Abstract
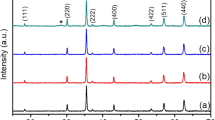
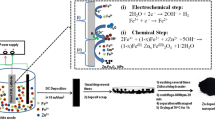
Magnetism in Ni1 −xMnxO (x = 0.0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3) nanoparticles synthesized by Sol–gel technique has been reported. X-ray diffraction (XRD), FESEM with EDAX, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and Vibrating Sample Magnetometer (VSM) were employed to understand the influence of Mn in the structural, functional and magnetic properties of NiO nanoparticles. XRD analysis confirmed the formation of single phase cubic structure. The average particle size was measured to be 29 and 23 nm for NiO and Mn doped NiO nanoparticles respectively. FESEM results revealed that particles were spherical in shape. The elemental composition was analyzed by EDAX and it was in good agreement with the starting stoichiometries. FTIR spectra confirmed the existence of NiO. Room temperature ferromagnetism was observed for pure and Mn doped NiO nanoparticles. Pure NiO particles show ferromagnetic behavior with high coercivity and it reduces gradually when doping ratio increases. Higher saturation magnetization was obtained for the sample 0.1% of Mn doped NiO nanoparticles. Electrochemical properties of Mn doped NiO was investigated regarding its performance as electrodes in supercapacitors. Pure NiO shows the maximum specific capacitance of 134.46 Fg−1 at a scan rate of 20 m Vs−1. It reveals that it is a good electrode material for super capacitor.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Wang, L. Zhang, J. Zhang, Chem. Soc. Rev. 41, 797–828 (2012)
K. Sathishkumar, N. Shanmugam, N. Kannadasan, S. Cholan, G. Viruthagiri, Mater. Sci. Semicond. Proces. 27, 846–853 (2014)
P. Mallick, C. Rath, Solid State Commun. 150, 1342–1345 (2010)
S. Thota, J.H. Shim, M. Seehra, J. Appl. Phys. 114, 214307 (2013). doi:10.1063/1.4838915
Z. Li, L. Wei, Y. Liu, Y. Su, X. Dong, Y. Zhang, J. Mater. Sci. (2017). doi:10.1007/s10854-017-7232-8
F.I. Dar, K.R. Moonooswamy, M. Es-Souni, Nanoscale Res. Lett. 8(1), 363 (2013). doi:10.1186/1556-276X-8-363
I. Hotovy, J. Huran, L. Spiess, S. Hascik, V. Rehacek, Sens. Actuators B 57, 147–152 (1999)
H. Sachdeva, D. Dwivedi, R.R. Bhattacharjee, S. Khaturia, R. Saroj, J. Chem. (2013). doi:10.1155/2013/606259
M. Martini, G.E.S. Brito, M.C.A. Fantini, A. Gorenstein, J. Elect. Acta 46(13–14), 2275–2279 (2001)
Y.J. Mai, J.P. Tu, X.H. Xia, C.D. Gu, X.L. Wang, J. Powrsour. 196, 6388–6393 (2011)
H. Zhu, D.C. Rosenfeld, M. Harb, D.H. Anjum, M.N. Hedhili, S. Ould-Chikh, J.-M. Basset, ACS Catal. 6(5), 2852–2866 (2016). doi:10.1021/acscatal.6b00044
D. Han, X. Jing, J. Wang, P. Yang, D. Song, J. Liu, J. Electroanal. Chem. 682, 37–44 (2012)
H.T. Rahal, R. Awad, A.M. Abdel-Gaber, D.E.-S. Bakeer, J. Nanomater. (2017). doi:10.1155/2017/7460323
M. George, A. Mary John, S.S. Nair, P.A. Joy, M.R. Anantharaman, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 302, 190–195 (2006)
Y.-D. Luo, Y.-H. Lin, X. Zhang, D. Liu, Y. Shen, C.-W. Nan, J. Nanometer. (2013). doi:10.1155/2013/252593
M. Tadic, D. Nikolic, M. Panjan, G.R. Blake, J. Allcom. 647, 1061–1068 (2015)
L. Li, L. Chen, R. Qihe, G. Li, Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 134102–134105 (2006)
K. Anandan, V. Rajendran, Mater. Sci. Eng. (2015). doi:10.1016/j.mseb.2015.04.015
H. Xiao, S. Yao, H. Liu, F. Qu, X. Zhang, X. Wu, Progress Nat. Sci. 26, 271–275 (2016)
H. Pang, B. Zhang, J. Du, J. Chen, J. Zhang, S. Li, RSC Adv. 2, 2257–2261 (2012)
H. Jiang, T. Zhao, C. Li, J. Ma, J. Mater. Chem. 21, 3818–3823 (2011)
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge Dr. P. Prabhu, Assistant Professor, Department of Physical Chemistry, University of Madras, Chennai, India for CV studies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bharathy, G., Raji, P. Room temperature ferromagnetic behavior of Mn doped NiO nanoparticles: a suitable electrode material for supercapacitors. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 28, 17889–17895 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-7730-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-7730-8