Abstract
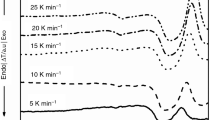
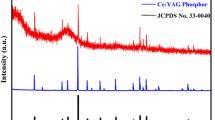
Ce:YAG phosphor in glass was prepared by co-sintering bismuthate glass frits and Ce:YAG phosphors at different temperatures in the 550–800 °C range. In this work, the effect of co-sintering temperature on the photoluminescence and chromaticity coordinates (CIE) of phosphor in glass was investigated. The results show that the CIE coordinates is tunable with the increase of co-sintering temperature. As temperature increased from 550 to 700 °C, the intensity of emission and excited peak increases until a maximum is reached, after which it rapidly drops off. The degradation of luminescence properties with the higher co-sintering temperature is due to the broken lattice surrounding the Ce3+ and oxidation of the Ce3+ caused by the reactions between the bismuthate glass and Ce:YAG phosphors.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Z.Y. Mao, Y.C. Zhu, L. Gan, Y. Zeng, F.F. Xu, Y. Wang, D.J. Wang, Novel white-light-emitting SiAlON-crystal/glass composite phosphor prepared by facile strategy for white light-emitting-diode. Mater. Lett. 80, 63–65 (2012)
B.B. Yang, J. Zou, F.C. Wang, C.Y. Zhang, J.Y. Xu, L. Li, L.H. Sun, Optical and reliability properties studies of green YAG phosphors by Ga substitution. J. Mater. Sci. 27, 3376–3383 (2016)
C.C. Tsai, W.C. Cheng, J.K. Chang, L.Y. Chen, Y.C. Hsu, W.H. Cheng, Ultra-high thermal-stable glass phosphor layer for phosphor-converted white light-emitting diodes. J. Disp. Technol. 9, 427–432 (2013)
C.C. Tsai, J. Wang, M.H. Chen, Y.C. Hsu, Y.J. Lin, C.W. Lee, Investigation of Ce:YAG doping effect on thermal aging for high-power phosphor-converted white-light-emitting diodes. IEEE 9, 367–370 (2009)
S. Fujita, S. Tanabe, Glass-ceramics and solid-state lighting. Appl. Glass Sci. 6, 356–363 (2015)
D.Q. Chen, W.D. Xiang, X.J. Liang et al., Advances in transparent glass–ceramic phosphors for white light-emitting diodes—a review. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 35(3), 859–869 (2014)
N.S. Sawala, S.K. Omanwar, Near-infrared DC approach by Bi3+-Yb3+ co-doped YAG phosphor. Res. Chem. Intermed. 43(2), 693–702 (2017)
N.S. Sawala, P.R Somani, S.K. Omanwar, Near-infrared downconversion in Ce3+-Yb3+ co-doped YAG. J. Mater. Sci. 1(28), 142–147 (2016)
N.S. Sawala, C.B. Palan, A.O. Chauhan et al., Photoluminescence properties of mixed fuel combustion synthesized Ce3+ ions doped Y3Al5O12 phosphor. Opt. Int. J. Light Electron Opt. 127(12), 5120–5123 (2016)
N.S. Sawala, S.K. Omanwar, Spectral downshifting from blue to near infer red region in Ce3+-Nd3+ co-doped YAG phosphor. Infrared Phys. Technol. 77, 480–484 (2016)
Y. Narukawa et al., Phosphor-conversion white light emitting diode using InGaN near-ultraviolet chip. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 41(4A), L371 (2002)
J.H. Yum, S.S. Kim, Y.E. Sung, Y3Al5O12:Ce0.05 phosphor coatings on a flexible substrate for use in white light-emitting diodes. Colloids Surf. A 251(1), 203–207 (2004)
S. Fujita, S. Yoshihara, A. Sakamoto, S. Yamamoto, S. Tanabe. YAG glass-ceramic phosphor for white LED (I): background and development. Proc. SPIE 5941, 594111 (2005)
S. Tanabe, S. Fujita, S. Yoshihara, A. Sakamoto, S. Yamamoto. YAG glass-ceramic phosphor for white LED (II): luminescence characteristics. Proc. SPIE 5941, 594112 (2005)
N.V. Nikonorov, E.V. Kolobkova, V.A. Aseev et al., Inorganic phosphors in lead–silicate glass for white LEDs. Opt. Spectrosc. 121(3), 379–383 (2016)
C. Zhu, Y. Yang, X. Liang et al., Rare earth ions doped full-color luminescence glasses for white LED. J. Lumin. 126(2), 707–710 (2007)
Z. Yan, L. Sheng, X. Hong-Jie et al., Preparation and performance of Ce:YAG phosphor-in-glass. J. Inorg. Mater. 30(6), 588–592 (2015)
K. Han, S.H. Lee, Y.G. Choi et al., Improved color rendering index and thermal stability of white LEDs with phosphor-in-glass using the SiO2-B2O3-ZnO-Na2O glass system. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 445, 77–80 (2016)
K. Damak, C. Rüssel, R. Maâlej, White light generation from Dy3+ doped tellurite glass. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 134, 55–63 (2014)
M.K. Hwang, I.G. Kim, Y.K. Jung et al., The study of optical properties as glass composition of Bi2O3-based glass/phosphor mixed paste. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 1(10), 7657–7663 (2015)
J. Zou, B.B. Yang, X.L. Qian, F.C. Wang, S.M. Zhu, J.R. Li, Effect of Al/Ga substitution on photoluminescence and chromatic properties of Y3Al5–XO12:Ce3+ phosphor. J. Mater. Sci. 27, 8074–8079 (2016)
S.H. Liu, D.H. Wang, C.H. Pan, Analysis of X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (Science Press of China, Beijing, 1988)
L.M. Wang, L.Q. Zhang, Y.X. Huang et al., Application of XPS in semi-quantitative estimation of Ce3+ in YAG:Ce3+ phosphor. J. East China Univ. Sci. Technol. 41(4), 484–488 (2015)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51302171), Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (14500503300), Shanghai Cooperative Project (Shanghai CXY-2013-61).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Zou, J., Li, Y. et al. The study of luminescence properties on Ce:YAG phosphor in glass co-sintered at different temperatures. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 28, 16633–16638 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-7574-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-7574-2