Abstract
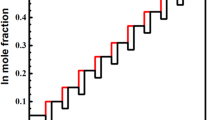
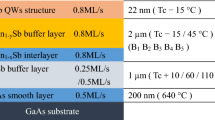
Undulating compositional step-graded AlGaInAs buffers are applied to transit the lattice mismatch of 3.8% between InP cap layer and GaAs substrates with misorientation of 2°, 7° and 15° toward (111)A by metal organic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD). The surface morphology and strain relaxation are strongly dependent on the substrate misorientation. The sample grown on 15° GaAs substrate showed a substantial improvement of surface roughness and reduction of dislocation pile-up densities compared with that on the 2° and 7° substrate. The experiment results showed that the substrate with 15° misorientation can maintain a smooth epitaxial film surface by increasing the possibility of atoms incorporating into the lattice and ease the imbalance of the misfit strain stress distributed between different slip systems to make dislocations distributed more uniformly, which can reduce the strain field to exaggerate the channel width for dislocation gliding along the interface and decrease the threading dislocation densities. Overall, this work provides a promising way to obtain virtual substrates for the achievement of desired metamorphic devices.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.J. Friedman, Progress and challenges for next-generation high-efficiency multijunction solar cells. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 14, 131 (2010)
A.Y. Kim, M.E. Groenert, E.A. Fitzgerald, Visible light-emitting diodes grown on optimized ∇x[InxGa1−x]P/GaP epitaxial transparent substrates with controlled dislocation density. J. Electron. Mater. 29, L9 (2000)
H.Q. Zheng et al., Metamorphic InP/InGaAs double-heterojunction bipolar transistors on GaAs grown by molecular-beam epitaxy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 77, 869 (2000)
J.F. Geisz et al., High-efficiency GaInP/GaAs/InGaAs triple-junction solar cells grown inverted with a metamorphic bottom junction. Appl. Phys. Lett. 91, 760 (2007)
C.L. Andre et al., Impact of dislocation densities on n+/p and p+/n junction GaAs diodes and solar cells on SiGe virtual substrates. J. Appl. Phys. 98, 3884 (2005)
C.L. Andre et al., Investigations of high-performance GaAs solar cells grown on Ge–Si/sub 1−x/Ge/sub x/-Si substrates. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 52, 1055 (2005)
C.L. Andre et al., Impact of dislocations on minority carrier electron and hole lifetimes in GaAs grown on metamorphic SiGe substrates. Appl. Phys. Lett. 84, 3447 (2004)
G. Balakrishnan et al., 2.0 µm wavelength InAs quantum dashes grown on a GaAs substrate using a metamorphic buffer layer. Appl. Phys. Lett. 84, 2058 (2004)
M.K. Hudait et al., Comparison of mixed anion, InAsyP1−y and mixed cation, InxAl1−xAs metamorphic buffers grown by molecular beam epitaxy on (100) InP substrates. J. Appl. Phys. 95, 3952 (2004)
Y.M. Kim et al., InP/In0.53Ga0.47As/InP double heterojunction bipolar transistors on a GaAs substrate using InP metamorphic buffer layer. Solid State Electron. 46, 1541 (2002)
M. Geddo et al., Metamorphic buffers and optical measurement of residual strain. Appl. Phys. Lett. 87, 1009 (2005)
K. Li, W. Wang, Improved quality of In0.30Ga0.70As layers grown on GaAs substrates using undulating step-graded GaInP buffers. J. Cryst. Growth 496, 31 (2018)
K. Kurihara et al., Phase separation in InAlAs grown by MOVPE with a low growth temperature. J. Cryst. Growth 271, 341 (2004)
J. Hellara et al., Optical properties of InP/InAlAs/InP grown by MOCVD on (100) substrates: influence of V/III molar ratio. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 21, 231 (2002)
G.P. Zhang et al., Influence of pulsed substrate bias on the structure and properties of Ti–Al–N films deposited by cathodic vacuum arc. Appl. Surf. Sci. 258, 7274 (2012)
L.B. Freund, A criterion for arrest of a threading dislocation in a strained epitaxial layer due to an interface misfit dislocation in its path. J. Appl. Phys. 68, 2073 (1990)
S.B. Samavedam, E.A. Fitzgerald, Novel dislocation structure and surface morphology effects in relaxed Ge/Si–Ge(graded)/Si structures. J. Appl. Phys. 81, 3108 (1997)
R.S. Goldman et al., Effects of GaAs substrate misorientation on strain relaxation in InxGa1–xAs films and multilayers. J. Appl. Phys. 83, 5137 (1998)
K.L. Li et al., Effects of substrate miscut on dislocation glide in metamorphic (Al)GaInP buffers. J. Cryst. Growth 380, 261 (2013)
J. Novák et al., Influence of surface strain on the MOVPE growth of InGaP epitaxial layers. Appl. Phys. A 87, 511 (2007)
F.K. Legoues, P.M. Mooney, J.O. Chu, Crystallographic tilting resulting from nucleation limited relaxation. Appl. Phys. Lett. 62, 140 (1993)
J.E. Ayers, S.K. Ghandhi, L.J. Schowalter, Crystallographic tilting of heteroepitaxial layers. J. Cryst. Growth 113, 430 (1991)
Y. Takano et al., Threading dislocations and phase separation in InGaAs layers on GaAs substrates grown by low-temperature metalorganic vapor phase epitaxy. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 44, 6403 (2005)
N.J. Quitoriano, E.A. Fitzgerald, Relaxed, high-quality InP on GaAs by using InGaAs and InGaP graded buffers to avoid phase separation. J. Appl. Phys. 102, 152101 (2007)
L. Yang et al., Compositionally-graded InGaAs–InGaP alloys and GaAsSb alloys for metamorphic InP on GaAs. J. Cryst. Growth 324, 103 (2011)
E.A. Fitzgerald et al., Influence of strain on semiconductor thin film epitaxy. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 15, 1048 (1997)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the University-level scientific research projects of Changzhou College of Information Technology [Grant number CXZK201806Q], Key Laboratory of Industrial IoT of Changzhou College of Information Technology (Grant number KYPT201803Z), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China [Grant number 617048186].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, Y., Yan, W., Dai, P. et al. Influence of GaAs substrate misorientation on the characteristics in undulating compositional step-graded AlGaInAs buffers. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 30, 7203–7208 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-00871-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-00871-7