Abstract
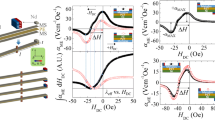
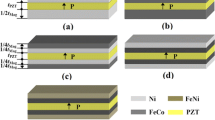
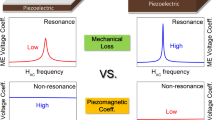
Asymmetrical equivalent circuits, making φmH as magnetic part for the direct magnetoelectric (DME) effect of magnetoelectric laminate composites of longitudinally magnetized and poled (L–L) mode, have been reported recently. In this paper, we developed a symmetrical magnetic–mechanical–electric equivalent circuit to study both the DME and converse magnetoelectric (CME) effects equivalently, predicting the DME and CME coefficients near the resonance frequency. The theoretical values are in good agreement with the corresponding experiments. The L–L mode laminate composites have higher DME voltage coefficient and CME coefficient in comparison with the longitudinally magnetized and transversely poled (L–T) mode. In particular, its voltage coefficient is almost ten times as large as that of the L–T mode composite. The results are significant for the fabrication of magnetoelectric transducer, energy capture device, electronically controlled magnetometers and magnetic field sensors.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Petrov, V. Petrov, M. Bichurin, Y. Zhou, S. Priya, Modeling of dimensionally graded magnetoelectric energy harvester. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 383, 246–249 (2015)
S. Reis, M. Silva, N. Castro, Electronic optimization for an energy harvesting system based on magnetoelectric metglas/poly(vinylidene fluoride)/metglas composites. Smart Mater. Struct. 25, 085028 (2016)
J. Ma, J. Hu, Z. Li, C.W. Nan, Recent progress in multiferroic magnetoelectric composites: from bulk to thin films. Adv. Mater. 23, 1062 (2011)
H. Talleb, A. Gensbittel, Z. Ren, Multiphysics modeling of a magnetoelectric composite Rosen-type device. Compos. Struct. 137, 1–8 (2016)
R. Brito-Pereira, C. Ribeiro, S. Lanceros-Mendez, P. Martins, Magnetoelectric response on Terfenol-D/P(VDF-TrFE) two-phase. Compos. B 20, 97–102 (2017)
G. Wu, T. Nan, R. Zhang, N. Zhang, S. Li, N.X. Sun, Inequivalence of direct and converse magnetoelectric coupling at electromechanical resonance. Appl. Phys. Lett. 103, 182905 (2013)
J.P. Zhou, Y. Yang, G.B. Zhang, J.H. Peng, P. Liu, Symmetric relationships between direct and converse magnetoelectric effects in laminate composites. Compos. Struct. 155, 107–117 (2016)
J.L. Hockel, T. Wu, G.P. Carman, Voltage bias influence on the converse magnetoelectric effect of PZT/terfenol-D/PZT laminates. J. Appl. Phys. 109, 064106 (2011)
J.P. Zhou, Y.X. Zhang, G.B. Zhang, P. Liu, Magnetodielectric effect and electric-induced magnetic permeability in magnetoelectric laminate composite under low inspiring signal. J. Appl. Phys. 113, 043907 (2013)
J.P. Zhou, Y.J. Ma, G.B. Zhang, X.M. Chen, A uniform model for direct and converse magnetoelectric effect in laminated composite. Appl. Phys. Lett. 104, 202904 (2014)
S.X. Dong, J. Cheng, J.F. Li, D. Viehland, Enhanced magnetoelectric effects in laminate composites of Terfenol-D/Pb(Zr,Ti)O3 under resonant drive. Appl. Phys. Lett. 83, 4812–4814 (2003)
L. Ying, B.H. Bao, Theory and caculation of magnetoelectric effect in longitudinally polarized and magnetized laminate materials. Acta Phys. Sin. 60, 067504 (2011)
L.F. Xu, X. Feng, K. Sun, Z.Y. Liang, Q. Xu, Adjustability of resonance frequency by external magnetic field and bias electric field of sandwich magnetoelectric PZT/NFO/PZT composites. Appl. Phys. A 123, 497 (2017)
H. Yang, G. Zhang, Y. Lin, Enhanced magnetoelectric properties of the laminated BaTiO3/CoFe2O4 composites. J. Alloy. Compd. 644, 390–397 (2015)
L. Chen, P. Li, Y.M. Wen, Y. Zhu, Resonance magnetoelectric effect in an asymmetric magnetostrictive/piezoelectric trilayered composite structure. J. Alloy. Compd. 646, 1032–1035 (2015)
L. Chen, P. Li, Y.M. Wen, Y. Zhu, Theoretical analyses of nonlinear magnetoelectric response in self-biased magnetostrictive/piezoelectric laminated composites. Compos. Struct. 119, 685–692 (2015)
Z. Shi, L.Z. Chen, Y.S. Tong, Z.B. Zheng, S.Y. Yang, C.P. Cui, X.J. Liu, Phase drift of magnetoelectric effect in Terfenol-D/PZT composite materials. Acta Phys. Sin. 62, 017501 (2013)
T.I. Muchenik, E.J. Barbero, Charge, voltage, and work-conversion formulas for magnetoelectric laminated composites. Smart Mater. Struct. 24, 025039 (2015)
X.J. Yu, T.Y. Wu, Z. Li, Wireless energy transfer system based on metglas/PFC magnetoelectric laminated composites. Acta Phys. Sin. 62, 058503 (2013)
S.X. Dong, D. Viehland, Longitudinal and transverse magnetoelectric voltage coefficients of magnetostrictive/piezoelectric laminate composite: theory. IEEE Tran. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 50, 1253–1261 (2003)
D.A. Filippova, G.S. Radchenko, T.O. Firsova, T.A. Galkin, A theory of the inverse magnetoelectric effect in layered magnetostrictive–piezoelectric structures. Phys. Solid State 59, 878–884 (2017)
H.M. Zhou, X.L. Cui, A theoretical study of the nonlinear thermomagneto- electric coupling effect in magnetoelectric laminates. Smart Mater. Struct. 23, 105104 (2014)
Y. Shi, Y.W. Gao, Theoretical study on nonlinear magnetoelectric effect and harmonic distortion behavior in laminated composite. J. Alloy. Compd. 646, 351–359 (2015)
Y. Shi, Modeling of nonlinear magnetoelectric coupling in layered magnetoelectric nanocomposites with surface effect. Compos. Struct. 185, 474–482 (2018)
J.Z. Li, Y.M. Wen, P. Li, J. Yang, Modeling of magnetoelectric effects in magnetostrictive/piezoelectric laminated composites using the energy method. IEEE Trans. Magn. 53, 2500406 (2017)
Y. Xiao, H.M. Zhou, X.L. Cui, Nonlinear resonant magnetoelectric coupling effect with thermal, stress and magnetic loadings in laminated composites. Compos. Struct. 128, 35–41 (2015)
H.M. Zhou, X.W. Ou, Y. Xiao, S.X. Qu, H.P. Wu, An analytical nonlinear magnetoelectric coupling model of laminated composites under combined pre-stress and magnetic bias loadings. Smart Mater. Struct. 22, 035018 (2013)
Y. Wang, D. Hasanyan, M. Li, J. Gao, J. Li, D. Viehland, H. Luo, Theoretical model for geometry-dependent magnetoelectric effect in magnetostrictive/piezoelectric composites. J. Appl. Phys. 111, 124513 (2012)
D. Hasanyan, Y. Wang, J. Gao, M. Li, Y. Shen, J. Li, D. Viehland, Modeling of resonant magneto-electric effect in a magnetostrictive and piezoelectric laminate composite structure coupled by a bonding material. J. Appl. Phys. 112, 064109 (2012)
Y. Gao, J. Zhang, Nonlinear magnetoelectric transient responses of a circular-shaped magnetoelectric layered structure. Smart Mater. Struct. 22, 015015 (2013)
S.X. Dong, J.F. Li, D. Viehland, A longitudinal-longitudinal mode Terfenol-D/Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3-PbTiO3 laminate composite. Appl. Phys. Lett. 85, 5305–5306 (2004)
S.Y. Lin, Principle and Design of Ultrasonic Transducer (Science Press, Beijing, 2004)
E. Göran, Handbook of Giant Magnetostrictive Materials (Academic Press, New York, 1999)
G. Liu, S. Dong, Uniformity of direct and converse magnetoelectric effects in magnetostrictive–piezoelectric composites. Appl. Phys. Lett. 105, 122903 (2014)
C.W. Nan, M.I. Bichurin, S. Dong, D. Viehland, G. Srinivasan, Multiferroic magnetoelectric composites: Historical perspective, status, and future directions. J. Appl. Phys. 103, 031101 (2008)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51672168, 11804215), the Special Research Project of Shaanxi Provincial Education Department (No. 17JK0019), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation Funded Project (No. 2017M623105), the Science and Technology Project, Ankang University (No. 2017AYJC04), and the Scientific Research Fund for High Level Talents, Ankang University (No. 2015AYQDZR01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Yao, X., Zhou, JP. et al. Comprehensive investigation on direct and converse magnetoelectric effects in longitudinally magnetized and polarized laminate composites by equivalent circuit and experiments. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 29, 17706–17713 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-9876-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-9876-4