Abstract
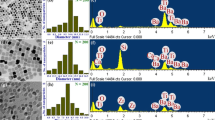
Polymer nanocomposites have proved to be promising energy storage devices for modern power electronic systems. In this work we have studied the dielectric properties and dielectric energy storage densities of 0–3 type BCZT/PVDF-HFP polymer nanocomposites with different filler volume concentrations. BCZT nanopowder was synthesized by solgel method through citrate precursor method. The structural and morphological features of the BCZT nanopowder were examined by X-ray diffraction and transmission electron microscopy. For better polymer ceramic interface coupling, BCZT was surface functionalized with extended aromatic ligand, naphthyl phosphate (NPh). The surface functionalization was validated and quantified by thermogravimetric analysis and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. The dielectric constant of surface passivated BCZT nanoparticles was estimated to be ~ 155 using slurry technique, while the dielectric permittivity of pristine BCZT nanopowder could not be assessed due to high innate surface conductivity. BCZT/PVDF-HFP polymer nanocomposite thin films were fabricated using solution casting technique. The dispersion quality of the ceramic fillers in the polymer matrix was examined by scanning electron microscopy. Due to better polymer ceramic interface, At 5 vol% filler concentration, NPh modified nanoBCZT/PVDF-HFP films showed enhanced dielectric breakdown strength and energy storage density than untreated nanoBCZT/PVDF-HFP and even pure polymer films. Maximum energy storage density of 8.5 J cm−3 was obtained at an optimum filler concentration of 10 vol% for surface functionalized BCZT/PVDF-HFP composite films of 10 μm thickness.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Z. Yao, Z. Song, H. Hao, Z. Yu, M. Cao, S. Zhang, M.T. Lanagan, H. Liu, Homogeneous/inhomogeneous-structured dielectrics and their energy-storage performances. Adv. Mater. 29, 1601727 (2017)
X. Hao, A review on the dielectric materials for high energy-storage application. J. Adv. Dielectr. 3, 1330001 (2013)
Q. Chen, Y. Shen, S. Zhang, Q.M. Zhang, Polymer-based dielectrics with high energy storage density. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 45, 433–458 (2015)
Q. Wang, L. Zhu, Polymer nanocomposites for electrical energy storage. J. Polym. Sci. Part B 49, 1421–1429 (2011)
F.A. Pearsall, J. Lombardi, S.O. Brien, Monomer derived poly (Furfuryl)/BaTiO3 0–3 nanocomposite capacitors: maximization of the effective permittivity through control at the interface. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9, 40324–40332 (2017)
S. Liao, Z. Shen, H. Pan, X. Zhang, Y. Shen, Y. Lin, C. Nan, A surface-modified TiO2 nanorod array/P(VDF–HFP) dielectric capacitor with ultra-high energy density and efficiency. J. Mater. Chem. C 5, 12777–12784 (2017)
G. Wu, Y. Cheng, K. Wang, Y. Wang, A. Feng, Fabrication and characterization of OMMt/BMI/CE composites with low dielectric properties and high thermal stability for electronic packaging. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 27, 5592–5599 (2016)
Z. Wang, T. Wang, C. Wang, Y. Xiao, The effect of interfacial interaction-induced soft percolation regime on dielectric properties in Ba(Fe0.5Nb0.5)O3/P(VDF-TrFE) nanocomposites. J. Mater. Sci. 52, 11496–11505 (2017)
M.T. Sebastian, Polymer–ceramic composites of 0–3 connectivity for circuits in electronics: a review. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 7, 415–434 (2010)
Y. Hao, X. Wang, K. Bi, J. Zhang, Y. Huang, L. Wu, P. Zhao, K. Xu, M. Lei, L. Li, Significantly enhanced energy storage performance promoted by ultimate sized ferroelectric BaTiO3 fillers in nanocomposite films. Nano Energy 31, 49–56 (2017)
H. Tang, Y. Lin, H.A. Sodano, Enhanced energy storage in nanocomposite capacitors through aligned PZT nanowires by uniaxial strain assembly. Adv. Energy Mater. 2, 469–476 (2012)
V.K. Thakur, R.K. Gupta, Recent progress on ferroelectric polymer-based nanocomposites for high energy density capacitors: synthesis, dielectric properties, and future aspects. Chem. Rev. 116, 4260–4317 (2016)
P. Kim, N.M. Doss, J.P. Tillotson, P.J. Hotchkiss, M. Pan, P. Marder, J. Li, J.P. Calame, J.W. Perry, High energy density nanocomposites based on surface-modified BaTiO3 and a ferroelectric polymer. ACS Nano 3, 2581–2592 (2009)
H. Luo, D. Zhang, C. Jiang, X. Yuan, C. Chen, K. Zhou, Improved dielectric properties and energy storage density of poly (vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene) nanocomposite with hydantoin epoxy resin coated BaTiO3. Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7, 8061–8069 (2015)
W. Liu, X. Ren, Large piezoelectric effect in Pb-free ceramics. Phy. Rev. Lett. 103, 257602 (2009)
B. Luo, X. Wang, Y. Wang, L. Li, Fabrication, characterization, properties and theoretical analysis of ceramic/PVDF composite flexible films with high dielectric constant and low dielectric loss. J. Mater. Chem. A 2, 510–519 (2014)
S.P.P. Sadhu, S. Siddabattuni, B. Ponraj, M. Molli, V. Sai Muthukumar, K.B.R. Varma, Enhanced dielectric properties and energy storage density of interface controlled ferroelectric BCZT-epoxy nanocomposites. Compos. Interfaces 24, 663–675 (2016)
S. Siddabattuni, T.P. Schuman, F. Dogan, Dielectric properties of polymer-particle nanocomposites influenced by electronic nature of filler surfaces. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 5, 1917–1926 (2013)
V. Petrovsky, F. Dogan, Fundamentals of impedance spectral analysis applied to determine permittivity of dielectric particles. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 92, 1054–1058 (2009)
V. Petrovsky, P. Jasinski, F. Dogan, Effective dielectric constant of two phase systems: application to mixed conducting systems. J. Appl. Phys. 112, 034107 (2012)
S. Siddabattuni, T.P. Schuman, V. Petrovsky, F. Dogan, Impedance analysis of dielectric nanoparticles enabled via a self-assembled monolayer. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 96, 1490–1496 (2013)
W.J. Li, Q.J. Meng, Y.S. Zheng, Z.C. Zhang, W.M. Xia, Electric energy storage properties of poly (vinylidene fluoride). Appl. Phys. Lett. 96, 192905 (2010)
K. Porkodi, S.D. Arokiamary, Synthesis and spectroscopic characterization of nanostructured anatase titania: a photocatalyst. Mater. Charact. 58, 495–503 (2007)
D.L. Reid, A.E. Russo, R.V. Carro, M.A. Stephens, A.R. LePagel, T.C. Spalding, E.L. Petersen, S. Seal, Nanoscale additives tailor energetic materials. Nano Lett. 7, 2157–2161 (2007)
H. Geng, R. Peng, S. Han, X. Gu, M. Wang, Surface-modified titania nanoparticles with conjugated polymer for hybrid photovoltaic devices. J. Electron. Mater. 39, 2346–2351 (2010)
A. Fadeev, Y. Helmy, R.S. Marcinko, Self-assembled monolayers of organosilicon hydrides supported on titanium, zirconium, and hafnium dioxides. Langmuir 18, 7521–7529 (2002)
C.D. Wagner, W.M. Riggs, L.E. Davis, J.F. Moulder, Handbook of X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy, 1st edn. (Perkin-Elmer Corporation (Physical Electronics), Minnesota, 1979)
S. Siddabattuni, A. Sri Harsha, G. Abilash, P. Sandeep, Impedance spectroscopy studies of surface engineered TiO2 nanoparticles using slurry technique. Bull. Mater. Sci. 38, 1399–1405 (2015)
S. Siddabattuni, T.P. Schuman, F. Dogan, Improved polymer nanocomposite dielectric breakdown performance through barium titanate to epoxy interface control. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 176, 1422–1429 (2011)
D. Stephen, An inside-out approach to storing electrostatic energy. ACS Nano 3, 2447–2450 (2009)
T.J. Lewis, Interfaces: nanometric dielectrics. J. Phys. D 38, 202–212 (2005)
P. Barber, S. Balasubramanian, Y. Anguchamy, S. Gong, A. Wibowo, H. Gao, H.J. Ploehn, H. Loye, Polymer composite and nanocomposite dielectric materials for pulse power energy storage. Materials 2, 1697–1733 (2009)
D. Ma, R.W. Siegel, J.I. Hong, L.S. Schadler, Influence of nanoparticle surfaces on the electrical breakdown strength of nanoparticle-filled low-density polyethylene. J. Mater. Res. 19, 857–863 (2004)
T.P. Schuman, S. Siddabattuni, O. Cox, F. Dogan, Improved dielectric breakdown strength of covalently-bonded interface polymer–particle nanocomposites. Compos. Interfaces 17, 719–731 (2010)
Acknowledgements
Authors from Department of Physics thanks DST-FIST. Authors at SSSIHL thank Sri Sathya Sai Central Trust for providing SSSIHL-Central Research Instruments Facility. SSPP acknowledges JRF fellowship provided by UGC (Sr. No. 2121351058). This work was made possible by the funds provided by the DST-SERB Start-Up Research Grant for Young Scientists (No. SB/FT/CS-019/2012), Government of India. We would like to acknowledge Dr. Vladimir Petrovsky from Missouri University of Science and Technology, USA, for his assistance in equivalent circuit modelling and the Micro and Nano Characterization Facility of Centre for Nano Science and Engineering, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore, for providing XPS characterization.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sadhu, S.P.P., Siddabattuni, S., Muthukumar V., S. et al. Enhanced dielectric properties and energy storage density of surface engineered BCZT/PVDF-HFP nanodielectrics. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 29, 6174–6182 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-8592-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-8592-4