Abstract
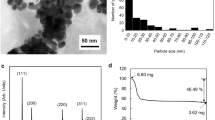
In this paper, humic acid (HA) was used as stabilizer to prepare silver nanoparticles (Ag NPs) by chemically reducing silver salts in water phase, which were employed to produce Ag NPs inks for inkjet printing conductive silver patterns. The obtained silver nanoparticles stabilized with HA (HA-Ag NPs) were all in spherical shape and the particle size was about 7–12 nm. By re-dispersing HA-Ag NPs in ultrapure water, conductive ink with excellent storage stability was prepared, which can be placed at room temperature for 30 days without any precipitation. The as-prepared HA-Ag NPs conductive ink was printed onto photopapers to fabricate conductive silver patterns with a domestic inkjet printer. The resistivity of the printed pattern could reach 135 μΩ cm after printed for 40 layers and sintered at 180 °C for 60 min. In addition, the printed conductive silver patterns could be integrated into a LED device or alarm apparatus, indicating it could be widely used in flexible printing electronics.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Woo, D. Kim, J.S. Kim et al., Inkjet printing of Cu-Ag-based highly conductive tracks on a transparent substrate. Langmuir 25(1), 429–433 (2009)
W. Wu, Stretchable electronics: Functional materials, fabrication strategies and applications. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 20(1), 187–224 (2019)
A. Kamyshny, M. Ben-Moshe, S. Aviezer, S. Magdassi, Ink-jet printing of metallic nanoparticles and microemulsions. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 26(4), 281–288 (2005)
N.C. Raut, K. Al-Shamery, Inkjet printing metals on flexible materials for plastic and paper electronics. J. Mater. Chem. C 6(7), 1618–1641 (2018)
W. Wu, Inorganic nanomaterials for printed electronics: a review. Nanoscale 9(22), 7342–7372 (2017)
D. Zhu, M. Wu, Highly conductive nano-silver circuits by inkjet printing. J. Electron. Mater. 47(9), 5133–5147 (2018)
Y.Y. Hao, N. Zhang, J. Luo, X.Y. Liu, Tannic acid stabilized antioxidation copper nanoparticles in aqueous solution for application in conductive ink. J. Mater. Sci. 29(24), 20603–20606 (2018)
P.S. Karthik, S. Singh, P, Conductive silver inks and their applications in printed and flexible electronics. RSC Adv. 5(95), 77760–77790 (2015)
K. Jaakkola, H. Sandberg, M. Lahti, V. Ermolov, Near-Field UHF RFID transponder with a screen-printed graphene antenna. IEEE Trans. Comput. Pack. Manuf. 9(4), 616–623 (2019)
W.F. Shen, X.P. Zhang, Q.J. Huang, Q.S. Xu, W.J. Song, Preparation of solid silver nanoparticles for inkjet printed flexible electronics with high conductivity. Nanoscale 6(3), 1622–1628 (2014)
S. Milardovic, I. Ivanisevic, A. Rogina, P. Kassal, Synthesis and electrochemical characterization of AgNP ink suitable for inkjet printing. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 13(11), 11136–11149 (2018)
S.A. Patil, C.H. Ryu, H.S. Kim, Synthesis and characterization of copper nanoparticles (Cu-Nps) using rongalite as reducing agent and photonic sintering of Cu-Nps ink for printed electronics. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 5(2), 239–245 (2018)
M. Singh, H.M. Haverinen, P. Dhagat, G.E. Jabbour, Inkjet printing-process and its applications. Adv. Mater. 22(6), 673–685 (2010)
A. Kamyshny, S. Magdassi, Conductive nanomaterials for printed electronics. Small 10(17), 3515–3535 (2014)
Y.Y. Hao, J. Gao, Z. Xu et al., Preparation of silver nanoparticles with hyperbranched polymers as a stabilizer for inkjet printing of flexible circuits. New J. Chem. 43(6), 2797–2803 (2019)
M. Wagner, C.D. O’Connell, D.G. Harman et al., Synthesis and optimization of PEDOT:PSS based ink for printing nanoarrays using dip-pen nanolithography. Synth. Met. 181, 64–71 (2013)
G.P. Evans, D.J. Buckley, N.T. Skipper, I.P. Parkin, Single-walled carbon nanotube composite inks for printed gas sensors: enhanced detection of NO2, NH3m EtOH and acetone. RSC Adv. 4(93), 51395–51403 (2014)
N.J. Zhang, R. Luo, X.Y. Liu, Liu, Tannic acid stabilized silver nanoparticles for inkjet printing of conductive flexible electronics. RSC Adv. 6(87), 83720–83729 (2016)
Q.F. Chen, G.H. Liu, G.X. Chen et al., Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles with glucose for conductivity enhancement of conductive ink. BioResources 12(1), 608–621 (2017)
M.C. Dang, T.M.D. Dang, E. Fribourg-Blanc, Silver nanoparticles ink synthesis for conductive patterns fabrication using inkjet printing technology. Adv. Nat. Sci. 6(1), 015003–015010 (2015)
Z. Khan, S.A. Al-Thabaiti, A.Y. Obaid et al., Preparation and characterization of silver nanoparticles by chemical reduction method. Colloid Surf. B 82(2), 513–517 (2011)
M.F. Zhang, A.W.B. Zhao, H.H. Sun et al., Rapid, large-scale, sonochemical synthesis of 3D nanotextured silver microflowers as highly efficient SERS substrates. J. Mater. Chem. 21(46), 18817–18824 (2011)
Y.Y. Hao, N. Zhang, J. Luo, X.Y. Liu, Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles by tannic acid with improved catalytic performance towards the reduction of methylene blue. NANO 13(01), 1850003–1850010 (2018)
J. Ding, J. Liu, Q. Tian et al., Preparing of highly conductive patterns on flexible substrates by screen printing of silver nanoparticles with different size distribution. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 11(1), 412–419 (2016)
A. Kamyshny, J. Steinke, S. Magdassi, Metal-based inkjet inks for printed electronics. Open Appl. Phys. J. 4(19), 19–36 (2011)
Z. Wang, X.W. Liang, T. Zhao et al., Facile synthesis of monodisperse silver nanoparticles for screen printing conductive inks. J. Mater. Sci. 28(22), 16939–16947 (2017)
X.Q. Zhou, W. Li, M.L. Wu et al., Enhanced dispersibility and dispersion stability of dodecylamine-protected silver nanoparticles by dodecanethiol for ink-jet conductive inks. Appl. Surf. Sci. 292, 537–543 (2014)
T.H. Chiang, K.D. Wu, T.E. Hsieh, Preparation of silver nanoparticles by using tripropylene glycol as the reducing agents of polyol process. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 13(1), 116–122 (2014)
E.K. Elumalai, K. Kayalvizhi, S. Silvan, Coconut water assisted green synthesis of silver nanoparticles. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 6(4), 241–245 (2014)
J. Bastos-Arrieta, A. Florido, C. Perez-Rafols et al., Green synthesis of Ag nanoparticles using grape stalk waste extract for the modification of screen-printed electrodes. Nanomaterials 8(11), 946–959 (2018)
J.M. Jacob, M.S. John et al., Bactericidal coating of paper towels via sustainable biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using ocimum sanctum leaf extract. Mater. Res. Express 6(4), 352–360 (2019)
S.T. Dubas, V. Pimpan, Humic acid assisted synthesis of silver nanoparticles and its application to herbicide detection. Mater. Lett. 62(17–18), 2661–2663 (2008)
I.L. Gunsolus, M.P.S. Mousavi et al., Effects of humic and fulvic acids on silver nanoparticle stability, dssolution, and toxicity. Environ. Sci. Technol. 49(13), 8078–8086 (2015)
Y. Liu, R.G. Jordan, S.L. Qiu, Electronic-structures of ordered Ag–Mg alloys. Phys. Rev. B 49(7), 4478–4484 (1994)
N.P. Bellafont, F. Vines, F. Illas, Performance of the TPSS functional on predicting core level binding energies of main group elements containing molecules: a good choice for molecules adsorbed on metal surfaces. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 12(1), 324–331 (2016)
J.M. Bingham, J.N. Anker, L.E. Kreno, R.P. Van Duyne, Gas sensing with high-resolution localized surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132(49), 17358–17359 (2010)
J. Sharma, N.K. Chaki, A.B. Mandale et al., Controlled interlinking of Au and Ag nanoclusters using 4-aminothiophenol as molecular interconnects. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 272(1), 145–152 (2004)
V.K. Kaushik, Xps core level spectra and auger parameters for some silver compounds. J. Electron. Spectrosc. 56(3), 273–277 (1991)
G. Zhang, H.Y. Gao, X.C. Tian et al., The performance study of OLED based on Cs2O doped Ag2O thin layer structure as the electronic injection layer. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 29(17), 1550080 (2015)
J.J. Alberts, Z. Filip, Metal binding in estuarine humic and fulvic acids: FTIR analysis of humic acid-metal complexes. Environ. Technol. 19(9), 923–931 (1998)
K.S. Moon, H. Dong, R. Maric et al., Thermal behavior of silver nanoparticles for low-temperature interconnect applications. J. Electron. Mater. 34(2), 168–175 (2005)
F. Zhang, Y.W. Li et al., Highly conductive, flexible and stretchable conductors based on fractal silver nanostructures. J. Mater. Chem. C 6, 3999–4006 (2018)
T.T. Nge, M. Nogi, K. Suganuma, Electrical functionality of inkjet-printed silver nanoparticle conductive tracks on nanostructured paper compared with those on plastic substrates. J. Mater. Chem. C 1, 5235–5243 (2013)
Acknowledgement
We acknowledge financial support from the National First-Class Discipline Program of Light Industry Technology and Engineering (LITE2018-19), MOE & SAFEA for the 111 Project (B13025) for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hao, Y., Xu, Z., Gao, J. et al. Humic acid assisted chemical synthesis of silver nanoparticles for inkjet printing of flexible circuits. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 30, 20400–20409 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-02372-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-02372-z