503 (2018)
Y. Ni, L. Chen, K.Y. Teng, J. Shi, X.M. Qian et al., Superior mechanical properties of epoxy composites reinforced by 3D interconnected graphene skeleton. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 7, 11583–11591 (2015)
Acknowledgements
The work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (11575126), the Natural Science Foundation of Tianjin (16JCZDJC37800, 16JCYBJC17700) and the Science and Technology Plans of Tianjin (16ZXCLGX00090).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, H., Liao, B., Wang, H. et al. Electromagnetic shielding of ultrathin, lightweight and strong nonwoven composites decorated by a bandage-style interlaced layer electropolymerized with polyaniline. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 30, 20420–20431 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-02379-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-02379-6