Abstract
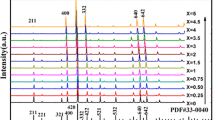
Lu3Al5O12:Ce3+ phosphor powder, which exhibits green emission band, was synthesized by the high-temperature solid-state reaction method with a flux BaF2. X-ray diffraction (XRD), photoluminescence (PL) spectra, and fluorescent lifetime spectra were used to characterize the structure and luminescent properties of the sample. The XRD patterns indicated that when prepared at 1550 °C for 3 h with 4 wt% flux, Lu3Al5O12:Ce3+ phosphors powder is the garnet cubic crystal system structure. Photoluminescence (PL) spectra showed that the Lu3Al5O12:Ce3+ phosphor powder can be effectively excited by near ultraviolet and blue light, emitting broad band peaking at 505 nm, which is attributed to 2F5/2 → 2D5/2 transition. The self-concentration quenching mechanism of Ce3+ is the dipole–dipole interaction. Small amount of Pr3+ increased red light emission at 610 nm. Photoluminescence (PL) spectra and fluorescent lifetime spectra indicated that there was an efficient energy transfer process between Ce3+ and Pr3+.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
W.S. Souza, R.O. Domingues, L.A. Bueno, E.B. da Costa, A.S. Gouveia-Neto, Gouveia-Neto, color tunable green-yellow-orange-red Er3+/Eu3+co-doped PbGeO3:PbF2:CdF2 glass phosphor for application in white-LED technology. J. Lumin. 144, 87–90 (2013)
G.J. Wang, B.X. Yu, D.Y. Duan, S.F. Ye, S.Z. Liu, Li doping effect on the photoluminescence behaviors of KSrPO4:Dy3+ phosphors for WLED light. Mater. Res. Bull 64, 364–369 (2015)
K. Li, Y.S. Chang et al., White LED based on nano-YAG:Ce3+/YAG:Ce3+, Gd3+ hybrid phosphors. Optik 123, 621–623 (2012)
R.Y. Hong, J.H. Li, Synthesis of Fe3O4 nanoparticles without inert gas protection used as precursors of magnetic fluids. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 320, 1605–1614 (2008)
Z. Chen, J.H. Zhang, S. Chen, M.Y. Lin, C.Q. He, Preparation and luminescence property of Eu2+, Mn2+ co-doped silicates phosphors for white LED. J. Alloys Compd. 632, 756–759 (2015)
H.-S. Roh, S. Hur, H.J. Song, I.J. Park, Luminescence properties of Ca5(PO4)2SiO4:Eu2+ green phosphor for near UV-based white LED. Mater. Lett. 70, 37–39 (2012)
M.L. Ye, L.Q. Zhou, F. Hong, L. Li, Q.H. Xia et al., Synthesis and photoluminescent properties of cuboid-like Y2 (C2O4)3:Tb3+ green-emitting phosphors. Opt. Mater. 47, 161–168 (2015)
Y.H. Jin, Y.H. Hu et al., Tunable blue-green color emission and energy transfer properties of Li2CaGeO4:Ce3+, Tb3+ phosphors for near-UV white-light LEDs. J. Alloys Compd. 610, 695–700 (2014)
L.X. Wang, H.J. Zhu, L. Yuan, Synthesis and luminescent properties of Ce3+ doped LuAG nanosized powders by mixed solvo-thermal method. J. Rare. Earth 16, 28 (2010)
A. Yoshikawa, H. Ogino et al., Growth and optical properties of Yb doped new scintillator crystals. Opt. Mater. 24, 275 (2003)
L. Chen, C.C. Lin et al., Light converting inorganic phosphors for white light-emitting diodes. J. Mater. 3, 2172–2195 (2010)
H.T. Kim, J.H. Kim, J.-K. Lee, Y.C. Kang, Green light-emitting Lu3Al5O12:Ce phosphor powders prepared by spray pyrolysis. Mater. Res. Bull. 47, 1428–1431 (2012)
A. Boukerika, L. Guerbous et al., Investigation of the structural and photoluminescence properties of Ce3+-doped LuAG nanopowders prepared via sol–gel method. Opt. Mater. 40, 14–19 (2015)
H.L. Li, X.J. Liu, L.P. Huang, Luminescent properties of LuAG:Ce phosphors with different Ce contents prepared by a sol–gel combustion method. Opt. Mater. 29, 1138–1142 (2007)
Z.F. Wang, M. Xu, W.P. Zhang, Synthesis and luminescent properties of nanoscale LuAG:RE3+ (Ce, Eu) phosphors prepared by co-precipitation method. J. Lumin. 122, 437–439 (2007)
J.J. Xie et al., Synthesis study of Lu3Al5O12 (Ce) nanoscaled powder by co-precipitation. J. Inorg. Mater. 79, 24 (in Chinese) (2009)
H.L. Li, X.J. Liu, L.P. Huang, Synthesis of nanocrystalline lutetium aluminum garnet powders by co-precipitation method. Ceram. Int. 32, 309 (2006)
E.L. Cates, A.P. Wilkinson et al., Delineating mechanisms of upconversion enhancement by Li+ codoping in Y2SiO5:Pr3+. J. Phys. Chem. 116(23), 12772 (2012)
J.S. Bae, J.H. Yoon, S.K. Park et al., Surf. Rev. Lett. 14(04), 535 (2007)
S.H. Byeon, M.G. Ko, J.C. Park et al., Low-temperature crystallization and highly enhanced photoluminescence of Gd2−xYxO3:Eu3+ by Li doping. Chem. Mater. 14(2), 603 (2002)
Y.H. Zhang, Y.B. Zhang et al., Synthesis and characteristics of fine crystalline LuAG:Ce phosphors by microwave-induced solution combustion method. J. Lumin. 181, 360–366 (2017)
J. Singh, J. Manam et al., Structural and spectroscopic behaviour of Eu3+-doped SrGd2O4 modified by thermal treatments. J. Mater. Sci. 51(6), 2886 (2016)
D.L. Dexter, J.A. Schulman et al., J. Chem. Phys. 22, 1063–1071 (1954)
X.Y. Mi, J.C. Sun, P. Zhou, H.Y. Zhou, Tunable luminescence and energy transfer properties in Ca8MgLu(PO4)7:Ce3+,Tb3+,Mn2+ phosphors. J. Mater. Chem. C 3, 4471–4481 (2015)
P. Dorenbos, J. Lumin. 15, 117–119 (2003)
P. Dorenbos, Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 65, 235110 (2002)
D.R. Mullins, S.H. Overbury, Electron spectroscopy of single crystal and polycrystalline cerium oxide surfaces. Surf. Sci. 409(2), 307–319 (1998)
X.W. Yu, C.W. Yan et al., XPS analysis of the cerium conversion coating on the anodized Al6061/SiCp. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 19(2), 357–360 (2003)
L.M. Wang, L.Q. Zhuang et al., J. East China Univ. Sci. Technol. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 4, 08 (2015)
M. Cabala, K. Veltruaka, V. Matolin et al., Adsorption properties of Ce/Ag system. In WDS 07 Proceedings of Contributed Papers Jana Safrankova, jiri Pavlu: prague, 2007, pp. 134–139
H. Shi, X.Y. Zhang, N.L. Wang, W.L. Dong, Preparation of Y2O3:Eu3+, Tb3+ nanopowders with tunable luminescence by ammonium bicarbonate co-precipitation method. Funct. Mater. Lett. 6, 8 (2015)
J.C. Sun, X.Y. Mi, L.J. Lei, Hydrothermal synthesis and photoluminescence properties of Ca9Eu(PO4)7 nanophosphors. CrystEngComm 17, 7888–7895 (2015)
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by the Scientific and Technological Department of Jilin Province (Nos. 20130522176JH and 20130102016JC), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61307118)and Changchun Science and Technology Bureau (No. 2013045).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Li, R. & Bai, Z. Luminescence properties and preparation of Lu3Al5O12 powder doped with Ce and Pr ions. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 29, 10753–10761 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-9141-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-9141-x