Abstract
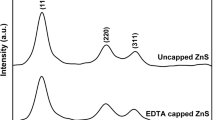
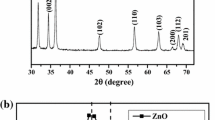
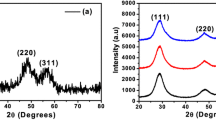
In this research, the surface capped pure ZnS nanoparticles, as well as the Cd- and Hg-doped ones were synthesized via a green ultrasonic-assisted co-precipitation route. The products were characterized by X-ray diffraction, scanning and transmission electron microscopies, Fourier transform infrared, UV–Vis and photoluminescence spectroscopies. The results showed that the synthesized spherical-like nanoparticles are single-phased and well-dispersed with diameters of about 3 nm. They were crystallized in a cubic zincblende structure whose lattice constants increase on doping due to the larger ionic radii of the dopants. The Cd/Hg substitution results in slightly less microstrain and so rather smaller particles. The studied nanoparticles are direct band gap materials whose band gap values vary with Cd/Hg doping from 4.31 eV for ZnS to 3.94/4.40 eV as a result of the competition between the quantum size effect and the composition effect. The effect of the isoelectronic Cd and Hg doping is also revealed as the weakening of the blue photoluminescence band around 430 nm originated from the defect states in ZnS matrix, and the appearance of a red excitonic emission at 640 nm. It was found that in these nanoparticles being smaller than Bohr dimension, the particle size is a determinative parameter for governing the efficiency of the radiative emissions.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
A.D. Yoffe, Semiconductor quantum dots and related systems: electronic, optical, luminescence and related properties of low dimensional systems. Adv. Phys. 50, 1–208 (2001)
W.L. Davidson, X-ray diffraction evidence for ZnS formation in zinc activated rubber vulcanizates. Phys. Rev. 74, 116–117 (1948)
W. Liu, Low temperature synthesis of hexagonal phase ZnS nanocrystals by thermolysis of an air-stable single-source molecular precursor in air. Mater. Lett. 60, 551–554 (2006)
P. Chansri, S. Arunrungrusmi, T. Yuji, N. Mungkung, An analysis of ZnS: Cu phosphor layer thickness influence on electroluminescence device performances (J. Photoenergy, Int, 2017). https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/6752984
R.H. Castillo, M. Acosta, I. Riech, G. Santana-Rodríguez, J. Mendez-Gamboa, C. Acosta, M. Zambrano, Study of ZnS/CdS structures for solar cells applications. Optik 148, 95–100 (2017)
M.D. Regulacio, K.Y. Win, S.L. Lo, S.-Y. Zhang, X. Zhang, S. Wang, M.-Y. Han, Y. Zhen, Aqueous synthesis of highly luminescent AgInS2-ZnS quantum dots and their biological applications. Nanoscale 5, 2322–2327 (2013)
H.S. Choi, Y. Kim, J.C. Park, M.H. Oh, D.Y. Jeon, Y.S. Nam, Highly luminescent, off-stoichiometric CuxInyS2/ZnS quantum dots for near-infrared fluorescence bio-imaging. RSC Adv. 5, 43449–43455 (2015)
S. Sahare, S.J. Dhoble, P. Singh, M. Ramrakhiani, Fabrication of ZnS: cu/PVA nanocomposite electroluminescence devices for flat panel displays. Adv. Mater. Lett. 4, 169–173 (2013)
Z. Zhang, K. Wang, K. Zheng, S. Deng, N. Xu, J. Chen, A flat panel photodetector formed by a ZnS photoconductor and ZnO nanowire field emitters achieving high responsivity from ultraviolet to visible light for indirect-conversion X-Ray imaging. J. Lightwave Technol. 36, 5010–5015 (2018)
H.R. Azimi, M. Ghoranneviss, S.M. Elahi, R. Yousefi, Photovoltaic and UV detector applications of ZnS/rGO nanocomposites synthesized by a green Method. Ceram. Int. 42, 14094–14099 (2016)
A.F. Mohammed, W.R. Salah, Synthesis of ZnS quantum dots for QDs-LED hybrid device with different cathode materials (IOP Publishing Ltd, Bristol, 2018)
S. Vasilyev, I. Moskalev, V. Smolski, J. Peppers, M. Mirov, V. Fedorov, D. Martyshkin, S. Mirov, V. Gapontsev, Octave-spanning Cr:ZnS femtosecond laser with intrinsic nonlinear interferometry. Optica 6, 126–127 (2019)
D. Okazaki, H. Arai, A. Anisimov, E.I. Kauppinen, S. Chiashi, S. Maruyama, N. Saito, S. Ashihara, Self-starting mode-locked Cr:ZnS laser using single-walled carbon nanotubes with resonant absorption at 2.4 μm. Opt Lett 44(7), 1750–1753 (2019)
H.Y. Huang, C.H. Chuang, C.K. Shu, Y.C. Pan, W.H. Lee, W.K. Chen, W.H. Chen, M.C. Lee, Photoluminescence and photoluminescence excitation studies of as-grown and P-implanted GaN: on the nature of yellow luminescence. Appl. Phys. Lett. 80, 3349–3351 (2002)
S.L. Chen, W.M. Chen, I.A. Buyanova, Magneto-optical properties and recombination dynamics of isoelectronic boundexcitons in ZnO. AIP Conf. Proc. 1583, 186–189 (2014)
R. Intartaglia, T. Taliercio, P. Valvin, B. Gil, T. Bretagnon, P. Lefebvre, Isoelectronic traps in heavily doped GaAs:(In, N). Phys. Rev. B 68(23), 235202 (2003)
J.J. Hopfield, D.G. Thomas, R.T. Lynch, Isoelectronic donors and acceptors. Phys. Rev. Lett. 17, 312–315 (1966)
Th Agne, M. Dietrich, J. Hamann, S. Lany, H. Wolf, Th Wichert, ISOLDE collaboration, optical properties of the isoelectronic trap Hg in ZnO. Appl. Phys. Lett. 82, 3448–3450 (2003)
P. Iranmanesh, S. Saeednia, N. Khorasanipoor, Tunable properties of cadmium substituted ZnS nanocrystals. Mater. Sci. Semicon. Proc. 68, 193–198 (2017)
Th Agne, M. Dietrich, J. Hamann, S. Lany, H. Wolf, Th Wichert, ISOLDE collaboration, optical properties of the isoelectronic trap Hg in ZnO. Appl. Phys. Lett. 82, 3448–3450 (2003)
S.M. Zhou, Near UV photoluminescence of Hg-doped GaN nanowires. Physica E 33, 394–397 (2006)
A. Pradhan, R.C. Jones, D. Caruntu, C.J. O’Connor, M.A. Tarr, Gold-magnetite nanocomposite materials formed via sonochemical methods. Ultrason. Sonochem. 15, 891–897 (2008)
U. Waggon, Optical properties of semiconductor quantum dots (Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1996), p. 250
J.-W. Lee, S.-M. Lee, Y.-D. Huh, C.-S. Hwang, EDTA surface capped water-dispersible ZnSe and ZnS: Mn nanocrystals. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 31, 1997–2002 (2010)
B.D. Cullity, S.R. Stock, Elements of X-ray diffraction, 3rd edn. (Prentice-Hall, New York, 2001)
J.I. Langford, A.J.C. Wilson, Scherrer after sixty years: a survey and some new results in the determination of crystallite size. J. Appl. Cryst. 11, 102–113 (1978)
A.S. Hassanien, A.A. Akl, A.H. Sáaedi, Synthesis, crystallography, microstructure, crystal defects, and morphology of BixZn1-xO nanoparticles prepared by sol-gel technique. CrystEngComm 20, 1716–1730 (2018)
N.W. Ashcroft, N.D. Mermin, Solid state physics (Holt, Rinehart and Winston, New York, 1976), p. 628
Börnstein L (1987) Numerical data and functional relationships in science and technology. New Series. Group III: crystal and solid state physics. Vol. 22: semiconductors. Subvolume a: Intrinsic properties of group IV elements and III‐V, II‐VI and I‐VII compounds. Madelun O (ed), Springer, Berlin, p 168
C.A. Klein, R.N. Donadio, Infrared-active phonons in cubic zinc sulfide. J. Appl. Phys. 51, 797–800 (1980)
Socrates G (2004) Infrared and Raman characteristic group frequencies: tables and charts. 3rd (ed). John Wiley & Sons Ltd, New Jersey, p 95–97
P.R. Collins, W.J. Fredericks, Note on the absorption spectrum of KBr: Cd 2+. Phys. Stat. Sol. (b) 134, K67–K70 (1986)
L. Kernazhitsky, V. Shymanovska, T. Gavrilko, V. Naumov, V. Kshnyakin, T. Khalyavka, A comparative study of optical absorption and photocatalytic properties of nanocrystalline single-phase anatase and rutile TiO2 doped with transition metal cations. J. Solid State Chem. 198, 511–519 (2013)
D.C. Onwudiwe, P.A. Ajibade, Zn(II), Cd(II) and Hg(II) complexes of N-methyl-N-phenyl dithiocarbamate as single-source precursors for the synthesis of metal sulfide nanoparticles. Mater. Lett. 65, 3258–3261 (2011)
U.S. Senapati, D. Sarkar, Synthesis and characterization of biopolymer protected zinc sulphide nanoparticles. Superlattice. Microst. 85, 722–733 (2015)
J. Tauc, Optical properties and electronic structure of amorphous Ge and Si. Mater. Res. Bul. 3, 37–46 (1968)
A.S. Hassanien, A.A. Akl, Optical characteristics of iron oxide thin films prepared by spray pyrolysis technique at different substrate temperatures. Appl. Phys. A 233(1–4), 307–319 (2018)
G. Murugadoss, Synthesis and photoluminescence properties of zinc sulfide nanoparticles doped with copper using effective surfactants. Particuology 11, 566–573 (2013)
D.C. Onwudiwe, P.A. Ajibade, ZnS, CdS and HgS nanoparticles via alkyl-phenyl dithiocarbamate complexes as single source precursors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 12, 5538–5551 (2011)
Y. Zhi-hao, Y. Wei, J. Jun-hui, Z. Li-de, Optical absorption red shift of capped ZnFe2O4 nanoparticle. Chin. Phys. Lett. 15(7), 535–536 (1998)
H.R. Azimi, M. Ghoranneviss, S.M. Elahi, R. Yousefi, Enhancing photovoltaic performance of PbS/rGO nanocomposites: the role of buffer layer of ZnS/rGO nanocomposites. Ceram. Int. 43, 128–132 (2017)
B. Ray, II-VI Compounds (Pergamon, Oxford, 1969), p. 153
H. Safardoust-Hojaghan, M. Shakouri-Arani, M. Salavati-Niasari, Structural and spectroscopic characterization of HgS nanoparticles prepared via simple microwave approach in presence of novel sulfuring agent. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 26, 759–766 (2016)
J.Z. Mbese, P.A. Ajibade, Synthesis, structural and optical properties of ZnS, CdS and HgS nanoparticles from dithiocarbamato single molecule precursors. J. Sulfur Chem. 35(4), 438–449 (2014)
B.K. Patel, S. Rath, S.N. Sarangi, S.N. Sahu, HgS nanoparticles: structure and optical properties. Appl. Phys. A 86, 447–450 (2007)
A. Marikani, Materials science (Dehli, PHI Learning Pvt. Ltd, 2017), p. 463
L.E. Brus, Electron–electron and electronhole interactions in small semiconductor crystallites: the size dependence of the lowest excited electronic state. J. Chem. Phys. 80, 4403–4409 (1984)
J.E. Bernard, A. Zunger, Optical bowing in zinc chalcogenide semiconductor alloys. Phys. Rev. B 34, 5992–5995 (1986)
S. Larach, R.E. Shrader, C.F. Stocker, Anomalous variation of band gap with composition in zinc sulfo- and seleno-tellurides. Phys. Rev. 108, 587–589 (1957)
J.U. Kim, M.H. Lee, H. Yang, Synthesis of Zn1 − xCdxS:Mn/ZnS quantum dots and their application to light-emitting diodes. Nanotechnology 19(46), 465605 (2008)
V. Ramasamy, K. Praba, G. Murugadoss, Synthesis and study of optical properties of transition metals doped ZnS nanoparticles. Spectrochim. Acta. A 96, 963–971 (2012)
X. Zeng, J. Zhang, F. Huang, Optical and magnetic properties of Cr-doped ZnS nanocrystallites. J. Appl. Phys. 111(12), 123525 (2012)
Y. Chang, M. Wang, X. Chen, S. Ni, W. Qiang, Field emission and photoluminescence characteristics of ZnS nanowires via vapor phase growth. Solid State Commun. 142, 295–298 (2007)
M. Sookhakian, Y.M. Amin, W.J. Basirun, M.T. Tajabadi, N. Kamarulzaman, Synthesis, structural, and optical properties of type-II ZnO–ZnS core–shell nanostructure. J. Lumin. 145, 244–252 (2014)
W.G. Becker, A.J. Bard, Photoluminescence and photoinduced oxygen adsorption of colloidal zinc sulfide dispersions. J. Phys. Chem. 87, 4888–4893 (1983)
G. Murugadoss, B. Rajamannan, V. Ramasamy, Synthesis, characterization and optical properties of water-soluble ZnS:Mn2+ nanoparticles. J. Luminescence 130, 2032–2039 (2010)
A.A. Bol, A. Meijerink, Luminescence quantum efficiency of nanocrystalline ZnS:Mn2+. 2. Enhancement by UV irradiation. J. Phys. Chem. B 105(42), 10203–10209 (2001)
Y. Jiang, X.M. Meng, J. Liu, Z.Y. Xie, C.S. Lee, S.T. Lee, Hydrogen-assisted thermal evaporation synthesis of ZnS nanoribbons on a large scale. Adv. Mater. 15, 323–327 (2003)
R.K. Chandrakar, R.N. Baghel, V.K. Chandra, B.P. Chandra, Synthesis, characterization and photoluminescence studies of Mn doped ZnS nanoparticles. Superlattices Microstruct. 86, 256–269 (2015)
A.A. Bol, J. Ferwerda, J.A. Bergwerff, A. Meijerink, Luminescence of nanocrystalline ZnS:Cu2+. J. Lumin. 99, 325–334 (2002)
D. Denzler, M. Olschewski, K. Sattler, Luminescence studies of localized gap states in colloidal ZnS nanocrystals. J. Appl. Phys. 84, 2841–2845 (1998)
T.T.Q. Hoa, N.D. The, S. Mcvitie, N.H. Nan, L.V. Vu, T.D. Canh, N.N. Long, Optical properties of Mn- doped ZnS semiconductor nanoclusters synthesized by a hydrothermal process. Opt. Mater. 33, 308–314 (2011)
K.M. Mullaugh, G.W.I.I.I. Luther, Spectroscopic determination of the size of cadmium sulfide nanoparticles formed under environmentally relevant conditions. J. Environ. Monit. 12, 890–897 (2010)
N. Moloto, N. Revaprasadu, M.J. Moloto, P. O’Brien, J. Raftery, N, N’-diisopropylthiourea and N, N’-dicyclohexylthiourea zinc(II) complexes as precursors for the synthesis of ZnS nanoparticles. S. Afr. J. Sci. 105, 258–263 (2009)
K. Sreejith, K.S. Mali, C.G.S. Pillai, A simple one step method for the synthesis of hexagonal Cd1 -xZnxS (x = 0–0.75). Mater. Lett. 62, 95–99 (2008)
S.K. Mishra, R.K. Srivastava, S.G. Prakash, R.S. Yadav, A.C. Panday, Structural, optical and photoconductivity characteristics of manganese doped cadmium sulfide nanoparticles synthesized by co-precipitation method. J. Alloys Compd. 513, 118–124 (2012)
A. Prudnikau, M. Artemyev, M. Molinari, M. Troyon, A. Sukhanova, I. Nabiev, A.V. Baranov, S.A. Cherevkov, A.V. Fedorov, Chemical substitution of Cd ions by Hg in CdSe nanorods and nanodots: spectroscopic and structural examination. Mater. Sci. Eng. 177, 744–749 (2012)
Prudnikau A, Artemyev M (2011) Optical properties of cadmium selenide nanocrystals with cadmium substitution by mercury Proc. Phys. Chem. Applications Nanostruct. https://doi.org/10.1142/9789814343909_0043
D.W. Oxtoby, H.P. Gillis, L.J. Butler, Principles of modern chemistry, 8th edn. (Cengage Learning, Boston, 2016), p. 82
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the supports from Vali-e-Asr University of Rafsanjan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tabatabai Yazdi, S., Iranmanesh, P., Khorasanipour, N. et al. A comparative study of the isoelectronic Cd and Hg substitution in EDTA-capped ZnS nanocrystals. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 30, 13191–13200 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-01682-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-01682-6