Abstract
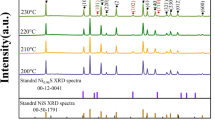
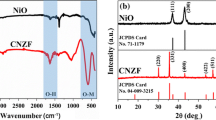
In this work, the spindle magnetite nanoparticles (SMNPs) and flower-like copper sulfide microspheres (FCSMSs) were synthesized via hydrothermal method. The structures, chemical composition and morphologies of samples were analyzed and characterized in detail. The microwave absorption properties of single-layer and double-layer absorbers were investigated based on the electromagnetic transmission line theory in the frequency range from 2 to 18 GHz. The results show that the double-layer absorbers consisting of FCSMSs as matching layer and SMNPs as absorbing layer display superior microwave absorbing performance compared to the single-layer ones due to the proper combination of magnetic loss of SMNPs and dielectric loss of FCSMSs, and the improved impedance matching characteristics. When the thicknesses of the absorbing layer and the matching layer are 1.6 and 0.4 mm, respectively, the minimum reflection loss reaches − 74.3 dB at 10.9 GHz, and the efficient absorption bandwidth is up to 5.34 GHz (8.46–13.8 GHz). The optimal SMNPs/FCSMSs double-layer absorbers can become a novel microwave absorption material with strong-absorption and broad-band.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Liu, R. Che, H. Chen et al., Microwave absorption enhancement of multifunctional composite microspheres with spinel Fe3O4 cores and anatase TiO2 shells. Small 8, 1214–1221 (2012)
W. Zhou, Y. Gong, L. Tu et al., Dielectric properties and thermal conductivity of core-shell structured Ni@NiO/poly(vinylidene fluoride) composites. J. Alloys Compd. 693, 1–8 (2017)
L. Li, S. Liu, L. Lu, Synthesis and significantly enhanced microwave absorption properties of cobalt ferrite hollow microspheres with protrusions/polythiophene composites. J. Alloys Compd. 722, 158–165 (2017)
Y. Wang, W. Zhang, X. Wu et al., Conducting polymer coated metal-organic framework nanoparticles: facile synthesis and enhanced electromagnetic absorption properties. Synth. Met. 228, 18–24 (2017)
S. Zhang, W. Wei, X. Xiao et al., Preparation and characterization of spindle-like Fe3O4 mesoporous nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 6, 89 (2011)
G. Wu, H. Wu, K. Wang et al., Facile synthesis and application of multi-shelled SnO2 hollow spheres in lithium ion battery. RSC Adv. 6(63), 58069–58076 (2016)
S. Qu, Y. Yu, K. Lin et al., Easy hydrothermal synthesis of multi-shelled La2O3 hollow spheres for lithium-ion batteries. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 29, 1232–1237 (2018)
H. Xu, H. Bi, R. Yang, Enhanced microwave absorption property of bowl-like Fe3O4 hollow spheres/reduced graphene oxide composites. J. Appl. Phys. 111, 16229 (2012)
H. Fan, G. You, Y. Li et al., Shape-controlled synthesis of single-crystalline Fe2O3 hollow nanocrystals and their tunable optical properties. J. Phys. Chem. C 113, 9928–9935 (2009)
A. Feng, G. Wu, C. Pan et al., The behavior of acid treating carbon fiber and the mechanical properties and thermal conductivity of phenolic resin matrix composites. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 17(6), 3786–3791 (2017)
C. Shi, J. Zhu, X. Shen et al., Flexible inorganic membranes used as a high thermal safety separator for the lithium-ion battery. RSC Adv. 8(8), 4072–4077 (2018)
A. Feng, Z. Jia, Y. Zhao et al., Development of Fe/Fe3O4@C composite with excellent electromagnetic absorption performance. J. Alloys Compd. 745, 547–554 (2018)
G. Wu, Y. Cheng, Z. Yang et al., Design of carbon sphere/magnetic quantum dots with tunable phase compositions and boost dielectric loss behavior. Chem. Eng. J. 333, 519–528 (2018)
X. Qing, X. Yue, B. Wang et al., Facile synthesis of size-tunable, multilevel nanoporous Fe3O4 microspheres for application in electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Alloys Compd. 595, 131–137 (2014)
T. Wei, Y. Liu, W. Dong et al., Surface-dependent localized surface plasmon resonances in CuS nanodisks. Appl. Mater. Interfaces 5, 10473–10477 (2013)
B. Zhao, G. Shao, B. Fan et al., Synthesis of flower-like CuS hollow microspheres based on nanoflakes self-assembly and their microwave absorption properties. J. Mater. Chem. A 3, 10345–10352 (2015)
G. Wu, Y. Cheng, K.Wang et al., Fabrication and characterization of OMMt/BMI/CE composites with low dielectric properties and high thermal stability for electronic packaging. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 27(6), 5592–5599 (2016)
K. Yuan, J. Wu, M. Liu et al., Fabrication and microstructure of p-type transparent conducting CuS thin film and its application in dye-sensitized solar cell. Appl. Phys. Lett. 93, 939 (2008)
O. Otelaja, D.-H. Ha, T. Ly et al., Highly conductive Cu2-xS nanoparticle films through room-temperature processing and an order of magnitude enhancement of conductivity via electrophoretic deposition. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 6, 18911–18920 (2014)
D. Yan, S. Cheng, R. Zhuo et al., Nanoparticles and 3D sponge-like porous networks of manganese oxides and their microwave absorption properties. Nanotechnology 20, 105706 (2009)
A. Feng, G. Wu, C. Pan et al., Synthesis, preparation and mechanical property of wood fiber-reinforced poly(vinyl chloride) composites. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 17(6), 3859–3863 (2017)
W. Du, X. Qian, X. Ma et al., Shape-controlled synthesis and self-assembly of hexagonal covellite (CuS) nanoplatelets. Chemistry 13, 3241–3247 (2007)
C. Wu, S. Yu, S. Chen et al., Large scale synthesis of uniform CuS nanotubes in ethylene glycol by a sacrificial templating method under mild conditions. J. Mater. Chem. 16, 3326–3331 (2006)
H. Wu, G. Wu, Y. Ren et al., Multi-shelled metal oxide hollow spheres: easy synthesis and formation mechanism. Chem.- Eur. J. 22(26), 8864–8871 (2016)
Q. Liu, Q. Cao, H. Bi et al., CoNi@SiO2@TiO2 and CoNi@Air@TiO2 microspheres with Strong wideband microwave absorption. Adv. Mater. 28, 486–490 (2016)
C. Wei, X. Shen, F. Song et al., Double-layer microwave absorber based on nanocrystalline Zn0.5Ni0.5Fe2O4/α-Fe microfibers. Mater. Des. 35, 363–368 (2012)
Y. Qing, W. Zhou, F. Luo et al., Optimization of electromagnetic matching of carbonyl iron/BaTiO3 composites for microwave absorption. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 323, 600–606 (2011)
C. Jia, L. Sun, Z. Yan et al., Single-crystalline iron oxide nanotubes. Angew. Chem. 44, 4328–4333 (2005)
Z. Jia, K. Kou, M. Qin et al., Controllable and large-scale synthesis of carbon nanostructures: a review on bamboo-like nanotubes. Catalysts 7(9), 256–276 (2017)
J. Liu, D. Xue, Solvothermal synthesis of CuS semiconductor hollow spheres based on a bubble template route. J. Cryst. Growth 311, 500–503 (2009)
H. Qi, J. Huang, L. Cao et al., One-dimensional CuS microstructures prepared by a PVP-assisted microwave hydrothermal method. Ceram. Int. 38, 2195–2200 (2012)
W. Zhou, L. Xu, L. Jiang et al., Towards suppressing loss tangent: Effect of SiO2 coating layer on dielectric properties of core-shell structure flaky Cu reinforced PVDF composites. J. Alloys Compd. 710, 47–56 (2017)
G. Deroubaix, P. Marcus, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy analysis of copper and zinc oxides and sulphides. Surf. Interfaces Anal. 18, 39–46 (1992)
P. Liu, Y. Huang, X. Zhang, Enhanced electromagnetic absorption properties of reduced graphene oxide–polypyrrole with NiFe2O4 particles prepared with simple hydrothermal method. Mater. Lett. 120, 143–146 (2014)
Z. Guo, M. Seol, M. Kim et al., Hollow CuO nanospheres uniformly anchored on porous Si nanowires: preparation and their potential use as electrochemical sensors. Nanoscale 4, 7525–7531 (2012)
C. Wang, X. Han, X. Zhang et al., Controlled synthesis and morphology-dependent electromagnetic properties of hierarchical cobalt assemblies. J. Phys. Chem. C 114, 3196–3203 (2010)
C. Pan, J. Zhang, K. Kou et al., Investigation of the through-plane thermal conductivity of polymer composites with in-plane oriented hexagonal boron nitride. Int. J. Heat. Mass. Tran. 120, 1–8 (2018)
W. Zhou, Z. Wang, L. Dong et al., Dielectric properties and thermal conductivity of PVDF reinforced with three types of Zn particles. Composites A 79, 183–191 (2015)
R. Kirian, R. Bean, K. Beyerlein et al., Direct phasing of finite crystals illuminated with a free-electron laser. Phys. Rev. X 5, 011015 (2015)
Z. Wang, W. Zhou, L. Dong et al., Dielectric spectroscopy characterization of relaxation process in Ni/epoxy composites. J. Alloys Compd. 682, 738–745 (2016)
J. Xiang, J. Li, X. Zhang et al., Magnetic carbon nanofibers containing uniformly dispersed Fe/Co/Ni nanoparticles as stable and high-performance electromagnetic wave absorbers. J. Mater. Chem. A 2, 16905–16914 (2014)
P. Liu, Z. Yao, J. Zhou et al., Small magnetic Co-doped NiZn ferrite/graphene nanocomposites and their dual-region microwave absorption performance. J. Mater. Chem. C 4, 9738–9749 (2016)
H. Lv, Z. Yang, P. Wang et al., A voltage-boosting strategy Enabling a low-frequency, flexible electromagnetic wave absorption device. Adv. Mater. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201706343
Z. Wang, W. Zhou, L. Dong et al., Dielectric relaxation dynamics of Al/epoxy micro-composites. J. Alloys Compd. 689, 342–349 (2016)
W. Zhou, Q. Chen, X. Sui et al., Enhanced thermal conductivity and dielectric properties of Al/β-SiCw/PVDF composites. Composites A 71, 184–191 (2015)
S. Wei, X. Wang, B. Zhang et al., Preparation of hierarchical core-shell C@NiCo2O4@Fe3O4 composites for enhanced microwave absorption performance. Chem. Eng. J. 314, 477–487 (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, S., Li, L., Zheng, S. et al. Microwave absorption properties of double-layer absorbers based on spindle magnetite nanoparticles and flower-like copper sulfide microspheres. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 29, 8978–8988 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-8922-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-8922-6