Abstract
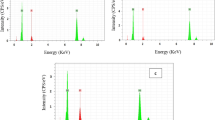
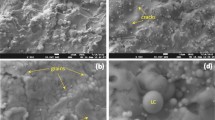
With the rapid increase of electric power use, wire and cable fire occurs more and more frequently. While the fire smoke could corrode the solders on the printed circuit boards, which seriously affects the function of electronic equipment. In this research, the long-term corrosion behavior of Sn–37Pb, Sn–0.7Cu, and Sn–3.0Ag solders under 140 g m−3 polyvinyl chloride fire smoke atmosphere were investigated. The mass loss of all solders increased sharply on the first day and then varied exponentially in the subsequent time period. Particularly, the mass loss of Sn–37Pb solder gradually stabilized after 10 days, while that of lead-free solders was after 12 days. Meanwhile, the corrosion morphology indicated that the corrosion products of both Sn–37Pb and Sn–0.7Cu solders grew to be larger and denser. While those of Sn–3.0Ag solder grew larger firstly and then became smaller and denser because the grain growth dominated firstly and then the nucleation dominated with corrosion time. The corrosion mechanism was analyzed by using EDS, XRD, and XPS. The result showed that the carbon particulates from the fire smoke was detected which might promote the corrosion process and all solders had a common corrosion product, Sn21Cl16(OH)14O6. Besides, Sn–37Pb solder also contained other corrosion product, PbCl2. The present work could provide guidance to the risk assessment for electronic equipment rescue after a fire.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Rerek, L. Skowronski, M. Kobierski, M.K. Naparty, B. Derkowska-Zielinska, Microstructure and opto-electronic properties of Sn-rich Au–Sn diffusive solders. Appl. Surf. Sci. 451, 32–39 (2018)
H. Chen, J. Peng, L. Fu, X. Wang, Y. Xie, Solder wetting behavior enhancement via laser-textured surface microcosmic topography. Appl. Surf. Sci. 368, 208–215 (2016)
H. Chen, H.Y. Lee, C.S. Ku, A.T. Wu, Evolution of residual stress and qualitative analysis of Sn whiskers with various microstructures. J. Mater. Sci. 51, 3600–3606 (2016)
M. Ramirez, L. Henneken, S. Virtanen, Oxidation kinetics of thin copper films and wetting behaviour of copper and organic solderability preservatives (OSP) with lead-free solder. Appl. Surf. Sci. 257, 6481–6488 (2011)
B. Medgyes, B. Horváth, B. Illés, T. Shinohara, A. Tahara, G. Harsányi, O. Krammer, Microstructure and elemental composition of electrochemically formed dendrites on lead-free micro-alloyed low Ag solder alloys used in electronics. Corros. Sci. 92, 43–47 (2015)
H. Huang, G. Shuai, X. Wei, C. Yin, Effects of sulfur addition on the wettability and corrosion resistance of Sn–0.7 Cu lead-free solder. MiRe 74, 15–21 (2017)
B. Horváth, T. Shinohara, B. Illés, Corrosion properties of tin–copper alloy coatings in aspect of tin whisker growth. J. Alloy. Compd. 577, 439–444 (2013)
M. Rasid, Z. Azwan, M.H. Zainol, M.F. Omar, M.N.B. Derman, M. Nazeri, M. Firdaus, Corrosion performance of Sn–9Zn and Sn–0.7 Cuin 3.5% NaCl solution, solid state phenomena (Trans Tech Publications, Zurich, 2018), pp. 56–60
M. Rasid, Z. Azwan, M.F. Omar, M. Nazeri, M. Firdaus, Polarization study of Sn-0.7 Cu solder alloy in 1 M hydrochloric solution, Materials Science Forum (Trans Tech Publications, Zurich, 2017), pp. 394–399
S. Choi, J. Lucas, K. Subramanian, T. Bieler, Formation and growth of interfacial intermetallic layers in eutectic Sn–Ag solder and its composite solder joints. J. Mater. Sci. 11, 497–502 (2000)
Z. Wang, C. Chen, J. Liu, G. Zhang, K. Suganuma, Corrosion mechanism of Zn-30Sn high-temperature, lead-free solder in neutral NaCl solution. Corros. Sci. 140, 40–50 (2018)
M. Wang, J. Wang, W. Ke, Corrosion behavior of Sn–3.0Ag–0.5Cu lead-free solder joints. MiRe 73, 69–75 (2017)
Y. Gao, C. Cheng, J. Zhao, L. Wang, X. Li, Electrochemical corrosion of Sn–0.75 Cu solder joints in NaCl solution. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 22, 977–982 (2012)
W.R. Osório, E.S. Freitas, J.E. Spinelli, A. Garcia, Electrochemical behavior of a lead-free Sn–Cu solder alloy in NaCl solution. Corros. Sci. 80, 71–81 (2014)
R. Ambat, P. Møller, A review of corrosion and environmental effects on electronics. The Technical University of Denmark, DMS Vintermøde Proceedings (2006)
W.R. Osorio, L.C. Peixoto, L.R. Garcia, A. Garcia, J.E. Spinelli, The effects of microstructure and Ag3Sn and Cu6Sn5 intermetallics on the electrochemical behavior of Sn–Ag and Sn–Cu solder alloys. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 7, 6436–6452 (2012)
W.R. Osório, C.M. Freire, R. Caram, A. Garcia, The role of Cu-based intermetallics on the pitting corrosion behavior of Sn–Cu, Ti–Cu and Al–Cu alloys. Electrochim. Acta 77, 189–197 (2012)
W.R. Osório, J.E. Spinelli, C.R.M. Afonso, L.C. Peixoto, A. Garcia, Microstructure, corrosion behaviour and microhardness of a directionally solidified Sn–Cu solder alloy. Electrochim. Acta 56, 8891–8899 (2011)
Q. Bui, N. Nam, B.I. Noh, A. Kar, J.G. Kim, S.B. Jung, Effect of Ag addition on the corrosion properties of Sn-based solder alloys. Mater. Corros. 61, 30–33 (2010)
A. Sharma, S. Das, K. Das, Electrochemical corrosion behavior of CeO2 nanoparticle reinforced Sn–Ag based lead free nanocomposite solders in 3.5 wt% NaCl bath. Surf. Coat. Technol. 261, 235–243 (2015)
J.S. Newman, P. Su, G.G. Yee, S. Chivukula, Development of smoke corrosion and leakage current damage functions. Fire Saf. J. 61, 92–99 (2013)
K. Xiao, X. Gao, L. Yan, P. Yi, D. Zhang, C. Dong, J. Wu, X. Li, Atmospheric corrosion factors of printed circuit boards in a dry-heat desert environment: salty dust and diurnal temperature difference. Chem. Eng. J. 336, 92–101 (2018)
Q. Li, X. Liu, S. Lu, Corrosion behavior assessment of tin–lead and lead free solders exposed to fire smoke generated by burning polyvinyl chloride. Mater. Chem. Phys. 212, 298–307 (2018)
Q. Li, X. Liu, C. Li, X. Chen, S. Lu, Corrosion behavior of Sn–3.0 Ag–0.5 Cu solder under different fire smoke atmospheres generated by burning polyvinyl chloride and polyethylene. Mater. Corros. 69(6), 793–803 (2018)
A. Salhi, S. Tighadouini, M. El-Massaoudi, M. Elbelghiti, A. Bouyanzer, S. Radi, S. El Barkany, F. Bentiss, A. Zarrouk, Keto-enol heterocycles as new compounds of corrosion inhibitors for carbon steel in 1M HCl: weight loss, electrochemical and quantum chemical investigation. J. Mol. Liq. 248, 340–349 (2017)
Y. Hua, R. Jonnalagadda, L. Zhang, A. Neville, R. Barker, Assessment of general and localized corrosion behavior of X65 and 13Cr steels in water-saturated supercritical CO2 environments with SO2/O2. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 64, 126–136 (2017)
Y. Zhao, E. Zhou, Y. Liu, S. Liao, Z. Li, D. Xu, T. Zhang, T. Gu, Comparison of different electrochemical techniques for continuous monitoring of the microbiologically influenced corrosion of 2205 duplex stainless steel by marine Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm. Corros. Sci. 126, 142–151 (2017)
M. Park, D. Nam, K. Jung, K. Hong, H. Kwon, Effects of the degradation of methane sulfonic acid electrolyte on the collapse failure of Sn–Ag alloy solders for flip-chip interconnections. RSC Adv. 7, 23136–23142 (2017)
M. Wang, J. Wang, H. Feng, W. Ke, Effect of Ag3Sn intermetallic compounds on corrosion of Sn–3.0Ag–0.5Cu solder under high-temperature and high-humidity condition. Corros. Sci. 63, 20–28 (2012)
C. Franch, E. Rodríguez Castellón, Á. Reyes Carmona, A.E. Palomares, Characterization of (Sn and Cu)/Pd catalysts for the nitrate reduction in natural water. Appl. Catal. A 425–426, 145–152 (2012)
B. Liao, Z. Chen, Q. Qiu, X. Guo, Inhibitory effect of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide on the electrochemical migration of tin in thin electrolyte layers containing chloride ions. Corros. Sci. 118, 190–201 (2017)
J. Byun, H.A. Patel, D. Thirion, C.T. Yavuz, Reversible water capture by a charged metal-free porous polymer. Polymer 126, 308–313 (2017)
U. Evans, Electrochemical mechanism of atmospheric rusting. Nature 206, 980 (1965)
M. Fayeka, A. Haseeb, M. Fazal, Electrochemical corrosion behaviour of Pb-free SAC 105 and SAC 305 solder alloys: a comparative study. Sains Malays. 46, 295–302 (2017)
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge financial support from the Fundamental Research the National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2016YFC0802101) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51704268).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Q., Lin, J., Li, C. et al. Effect of polyvinyl chloride fire smoke on the long-term corrosion kinetics and surface microstructure of tin–lead and lead-free solders. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 30, 16395–16406 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-02013-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-02013-5