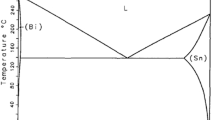
Abstract
In this paper, the influences of adding Titanium (Ti) nanoparticles on melting characteristics, wettability, shear properties and the growth of interfacial intermetallic compounds (IMC) of Sn58Bi solder were investigated. The results show that the addition of Ti nanoparticles improved the wettability and shear strength of Sn58Bi solder, and the optimum additive content was 0.1 wt%. The microstructure of the Sn58Bi solder was refined obviously with the addition of Ti nanoparticles. The thickness of interfacial IMC reduced significantly by adding Ti nanoparticles. However, doping Ti nanoparticles had the slight effect on the melting temperature of Sn58Bi solder. Moreover, the thickness of IMC at the Sn58Bi/Cu interface was distinctly larger than that of Sn58Bi-0.1Ti/Cu solder after multiple reflows, which means that the addition of Ti nanoparticles could suppress the growth of IMC at solder/Cu interface during multiple reflows.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Z.Q. Liu, M.Y. Li, Foundation of Lead-Free Soldering Technology (Science Press, Beijing, 2017)
M.Y. Xiong, L. Zhang, Interface reaction and intermetallic compound growth behavior of Sn-Ag-Cu lead-free solder joints on different substrates in electronic packaging. J. Mater. Sci. 54(2), 1741–1768 (2019)
L. Zhang, S.B. Xue, G. Zeng et al., Interface reaction between SnAgCu/SnAgCuCe solders and Cu substrate subjected to thermal cycling and isothermal aging. J. Alloys Compd. 510(1), 38–45 (2012)
L. Zhang, L. Sun, Y.H. Guo, Microstructures and properties of Sn58Bi, Sn35Bi0.3Ag, Sn35Bi1.0Ag solder and solder joints. J. Mater. Sci. 26(10), 7629–7634 (2015)
O. Mokhtari, H. Nishikawa, Correlation between microstructure and mechanical properties of Sn-Bi-x solders. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 651, 831–839 (2016)
K. Kanlayasiri, T. Ariga, Physical properties of Sn58Bi-xNi lead-free solder and its interfacial reaction with copper substrate. Mater. Des. 86, 371–378 (2015)
J. Shen, Y.C. Chan, Research advances in nano-composite solders. Microelectron. Reliab. 49(3), 223–234 (2009)
L. Yang, C.C. Du, J. Dai et al., Effect of nanosized graphite on properties of Sn-Bi solder. J. Mater. Sci. 24(11), 4180–4185 (2013)
Y. Li, Y.C. Chan, Effect of silver (Ag) nanoparticle size on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Sn58Bi-Ag composite solders. J. Alloys Compd. 645, 566–576 (2015)
T.W. Hu, Y. Li, Y.C. Chan et al., Effect of nano Al2O3 particles doping on electromigration and mechanical properties of Sn-58Bi solder joints. Microelectron. Reliab. 55(8), 1226–1233 (2015)
L. Yang, J. Dai, Y.C. Zhang et al., Influence of BaTiO3 nanoparticle addition on microstructure and mechanical properties of Sn-58Bi solder. J. Electron. Mater. 44(7), 2473–2478 (2015)
X. Li, Y. Ma, W. Zhou et al., Effects of nanoscale Cu6Sn5 particles addition on microstructure and properties of SnBi solder alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 684, 328–334 (2017)
S.Q. Zhou, C.H. Yang, S.K. Lin et al., Effects of Ti addition on the microstructure, mechanical properties and electrical resistivity of eutectic Sn58Bi alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 740, 560–569 (2019)
W.M. Chen, S.K. Kang, C.R. Kao, Effects of Ti addition to Sn-Ag and Sn-Cu solders. J. Alloys Compd. 520, 244–249 (2012)
C.L. Chuang, L.C. Tsao, H.K. Lin et al., Effects of small amount of active Ti element additions on microstructure and property of Sn3.5Ag0.5Cu solder. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 558, 478–484 (2012)
C. Wang, M. Li, Y. Tian, Review of JIS Z 3198: test method for lead-free solders. Electron. Process Technol. 25, 47–54 (2004)
L. Sun, M.H. Chen, C.C. Wei et al., Effect of thermal cycles on interface and mechanical property of low-Ag Sn1.0Ag0.5Cu(nano-Al)/Cu solder joints. J. Mater. Sci. 29(12), 9757–9763 (2018)
L. Sun, M.H. Chen, L.S. Xie et al., Properties and mechanism of nano Al particles reinforced Sn1.0Ag0.5Cu solders. Trans. China Weld. Inst. 39(8), 47–50 (2018)
F. Yang, L. Zhang, Z.Q. Liu et al., Effects of CuZnAl particles on properties and microstructure of Sn-58Bi solder. Materials 10(5), 558–568 (2017)
L.C. Tsao, S.Y. Chang, C.I. Lee et al., Effects of nano-Al2O3 additions on microstructure development and hardness of Sn35Ag05Cu solder. Mater. Des. 31(10), 4831–4835 (2010)
Acknowledgements
The present work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2017YFB0305700); Natural Science Foundation of China (51475220); Key project of State Key Laboratory of Advanced Welding and Joining (AWJ-19Z04); Six talent peaks project in Jiangsu Province (XCL-022); the Qing Lan Project, the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation funded project (2016M591464); International Cooperation Project (2015DFA50470).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, N., Zhang, L., Liu, Zq. et al. Influences of doping Ti nanoparticles on microstructure and properties of Sn58Bi solder. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 30, 17583–17590 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-02107-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-02107-0