Abstract
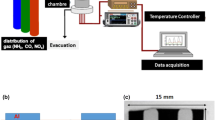
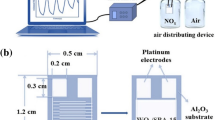
The high porous surface of tungsten oxide (WO3) gas sensor was deposited by physical vapor deposition (PVD) technique on interdigital FTO-glass substrate deposited by DC sputtering method through the change of substrate position. In order to investigation the effect of Au nanoparticles as dopant on gas sensor performance, these nanoparticles were decorated by PVD method on the surface of high porous WO3 gas sensor. The crystal structure and morphology properties of WO3 gas sensor were evaluated by XRD and FESEM. Furthermore, the NO2 gas sensing properties for three samples including common, high porous and Au decorated high porous surfaces were detected. The Au decorated high porous gas sensor exhibited much higher response, shorter response and recovery time and excellent selectivity to NO2 gas at an operating temperature of 130 °C in compared to other samples.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Liu et al., Physically flexible, rapid-response gas sensor based on colloidal quantum dot solids. Adv. Mater. 26(17), 2617–2718 (2014)
Q. Xiang et al., Au Nanoparticle modified WO3 nanorods with their enhanced properties for photocatalysis and gas sensing. J. Phys. Chem. C 114, 2049–2055 (2012)
C. Wang et al., Nanosheets assembled hierarchical flower-like WO3 nanostructures: synthesis, characterization, and their gas sensing properties. Sens. Actuators B 210, 75–81 (2015)
Y.-F. Sun et al., Metal oxide nanostructures and their gas sensing properties: a review. Sensors 12, 2610–2631 (2012)
K. Wetchakun et al., Semiconducting metal oxides as sensors for environmentally hazardous gases. Sens. Actuators B 160, 580–591 (2011)
Y. Wang et al., Preparation of Ag-loaded mesoporous WO3 and its enhanced NO2 sensing performance. Sens. Actuators B 225, 544–552 (2016)
L.G. Teoh et al., Sensitivity properties of a novel NO2 gas sensor based on mesoporous WO3 thin film. Sens. Actuators B 96, 219–225 (2003)
T. Siciliano et al., WO3 gas sensors prepared by thermal oxidization of tungsten. Sens. Actuators B 133, 321–326 (2008)
Z. Hua et al., An investigation on NO2 sensing mechanism and shielding behavior of WO3 nanosheets. Sens. Actuators B 259, 250–257 (2018)
J. Sarfraz et al., The performance of inkjet-printed copper acetate based Hydrogen sulfide gas sensor on a flexible plastic substrate—varying ink composition and print density. Appl. Surf. Sci. 445, 89–96 (2018)
S.A. Vanalakar et al., Controlled growth of ZnO nanorod arrays via wet chemical route for NO2 gas sensor applications. Sens. Actuators B 221, 1195–1201 (2015)
J. Kathirvelan, R. Vijayaraghavan, A. Thomas, Ethylene detection using TiO2–WO3 composite sensor for fruit ripening applications. Sens. Rev. 37, 147–154 (2017)
G. Wang et al., Fabrication and characterization of polycrystalline WO3 nanofibers and their application for ammonia sensing. J. Phys. Chem. B 110, 23777–23782 (2006)
S. Vallejos et al., Au nanoparticle-functionalised WO3 nanoneedles and their application in high sensitivity gas sensor devices. Chem. Commun. (Camb.) 47(1), 565–567 (2011)
S.S. Shendage et al., Sensitive and selective NO2 gas sensor based on WO3 nanoplates. Sens. Actuators B 240, 426–433 (2017)
Z. Zhang et al., Ultrasensitive ppb-level NO2 gas sensor based on WO3 hollow nanosphers doped with Fe. Appl. Surf. Sci. 434, 891–897 (2018)
Y. Shen et al., Low-temperature and highly enhanced NO2 sensing performance of Au-functionalized WO3 microspheres with a hierarchical nanostructure. Appl. Surf. Sci. 434, 922–931 (2018)
D.-S. Lee, K.-H. Nam, D.-D. Lee, Effect of substrate on NO -sensing properties of WO thin film 23 gas sensors. Thin Solid Films 375, 142–146 (2000)
Z. Liu et al., Dealloying derived synthesis of W nanopetal films and their transformation into WO3. J. Phys. Chem. C 112, 1391–1395 (2008)
R. Jolly Bose et al., Preparation and characterization of Pt loaded WO3 films suitable for gas sensing applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 440, 320–330 (2018)
C. Liu et al., The effect of noble metal (Au, Pd, Pt) nanoparticles on the gas sensing performance of SnO2-based sensors: a case study on the 221 high-index faceted SnO2 octahedra. CrystEngComm 17(33), 6308–6313 (2015)
L. Chen, S.C. Tsang, Ag doped WO3-based powder sensor for the detection of NO gas in air. Sens. Actuators B 89, 68–75 (2003)
Q. Xiang et al., Au nanoparticle modified WO3 nanorods with their enhanced properties for photocatalysis and gas sensing. J. Phys. Chem. C 114, 2049–2055 (2010)
R. Ganesan et al., Evolution of target condition in reactive HiPIMS as a function of duty cycle: an opportunity for refractive index grading. J. Appl. Phys. 121(17), 171909 (2017)
A.P. Shpak et al., XPS studies of active elements surface of gas sensors based on WO3−x nanoparticles. J. Electron Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 156–158, 172–175 (2007)
F. Lin et al., Low-temperature ozone exposure technique to modulate the stoichiometry of WOx nanorods and optimize the electrochromic performance. Nanotechnology 23(25), 255601 (2012)
H. Najafi-Ashtiani, A. Bahari, S. Gholipour, Investigation of coloration efficiency for tungsten oxide–silver nanocomposite thin films with different surface morphologies. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 29, 5820–5829 (2018)
Z. Aghagoli, M. Ardyanian, Synthesis and study of the structure, magnetic, optical and methane gas sensing properties of cobalt doped zinc oxide microstructures. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 29(9), 7130–7141 (2018)
M. Stankova et al., Influence of the annealing and operating temperatures on the gas-sensing properties of rf sputtered WO3 thin-film sensors. Sens. Actuators B 105, 271–277 (2005)
X. An et al., WO3 nanorods/graphene nanocomposites for high-efficiency visible-light-driven photocatalysis and NO2 gas sensing. J. Mater. Chem. 22, 8525–8531 (2012)
G. Xie et al., Gas sensing characteristics of WO3 vacuum deposited thin films. Sens. Actuators B 123, 909–914 (2007)
D. Meng et al., Preparation of WO3 nanoparticles and application to NO2 sensor. Appl. Surf. Sci. 256, 1050–1053 (2009)
J. Zeng et al., NO2-sensing properties of porous WO3 gas sensor based on anodized sputtered tungsten thin film. Sens. Actuators B 161, 447–452 (2012)
Y.-S. Shim et al., Highly sensitive and selective H2 and NO2 gas sensors based on surface-decorated WO3 nanoigloos. Sens. Actuators B 198, 294–301 (2014)
Y. Shen et al., Influence of effective surface area on gas sensing properties of WO3 sputtered thin films. Thin Solid Films 517, 2069–2072 (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Najafi-Ashtiani, H. The effect of different surface morphologies on WO3 and WO3-Au gas-sensors performance. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 30, 12224–12233 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-01581-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-01581-w