Abstract
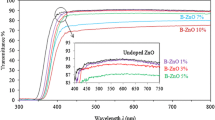
Boron doped zinc oxide (ZnO:B) thin films with low B concentration, varied between 0.50 and 1.50 atomic percentages (at%) are prepared at substrate temperatures (TS) between 300 and 450 °C using spray pyrolysis technique. Polycrystalline wurtzite structure is observed in the X-ray diffraction patterns of ZnO:B thin films, where (002) is the predominant peak. Texture coefficient corresponding to (002) peak increases with B concentration from 0.50 to 1.00 at%. Crystallite size is found between 22 and 64 nm. Nanofibrous surface morphology is observed in the field emission scanning electron microscopic images of ZnO:B thin films. The average nanofiber thickness value varies from 198 to 498 nm. Atomic force microscopic images show the nanotip-like topology of ZnO:B thin films. The average surface roughnesses of the films are found in the range of 2.99–12.45 nm. ZnO:B thin films are found to be highly transparent between visible to near infrared region of the electromagnetic spectrum. The highest transmittance of 87% is noticed for the 1.00 at% ZnO:B thin film prepared at the TS of 450 °C. Optical band gaps of ZnO:B thin films vary between 3.15 and 3.31 eV. 1.00 at% ZnO:B thin films prepared at various TS show lower values of the band gap, refractive index and extinction coefficient at the photon wavelength of 750 nm. Electrical resistivity of ZnO:B thin films are found to be between 0.25 × 104 and 1.39 × 104 Ω m. 1.00 at% ZnO:B thin films prepared at various TS show less electrical resistivity. Arrhenius plots of ZnO:B thin films prepared at various TS show two conduction regions and activation energies of ZnO:B thin films are higher for the films deposited at lower TS. ZnO:B thin films show n-type conductivity and carrier concentration increases with the increase of B concentration.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Kerli, U. Alver, A. Tanrıverdi, B. Avar, Crystallogr. Rep. 61(6), 946 (2015)
R.S. Gaikwad, S.S. Bhande, R.S. Mane, B.N. Pawar, S.L. Gaikwad, S.H. Han, O.S. Joo, Mater. Res. Bull. 47, 4257 (2012)
C.C. Yu, Y.T. Hsu, S.Y. Lee, W.H. Lan, H.H. Kuo, M.C. Shih, D.J.Y. Feng, K.F. Huang, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 52, 065501–065502 (2013)
C.G. Janotti, Van de Walle, Rep. Prog. Phys. 72, 12650–12651 (2009)
R. Wang, A.W. Sleight, D. Cleary, Chem. Mater. 8, 433 (1996)
K.S. Kim, T.S. Lee, J.H. Lee, B.K. Jeong, Y.J. Cheong, W.M. Baik, Kim, J. Appl. Phys. 100, 063701 (2006)
M. Caglar, S. Ilican, Y. Caglar, F. Yakuphanoglu, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 19, 704–708 (2008)
M.V. Castro, C.J. Tavares, Thin Solid Films 586, 13 (2015)
Y. Zhang, Inorg. Chem. 21(11), 3889 (1982)
R.B.H. Tahar, N.B.H. Tahar, J. Mater. Sci. 40, 5285 (2005)
B. Olofinjana, U.S. Mbamara, O. Ajayi, C.L. Martin, E.I. Obiajuuwa, E.O.B. Ajayi, Friction 5, 402 (2017)
W. Bin, L.I.U. Chaoqian, F.E.I. Weidong, W. Hualin, L.I.U. Shimin, W. Nan, C. Weiping, Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 30(3), 509 (2014)
N.P. Poddar, S.K. Mukherjee, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. (2018) https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-0320-6
N.L. Tarwal, V.V. Shinde, A.S. Kamble, P.R. Jadhav, D.S. Patil, V.B. Patil, P.S. Patil, Appl. Surf. Sci. 257, 10789 (2011)
R. Ayouchi, F. Martin, D. Leinen, J.R.R. Barrado, J. Cryst. Growth 247, 497 (2003)
Y. Larbah, M. Adnane, T. Sahraoui, Mater Sci. Poland. 33, 491 (2015)
S. olansky, Multiple beam interferometry of surfaces and films (Oxford Clarendon Press, London, 1948)
C. Barret, T.B. Massalski, Structure of metals (Oxford, Pergamon, 1980)
C. Kittel, Introduction to solid state physics (Wiley, New York, 1976)
P. Scherrer, Bestimmung der Grösse und der inneren Struktur von Kolloidteilchen mittels Röntgensrahlen (Springer, Berlin, 1918)
Y. Zhao, J. Zhang, J. Appl. Cryst. 41, 1095 (2008)
G.K. Williamson, R.E. Smallman, Philos. Mag. 1(1), 34 (1956)
A.D. Sathe, E.S. Kim, Proceeding the 7th international conference on solid state sensors and actuators transducers, Yokohoma, Japan, 158 (1993)
H. Landolt, R. Börnstein, Landolt-Börnstein: numerical data and functional relationships in science and technology, vol. 2 (Springer, Berlin, 1946)
J.D. Hanawalt, H.W. Rinn, L.K. Frevel, Ind. Eng. Chem. Anal. Ed. 10(9), 457 (1938)
R.E. Hummel, Electronic properties of materials, 3rd edn. (Springer, New York, 2000)
E.A. Davies, N.F. Mott, Philos. Mag. 22, 903 (1970)
W.D. Callister Jr., Fundamentals of materials science and engineering, 5th edn. (Wiley, New York, 2001)
L.L. Kazmerski, Polycrystalline and amorphous thin films and devices (Academic Press, New York, 1980)
F. Zahedi, R.S. Dariani, S.M. Rozati, Mat. Sci. Semicon. Proc. 16, 245–249 (2013)
X.B. Wang, C. Song, K.W. Geng, F. Zeng, F. Pan, J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 39, 4992 (2006)
G. Kim, J. Bang, Y. Kim, S.K. Rout, S.I. Woo, Appl. Phys. A 97, 821–828 (2009)
S. Singhal, T. Namgyal, S. Bansal, K. Chandra, J. Electromagn. Anal. Appl. 2, 376 (2010)
B.J. Lokhande, P.S. Patil, M.D. Uplane, Phys. B 302–303, 59 (2001)
M. Sharmin, A.H. Bhuiyan, Appl. Phys. A 124(1), 57 (2018)
B.N. Pawar, S.R. Jadkar, M.G. Takwale, J. Phys. Chem. Solids 66, 1779 (2005)
E. Burstein, Phys. Rev. 93, 632 (1954)
S. Kim, H. Yoon, D.Y. Kim, S.O. Kim, J.Y. Leem, Opt. Mater. 35(12), 2418 (2013)
S.C. Yadav, M.D. Uplane, Int. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 4(12), 4893 (2012)
J.C. Simpson, J.F. Cordaro, J. Appl. Phys. 63, 1781 (1988)
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the authority of Bangladesh University of Engineering and Technology for financial support and Material Science Division, Atomic energy Centre, Dhaka, Bangladesh, for providing necessary laboratory support to this research work. The authors express sincere thanks to the Centre for Nano Science and Engineering, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore, India for providing the laboratory facility for AFM analysis. The authors are grateful to Prof. Dr. Jiban Podder, Department of Physics, BUET for fruitful discussion.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharmin, M., Bhuiyan, A.H. Modifications in structure, surface morphology, optical and electrical properties of ZnO thin films with low boron doping. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 30, 4867–4879 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-00781-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-00781-8