Abstract
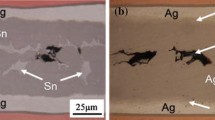
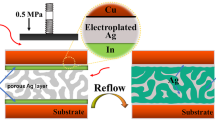
In this paper, we investigated the microstructure evolution and the resulting change in mechanical properties in a Ag@Sn TLP bondline during reflow and thermal aging. A Ag@Sn high-remelting-point bondline was rapidly achieved with thermocompression bonding of Ag@Sn powder in only 5 min at 250 °C. After reducing the thickness of the Sn coating on the Ag particles, the main phases in the resulting bondlines changed from Ag/Ag3Sn to Ag/ζ-Ag, increasing the remelting temperatures to 480 °C and above. The voids were effectively controlled by reducing the thickness of the Sn coating, thereby increasing the shear strength by 38%. The large surface area of the Ag/Sn interface, provided by a high density of core–shell Ag@Sn particles, enabled the rapid formation of an interconnection that is entirely composed of Ag and ζ-Ag. After thermal aging, the main phases transformed from Ag/ζ-Ag to Ag/Ag (Sn) solid solution/ζ-Ag, which causes an increase in the remelting temperature of aged interconnections up to 724 °C. The thermal aged samples showed slight decreases in shear strength, but the morphology of the fracture surfaces indicated better ductility.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Biela, M. Schweizer, S. Waffler, J.W. Kolar, SiC versus Si: evaluation of potentials for performance improvement of inverter and DC–DC converter systems by SiC power semiconductors. Mater. Sci. Forum. 58(7), 2872–2882 (2011)
W. Zhou, X. Zhong, K. Sheng, High temperature stability and the performance degradation of SiC MOSFETs. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 29(5), 2329–2337 (2014)
R. Wang, D. Boroyevich, P. Ning, Z. Wang, F. Wang, P. Mattavelli, K.D.T. Ngo, K. Rajashekara, A high-temperature SiC three-phase AC–DC converter design for > 100 °C ambient temperature. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 28(1), 555–572 (2013)
E.P. Wood, K.L. Nimmo, In search of new lead-free electronic solders. J. Electron. Mater. 23(8), 709–713 (1994)
D.G. Ivey, Microstructural characterization of Au/Sn solder for packaging in optoelectronic applications. Micron 29(4), 281–287 (1998)
S. Sakamoto, S. Nagao, K. Suganuma, Thermal fatigue of Ag flake sintering die-attachment for Si/SiC power devices. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 24(7), 2593–2601 (2013)
C. Chen, S. Nagao, H. Zhang, J. Jiu, T. Sugahara, K. Suganuma, T. Iwashige, K. Sugiura, K. Tsuruta, Mechanical deformation of sintered porous Ag die attach at high temperature and its size effect for wide-bandgap power device design. J. Electron. Mater. 46(3), 1576–1586 (2016)
S.A. Paknejad, A. Mansourian, Y. Noh, K. Khtatba, S.H. Mannan, Thermally stable high temperature die attach solution. Mater. Des. 89, 1310–1314 (2016)
K.S. Tan, K.Y. Cheong, Mechanical properties of sintered Ag–Cu die-attach nanopaste for application on SiC device. Mater. Des. 64, 166–176 (2014)
J. Bultitude, J. Mcconnell, C. Shearer, High temperature capacitors and transient liquid phase interconnects for Pb-solder replacement. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 26(12), 9236–9242 (2015)
A. Davoodi Jamaloei, H.R. Salimijazi, H. Edris, J. Mostaghimi, Study of TLP bonding of Ti-6Al-4V alloy produced by vacuum plasma spray forming and forging. Mater. Des. 121, 355–366 (2017)
R. Khazaka, L. Mendizabal, D. Henry, R. Hanna, Survey of high-temperature reliability of power electronics packaging components. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 30(5), 2456–2464 (2015)
A. Lis, C. Leinenbach, Effect of process and service conditions on TLP-bonded components with (Ag, Ni–)Sn interlayer combinations. J. Electron. Mater. 44(11), 1–13 (2015)
H. Shao, A. Wu, Y. Bao, Y. Zhao, Elimination of pores in Ag–Sn TLP bonds by the introduction of dissimilar intermetallic phases. J. Mater. Sci. 52(6), 3508–3519 (2016)
H. Shao, A. Wu, Y. Bao, Y. Zhao, G. Zou, Interfacial reaction and mechanical properties for Cu/Sn/Ag system low temperature transient liquid phase bonding. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 27(5), 1–10 (2016)
V. Chidambaram, B. Chen, C.L. Gan, D.R.M. Woo, Au–In-based hermetic sealing for MEMS packaging for down-hole application. J. Electron. Mater. 43(7), 2498–2509 (2014)
J.B. Lee, H.Y. Hwang, M.W. Rhee, Reliability investigation of Cu/In TLP bonding. J. Electron. Mater. 44(1), 435–441 (2015)
K. Chu, Y. Sohn, C. Moon, A comparative study of Cn/Sn/Cu and Ni/Sn/Ni solder joints for low temperature stable transient liquid phase bonding. Scripta Mater. 109, 113–117 (2015)
H. Xu, V. Vuorinen, H. Dong, M. Paulasto-Kröckel, Solid-state reaction of electroplated thin film Au/Sn couple at low temperatures. J. Alloys Compd. 619, 325–331 (2015)
X. Deng, M. Koopman, N. Chawla, K.K. Chawla, Young’s modulus of (Cu, Ag)–Sn intermetallics measured by nanoindentation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 364(1–2), 240–243 (2004)
W.F. Gale, D.A. Butts, Transient liquid phase bonding. Sci. Technol. Weld. Joining 9(9), 283–300 (2013)
H. Liu, K. Wang, K.E. Aasmundtveit, N. Hoivik, Intermetallic compound formation mechanisms for Cu–Sn Solid–liquid interdiffusion bonding. J. Electron. Mater. 41(9), 2453–2462 (2012)
J.F. Li, P.A. Agyakwa, C.M. Johnson, Kinetics of Ag3Sn growth in Ag–Sn–Ag system during transient liquid phase soldering process. Acta Mater. 58(9), 3429–3443 (2010)
Z.L. Li, H.J. Dong, X.G. Song, H.Y. Zhao, J.C. Feng, J.H. Liu, H. Tian, S.J. Wang, Rapid formation of Ni3Sn4 joints for die attachment of SiC-based high temperature power devices using ultrasound-induced transient liquid phase bonding process. Ultrason. Sonochem. 36, 420–426 (2017)
M. Hizukuri, N. Watanabe, T. Asano, Dynamic strain and chip damage during ultrasonic flip chip bonding. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 40(40), 3044–3048 (2001)
O. Mokhtari, H. Nishikawa, The shear strength of transient liquid phase bonded Sn–Bi solder joint with added Cu particles. Adv. Powder Technol. 27(3), 1000–1005 (2016)
O. Mokhtari, H. Nishikawa, Transient liquid phase bonding of Sn–Bi solder with added Cu particles. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 27(5), 4232–4244 (2016)
M. Fujino, H. Narusawa, Y. Kuramochi, E. Higurashi, T. Suga, T. Shiratori, M. Mizukoshi, Transient liquid-phase sintering using silver and tin powder mixture for die bonding. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 55(4S), 04EC14 (2016)
J.F. Li, P.A. Agyakwa, C.M. Johnson, Suitable thicknesses of base metal and interlayer, and evolution of phases for Ag/Sn/Ag transient liquid-phase joints used for power die attachment. J. Electron. Mater. 43(4), 983–995 (2014)
I. Karakaya, W.T. Thompson, The Ag–Sn (Silver–Tin) system. J. Phase Equilib. 8(4), 340–347 (1987)
S. Kumar, J. Jung, Mechanical and electronic properties of Ag3Sn intermetallic compound in lead free solders using ab initio atomistic calculation. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 178(1), 10–21 (2013)
C.P. Lin, C.M. Chen, C.H. Lin, W.C. Su, Interfacial reactions of Sn/Ag/Cu tri-layer on a deformed polyimide substrate. J. Alloys Compd. 502(2), L17–L19 (2010)
H. Shao, A. Wu, Y. Bao, Y. Zhao, G. Zou, Microstructure characterization and mechanical behavior for Ag3Sn joint produced by foil-based TLP bonding in air atmosphere. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 680, 221–231 (2017)
K. Suzuki, S. Kano, M. Kajihara, N. Kurokawa, K. Sakamoto, Reactive diffusion between Ag and Sn at solid state temperatures. Mater. Trans. JIM 46(5), 969–973 (2005)
G. Ghosh, Elastic properties, hardness, and indentation fracture toughness of intermetallics relevant to electronic packaging. J. Mater. Res. 19(5), 1439–1454 (2004)
Acknowledgements
This work is financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51375116) and the Science and Technology Project of Shenzhen (No. JCYJ20160318095308401).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, Q., Yu, F., Chen, H. et al. Microstructure evolution during reflow and thermal aging in a Ag@Sn TLP bondline for high-temperature power devices. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 29, 3014–3024 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-8232-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-8232-4