Abstract
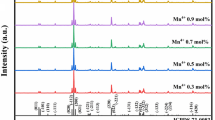
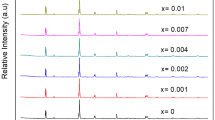
The red-emitting phosphors Ca2AlNbO6: xmol%Mn4+ (CAN: xmol%Mn4+) (0.1 ≤ x ≤ 0.9) were successfully synthesized via a conventional high temperature solid-state method at air atmosphere. A band was located at 320 nm in diffuse reflection spectra (DRS) because of the spin-allowed 4A2g → 4T1g transition of Mn4+. Moreover, there were two broad bands located at photoluminescence excitation (PLE) spectra due to the spin-allowed transitions of Mn4+ upon the excitation of 712 nm. And the phosphors exhibited the far-red emission bands centered at ~ 712 nm on account of the spin-forbidden 2Eg → 4A2g transition of Mn4+ under the excitation of 355 nm. And the optimum one was CAN: 0.3 mol%Mn4+ which yields the brightest red light due to the concentration quenching effect. Furthermore, it could be confirmed that the existence of nonradiative among Mn4+ ions because the lifetime of the phosphors was decreased as the concentration of Mn4+ in CAN increased from 0.1% to 0.9 mol%. The average lifetime of the phosphors was in the range of miscroscend. In addition, the CIE chromaticity coordinates of CAN: 0.3 mol%Mn4+ were (0.7319, y = 0.2618). Finally, a blue LED chip combined with YAG: Ce3+ yellow and CAN: 0.3 mol% Mn4+ red phosphors to fabricate a warm white light emitting-diode (WLED). And the CIE chromaticity coordinates, color rendering index (CRI) and the corrected color temperature (CCT) of the device were (0.3799, 0.3432), 74.2 and 3727 K, respectively.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Z.G. Xia, Q.L. Liu, Progr. Mater. Sci. 84, 59–117 (2016)
M.H. Du, J. Mater. Chem. C 2, 2475–2481 (2014)
H. Nguyen, R.S. Liu, J. Mater. Chem. C 4, 10759–10775 (2016)
Y.D. Li, S. Qi, P.L. Li, Z.J. Wang, RSC Adv. 7, 38318–38334 (2017)
P. Pust, V. Weiler, C. Hecht, A. Tücks, A.S. Wochnik, A.K. Henß, D. Wiechert, C. Scheu, P.J. Schmidt, W. Schnick, Nat. Mater. 13, 891–896 (2014)
K. Uheda, N. Hirosaki, Y. Yamamoto, A. Naito, T. Nakajima, H. Yamamoto, Electrochem. Solid State Lett. 9, 22–25 (2006)
Y.Q. Li, J.E.J. Steen, J.W.H. Krevel, G. Botty, A.C.A. Delsing, F.J. DiSalvo, G.D. With, H.T. Hintzen, J. Alloys Compd. 417, 273–279 (2006)
T. Nakano, Y. Kawakami, K. Uematsu, T. Ishigaki, K. Toda, M. Sato, J. Lumin. 129, 1654–1657 (2009)
Y.K. Xu, S. Adachi, J. Electrochem. Soc. 158, 58–65 (2011)
Y.W. Zhu, L.Y. Cao, M.G. Brik, X.J. Zhang, L. Huang, T.T. Xuan, J. Wang, J. Mater. Chem. C 5, 6420–6426 (2017)
M.M. Zhu, Y.X. Pan, Y.Q. Huang, H.Z. Lian, J. Lin, J. Mater. Chem. C 6, 491–499 (2018)
Y.W. Zhu, J.B. Yu, Y. Liu, M.G. Brik, L. Huang, T.T. Xuan, J. Wang, RSC Adv. 7, 30588–30593 (2017)
J.Q. Long, C.Y. Ma, Y.Z. Wang, X.Y. Yuan, M.M. Du, R. Ma, Z.C. Wen, J.T. Zhang, Y.G. Cao, Mater. Res. Bull. 85, 234–239 (2017)
C.D. Brandle, V.J. Fratello, J. Mater. Res. 5, 2160–2164 (1990)
T.A. Vanderah, W. Febo, J.Y. Chan, R.S. Roth, J.M. Loezos, L.D. Rotter, R.G. Geyer, D.B. Minor, J. Solid State Chem. 155, 78–85 (2000)
C.C. Zhao, X. Yin, F.Q. Huang, Y. Hang, Phys. B 406, 4608–4611 (2011)
I. Levin, J.Y. Chan, J.E. Maslar, T.A. Vanderah, J. Appl. Phys. 90, 904–914 (2001)
B.H. Toby, J. Appl. Crystallogr. 34, 210–213 (2001)
P.Q. Cai, L. Qin, C.L. Chen, J. Wang, S.L. Bi, S. Kim, Y.L. Huang, J. Seo, Inorg. Chem. 57, 3073–3081 (2018)
B. Li, X.Y. Huang, Ceram. Int. 44, 4915–4923 (2018)
X.L. Wu, Y.H. Jiao, O. Hui, Q. Ren, F. Lin, H.H. Li, J. Alloy. Compd. 730, 521–527 (2018)
X. Ding, G. Zhu, W.Y. Geng, Q. Wang, Y.H. Wang, Inorg. Chem. 55, 154–162 (2016)
H.J. Jeon, Y.S. Kang, AsiaNano 2002, 121–125 (2003)
A.P. Jadhav, A. Pawar, C.W. Kim, H.G. Cha, U. Pal, Y.S. Kang, J. Phys. Chem. C 113, 16652–16657 (2009)
T.T. Deng, E.H. Song, Y.Y. Zhou, L.Y. Wang, Q.Y. Zhang, J. Mater. Chem. C. 5, 12422–12429 (2017)
H.M. Zhu, C.C. Lin, W.Q. Luo, S.T. Shu, Z.G. Liu, Y.S. Liu, J.T. Kang, E. Ma, Y.G. Cao, R.S. Liu, X.Y. Chen, Nat. Commun. 5, 4312–4321 (2014)
W. Xu, D.Q. Chen, S. Yuan, Y. Zhou, S.H. Li, Chem. Eng. J. 317, 854–861 (2017)
D.Q. Chen, Y. Zhou, W. Xu, J.S. Zhong, Z.G. Ji, W.D. Xiang, J. Mater. Chem. C 4, 1704–1712 (2016)
D. Dexter, J.H. Schulman, J. Chem. Phys. 22, 1063–1070 (1954)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Foundation of Shanghai Institute of Technology (XTCX2018-6), Shanghai Municipal Education Commission (14YZ145), Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai (16ZR1435900), National Science Foundation for Young Scientists of China (61605116), and National Natural Science Foundation of China (51572175).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, K., Zhang, Y., Xu, J. et al. Double-perovskite Ca2AlNbO6: Mn4+ red phosphor for white light emitting diodes: synthesis, structure and luminescence properties. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 30, 9903–9909 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-01328-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-01328-7