Abstract
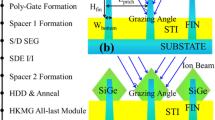
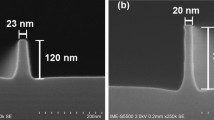
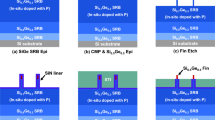
In this study, the integration of Si1−xGex (50% ≤ x ≤ 60%) selective epitaxy on source/drain regions in 10 nm node FinFET has been presented. One of the major process issues was the sensitivity of Si-fins’ shape to ex- and in-situ cleaning prior to epitaxy. For example, the sharpness of Si-fins could easily be damaged during the wafer washing. The results showed that a DHF dip before the normal cleaning, was essential to clean the Si-fins while in-situ annealing in range of 780–800 °C was needed to remove the native oxide for high epitaxial quality. Because of smallness of fins, the induced strain by SiGe could not be directly measured by X-ray beam in a typical XRD tool in the lab or even in a Synchrotron facility. Further analysis using nano-beam diffraction technique in high-resolution transmission electron microscope also failed to provide information about strain in the FinFET structure. Therefore, the induced strain by SiGe was simulated by technology computer-aided design program and the Ge content was measured by using energy dispersive spectroscopy. Simulation results showed 0.8, 1 and 1.3 GPa for Ge content of 40%, 50% and 60%, respectively. A kinetic gas model was also introduced to predict the SiGe profile on Si-fins with sharp triangular shape. The input parameters in the model includes growth temperature, partial pressure of the reactant gases and the exposed Si coverage in the chip area.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
V. Chan, R. Rengarajan, N. Rovedo, W. Jin, T. Hook, P. Nguyen et al., “High speed 45 nm gate length CMOSFETs integrated into a 90 nm bulk technology incorporating strain engineering,” in Electron Devices Meeting, 2003. IEDM’03 Technical Digest. IEEE International (2003), pp. 3.8.1–3.8.4
P. Bai, C. Auth, S. Balakrishnan, M. Bost, R. Brain, V. Chikarmane et al., “A 65 nm logic technology featuring 35 nm gate lengths, enhanced channel strain, 8 Cu interconnect layers, low-k ILD and 0.57 µm 2 SRAM cell” in Electron Devices Meeting (2004). IEEE International, pp. 657–660
P. Chidambaram, B. Smith, L. Hall, H. Bu, S. Chakravarthi, Y. Kim et al., “35 drive current improvement from recessed-SiGe drain extensions on 37 nm gate length PMOS,” in VLSI Technology, pp. 48–49 (2004)
S.E. Thompson, M. Armstrong, C. Auth, S. Cea, R. Chau, G. Glass et al., “A logic nanotechnology featuring strained-silicon”. Electron Device Lett. 25, 191–193 (2004)
S. Thompson, N. Anand, M. Armstrong, C. Auth, B. Arcot, M. Alavi et al., “A 90 nm logic technology featuring 50 nm strained silicon channel transistors, 7 layers of Cu interconnects, low k ILD, and 1/spl mu/m/sup 2/SRAM cell” in Electron Devices Meeting (2002). IEEE International, pp. 61–64
T. Ghani, M. Armstrong, C. Auth, M. Bost, P. Charvat, G. Glass et al., “A 90 nm high volume manufacturing logic technology featuring novel 45 nm gate length strained silicon CMOS transistors” in Electron Devices Meeting (2003). IEEE International, pp. 11.6.1–11.6.3
C.H. Jan, P. Bai, S. Biswas, M. Buehler, Z.P. Chen, G. Curello et al., “A 45 nm low power system-on-chip technology with dual gate (logic and I/O) high-k/metal gate strained silicon transistors”. In Electron Devices Meeting (2008). IEEE International pp. 1–4
C. Auth, C. Allen, A. Blattner, D. Bergstrom, M. Brazier, M. Bost et al., “A 22 nm high performance and low-power CMOS technology featuring fully-depleted tri-gate transistors, self-aligned contacts and high density MIM capacitors,” in VLSI Technology (VLSIT) (2012) Symposium on, pp. 131–132
S. Natarajan, M. Armstrong, M. Bost, R. Brain, M. Brazier, C.-H. Chang et al., “A 32 nm logic technology featuring 2 nd-generation high-k + metal-gate transistors, enhanced channel strain and 0.171 µm 2 SRAM cell size in a 291 Mb array” in Electron Devices Meeting (2008). IEEE International, pp. 1–3
M. Kolahdouz, L. Maresca, R. Ghandi, A. Khatibi, H.H. Radamson, Kinetic model of SiGe selective epitaxial growth using RPCVD technique. ECS Trans. 33(6), 581–593 (2010)
H.H. Radamson, L. Thylen, Monolithic Nanoscale Photonics-Electronics Integration in Silicon and Other Group 1V Elements, (Elsevier Science & Technology, Amsterdam, 2014)
G.L. Wang, M. Moeen, A. Abedin, M. Kolahdouz, J. Luo, C.L. Qin, H.L. Zhu, J. Yan, H.Z. Yin, J.F. Li, C. Zhao, H.H. Radamson, Optimization of SiGe selective epitaxy for source/drain engineering in 22 nm node complementary metal-oxide semiconductor (CMOS). J. Appl. Phys. 114(12), 123511 (2013)
G.L. Wang, A. Abedin, M. Moeen, M. Kolahdouz, J. Luo, Y. Guo, T. Chen, H. Yin, H. Zhu, J. Li, C. Hao, H.H. Radamson, Integration of highly-strained SiGe materials in 14 nm and beyond nodes FinFET technology. Solid-State Electron. 103, 222–228 (2015)
R.T. Buhler, J.A. Martino, P.G.D. Agopian, R. Giacomini, E. Simoen, C. Claeys, Fin shape influence on the analog performance of standard and strained MuGFETs. In SOI Conference (SOI), IEEE International pp. 1–2 (2010)
H.H. Radamson, M. Kolahdouz, Selective epitaxy growth of Si1-x Gex layers for MOSFETs and FinFET. J. Mater. Sci. 26, 4584–4603 (2015)
J. Hallstedt, P.-E. Hellstrom, H.H. Radamson, Sidewall transfer lithography for reliable fabrication of nanowires and deca-nanometer MOSFETs. Thin Solid Films 517, 117 (2008)
G.L. Wang, J. Luo, C. Qin, R. Liang, Y. Xu, J. Liu et al., Integration of highly strained SiGe in source and drain with HK and MG for 22 nm bulk PMOS transistors. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 12(1), 123 (2017)
G. Wang, C. Qin, H. Yin, J. Luo, N. Duan, P. Yang et al., Study of SiGe selective epitaxial process integration with high-k and metal gate for 16/14 nm nodes FinFET technology. Microelectron. Eng. 163, 49–54 (2016)
C. Qin, G. Wang, M. Kolahdouz, J. Luo, H. Yin, P. Yang et al., Impact of pattern dependency of SiGe layers grown selectively in source/drain on the performance of 14 nm node FinFETs. Solid-State Electron. 124, 10–15 (2016)
M. Kolahdouz, L. Maresca, M. Ostling, D. Riley, R. Wise, H.H. Radamson, New method to calibrate the pattern dependency of selective epitaxy of SiGe layers. Solid-State Electron. 53(8), 858–861 (2009)
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFA0301701), and the Youth Innovation Promotion Association of CAS under Grant No 2016112.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, G., Kolahdouz, M., Luo, J. et al. Growth of SiGe layers in source and drain regions for 10 nm node complementary metal-oxide semiconductor (CMOS). J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 31, 26–33 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-00661-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-00661-7