Abstract
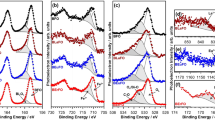
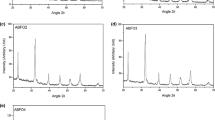
Bi2−xSrxFe4O9, 0 ≤ x ≤ 0.25 (BSFO) powders have been successfully synthesized by the reverse chemical co-precipitation method with a pH value of 9 at room temperature. In this study, the effect of Sr2+ doping on the structural, morphological, magnetic and electrical properties of BSFO was investigated and then the as-prepared powders were fabricated by microwave sintering at 800 °C. The X-ray diffraction (XRD) reveals the formation of the pure phase orthorhombic structure with Bi2O3 impurity for samples with x = 0.15, 0.20 and 0.25. Also, XRD patterns showed that by increasing the Sr2+ concentration, the amount of Bi2O3 impurity increases. In addition, the field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) indicates by increasing the Sr content, the particle size decreases from 215 for a pure sample to 40 nm for BSFO with x = 0.25, approximately. The thermogravimetric–differential scanning calorimeter (TG–DSC) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) were carried out for the estimation and conformation of the as-selected calcination temperature, weight loss and vibrational bounding mode, respectively. The magnetic properties of the nanoparticles and dielectric properties of the bulk samples were measured using the vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM) and inductance–capacitance–resistance (LCR-meter), respectively. The magnetization (M) was elevated from 0.190 to 0.358 emu/g by adding the 0.10 and then falls down to 0.217 emu/g for x = 0.20 strontium molar ratio as a result of the spiral spin structure collapse and formation of diamagnetic Bi2O3 phase, respectively. Besides, a decrease in the particles size by increasing the Sr amount resulted in more uncompensated spins, thereby improving the saturation magnetization. Furthermore, The coercivity of as-synthesized powder samples greatly increase with increasing the dopant concentration from 125 Oe for pure BFO to 3289 Oe for samples with x = 0.10 and then decreases to 940 Oe for x = 0.25 due to increasing the non-uniformity in the grain size distribution by addition the more dopant ions. In addition, the dielectric constant and dielectric loss were improved up to x = 0.25.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Wu, M. Siegel, Odor-Based Incontinence Sensor, Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference, 2000. IEEE, 2000, pp. 63–68
L. Dori, S. Nicoletti, I. Elimi, A.R. Mastrogiacomo, L. Sampaolo, E. Pierini, A gas chromatographic-like system for the separation and monitoring of benzene, toluene and xylene compounds at the ppb level using solid state metal oxide gas sensors. J. Sens. Mater. 12, 163–174 (2000)
A. Poghossian, H. Abovian, P. Avakian, S. Mkrtchian, V. Haroutunian, Bismuth ferrites: new materials for semiconductor gas sensors. J. Sens. Actuators B 4, 545–549 (1991)
W. Göpel, New materials and transducers for chemical sensors. J. Sens. Actuators B 18, 1–21 (1994)
H. Xie, K. Wang, Y. Jiang, Y. Zhao, X. Wang, An improved co-precipitation method to synthesize three bismuth ferrites. J. Synth. React. Inorg. Met.-Org. Nano-Met. Chem. 44, 1363–1367 (2014)
P. Hajra, R. Maiti, D. Chakravorty, Room temperature magnetoelectric coupling in single crystal Bi2Fe4O9 nanotubes grown within an anodic aluminum oxide template. Mater. Lett. 81, 138–141 (2012)
A. Tutov, V. Markin, The X-ray structural analysis of the antiferromagnetic Bi2Fe4O9 and the isotypical combinations Bi2Ga4O9 and Bi2Al4O9. Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR Neorg. Mater. 6 (1970)
E. Zahedi, B. Xiao, M. Shayestefar, First-principles investigations of the structure, electronic, and optical properties of mullite-type orthorhombic Bi2M4O9 (M = Al3+, Ga3+). J. Inorg. Chem. 55, 4824–4835 (2016)
Y. Xiong, M. Wu, Z. Peng, N. Jiang, Q. Chen, Hydrothermal synthesis and characterization of Bi2Fe4O9 nanoparticles. J. Chem. Lett. 33, 502–503 (2004)
D. Astrov, Magnetoelectric effect in chromium oxide. J. Sov. Phys. 13, 729–733 (1961)
I. Dzyaloshinskii, On the magneto-electrical effect in antiferromagnets. J. Sov. Phys. 10, 628–629 (1960)
Z. Yang, Y. Huang, B. Dong, H.-L. Li, S.-Q. Shi, Densely packed single-crystal Bi2Fe4O9 nanowires fabricated from a template-induced sol–gel route. J. Solid State Chem. 179, 3324–3329 (2006)
N. Niizeki, M. Wachi, The crystal structures of Bi2Mn4O10, Bi2Al4O9 and Bi2Fe4O9. J. Cryst. Mater. 127, 173–187 (1968)
H. Schmid, Multi-ferroic magnetoelectrics. Ferroelectrics 162, 317–338 (1994)
M. Fiebig, Revival of the magnetoelectric effect. J. Phys. D 38, R123 (2005)
W. Eerenstein, N. Mathur, J.F. Scott, Multiferroic and magnetoelectric materials. Nature 442, 759 (2006)
A. Singh, S. Kaushik, B. Kumar, P. Mishra, A. Venimadhav, V. Siruguri, S. Patnaik, Substantial magnetoelectric coupling near room temperature in Bi2Fe4O9. J. Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 132910 (2008)
P.K. Rao, S. Krishnan, M. Pattabi, G. Sanjeev, Magnetic and photoluminescence studies of electron irradiated Bi2Fe4O9 nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 401, 77–80 (2016)
H. Ke, W. Wang, Y. Wang, J. Xu, D. Jia, Z. Lu, Y. Zhou, Factors controlling pure-phase multiferroic BiFeO3 powders synthesized by chemical co-precipitation. J. Alloy. Compd. 509, 2192–2197 (2011)
L. Wang, J. Li, J.-B. Xu, A.-M. Chang, L. Bian, B. Gao, K.-T. Liu, Bi2Fe4O9 submicron-rods synthesized by a low-heating temperature solid state precursor method. J. Alloy. Compd. 562, 64–68 (2013)
A. Maitre, M. Francois, J. Gachon, Experimental study of the Bi2O3-Fe2O3 pseudo-binary system. J. Phase Equilib. Diffus. 25, 59–67 (2004)
M. Basiri, H. Shokrollahi, G. Isapour, Effects of La content on the magnetic, electric and structural properties of BiFeO3. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 354, 184–189 (2014)
H. Shokrollahi, Magnetic, electrical and structural characterization of BiFeO3nanoparticles synthesized by co-precipitation. J. Powder Technol. 235, 953–958 (2013)
I.A. Kornev, S. Lisenkov, R. Haumont, B. Dkhil, L. Bellaiche, Finite-temperature properties of multiferroic BiFeO3. J. Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 227602 (2007)
Y. Liu, R. Zuo, Morphology and optical absorption of Bi2Fe4O9 crystals via mineralizer-assisted hydrothermal synthesis. J. Particuology 11, 581–587 (2013)
T. Liu, Y. Xu, C. Zeng, Synthesis of Bi2Fe4O9 via PVA sol–gel route. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 176, 535–539 (2011)
B. Kaur, L. Singh, V.A. Reddy, D.-Y. Jeong, N. Dabra, J.S. Hundal, Study of A-site divalent doping on multiferroic properties of BFO nanoparticles processed via combustion method. J. Struct. 25, 28 (2016)
Y. Qiu, Z. Zou, R. Sang, H. Wang, D. Xue, Z. Tian, G. Gong, S. Yuan, Enhanced magnetic and ferroelectric properties in Cr doped Bi2Fe4O9 ceramics. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 26, 1732–1736 (2015)
T. Hussain, S.A. Siddiqi, S. Atiq, M. Awan, Induced modifications in the properties of Sr doped BiFeO3 multiferroics. Prog. Nat. Sci.: Mater. Int. 23, 487–492 (2013)
Q.-J. Ruan, W.-D. Zhang, Tunable morphology of Bi2Fe4O9 crystals for photocatalytic oxidation. J. Phys. Chem. C 113, 4168–4173 (2009)
J.T. Han, Y.H. Huang, X.J. Wu, C.L. Wu, W. Wei, B. Peng, W. Huang, J.B. Goodenough, Tunable synthesis of bismuth ferrites with various morphologies. Adv. Mater. 18, 2145–2148 (2006)
J. Wang, Y. Wei, J. Zhang, L. Ji, Y. Huang, Z. Chen, Synthesis of pure-phase BiFeO3 nanopowder by nitric acid-assisted gel. J. Mater. Lett. 124, 242–244 (2014)
G. Biasotto, A.Z. Simões, C.R. Foschini, S.G. Antônio, M.A. Zaghete, J.A. Varela, A novel synthesis of perovskite bismuth ferrite nanoparticles. J. Process. Appl. Ceram. 5, 171–179 (2011)
J. Zhao, T. Liu, Y. Xu, Y. He, W. Chen, Synthesis and characterization of Bi2Fe4O9 powders. Mater. Chem. Phys. 128, 388–391 (2011)
A. Beran, D. Voll, H. Schneider, Dehydration and structural development of mullite precursors: an FTIR spectroscopic study. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 21, 2479–2485 (2001)
Z. Tian, Y. Qiu, S. Yuan, M. Wu, S. Huo, H. Duan, Enhanced multiferroic properties in Ti-doped Bi2Fe4O9 ceramics. J. Appl. Phys. 108, 064110 (2010)
R. Maiti, S. Basu, D. Chakravorty, Synthesis of nanocrystalline YFeO3 and its magnetic properties. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 321, 3274–3277 (2009)
T. Kimura, S. Kawamoto, I. Yamada, M. Azuma, M. Takano, Y. Tokura, Magnetocapacitance effect in multiferroic BiMnO3. J. Phys. Rev. B 67, 180401 (2003)
J.-T. Han, Y.-H. Huang, R.-J. Jia, G.-C. Shan, R.-Q. Guo, W. Huang, Synthesis and magnetic property of submicron Bi2Fe4O9. J. Cryst. Growth 294, 469–473 (2006)
T. Hussain, S.A. Siddiqi, S. Atiq, S. Riaz, S. Naseem, Induced Modifications in the Structural, Electrical and Magnetic Properties of Sr-Doped BiFeO 3 Multiferroics. Advances in civil, environmental, and materials research, 2012
G. Wang, S. Nie, J. Sun, S. Wang, Q. Deng, Effects of Zr4+ doping on structure, magnetic and optical properties of Bi2Fe4O9 powders. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 27, 9417–9422 (2016)
F.J.G. Landgraf, J.R.F. Da Silveira, D. Rodrigues-Jr, Determining the effect of grain size and maximum induction upon coercive field of electrical steels. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 323, 2335–2339 (2011)
M. Ahmed, E. Dhahri, S. El-Dek, M. Ayoub, Size confinement and magnetization improvement by La3+ doping in BiFeO3 quantum dots. Solid State Sci. 20, 23–28 (2013)
B. Bhushan, A. Basumallick, N. Vasanthacharya, S. Kumar, D. Das, Sr induced modification of structural, optical and magnetic properties in Bi1– xSrxFeO3 (x = 0, 0.01, 0.03, 0.05 and 0.07) multiferroic nanoparticles. J. Solid State Sci. 12, 1063–1069 (2010)
G. Song, H. Zhang, T. Wang, H. Yang, F. Chang, Effect of Sm, Co codoping on the dielectric and magnetoelectric properties of BiFeO3 polycrystalline ceramics. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 324, 2121–2126 (2012)
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge Shiraz University of Technology for the partial financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Daneshmand, N., Shokrollahi, H. & Lavasani, S.A.N.H. Enhanced magnetic and dielectric properties in bismuth ferrite (Bi2−xSrxFe4O9) derived by the reverse chemical co-precipitation method. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 29, 3201–3209 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-8255-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-8255-x