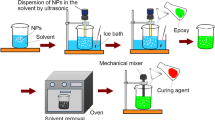
Abstract
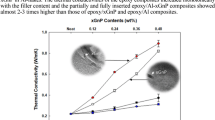
The demands for high performance electronic devices have been increasing recently. This continuous demand simultaneously put forward stringent requirements for effective thermal management solutions. In this study, improved thermal and mechanical properties of epoxy composites consisting of milled carbon fiber (MCF) and polyhedral aluminium oxide (Al2O3) fillers have been reported. By adding 14.5 wt% MCF and 60 wt% Al2O3 particles into epoxy, the maximum thermal conductivity reached were 3.3 and 7.9 times that of neat epoxy respectively. To further improve the composite thermal conductivity, a mixture of the two fillers was utilized. Milled carbon fiber with high aspect ratio enables it to act as heat conducting bridges among 3-D Al2O3 irregular particles; contributing considerably to the formation of a more efficient percolating network for heat flow. This resulted in an exceptionally high thermal conductivity with relatively lower filler content. A thermal conductivity of ten times that of neat epoxy was obtained with 42 wt% Al2O3 + 8 wt% MCF thus not only break the bottleneck of further improving the thermal conductivity of epoxy composite but also broaden the application of MCF in the field of thermal management solutions.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.W. Xu, K.S. Moon, C. Tison, C.P. Wong, IEEE Trans. Adv. Packag. 29, 295–305 (2006)
H. Im, J. Kim, Carbon 49, 3503–3511 (2011)
S. Sun, S. Chen, X. Luo, Y. Fub, L. Ye, J. Liu, Microelectron. Reliab. 56, 129–135 (2016)
E.S. Lee, S.M. Lee, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 91, 1169–1174 (2008)
Y. Zhou, H. Wang, L. Wang, K. Yu, Z. Lin, Li He, Y. Bai, Mater. Sci. Eng. B 177, 892–896 (2012)
A. Balakrishnan, M.C. Saha, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 528, 906–913 (2011)
Q. Wang, J. Dai, W. Li, Z. Wei, J. Jiang, Compos. Sci. Technol. 68, 1644–1648 (2008)
G. Wu, Y. Cheng, Y. Ren, Y. Wang, Z. Wang, H. Wu, J. Alloys Compd. 652, 346–350 (2015)
J.N. Coleman, U. Khan, W.J. Blau, Y.K. Gun’ko, Carbon 44, 1624–1652 (2006)
B. Arash, Q. Wang, V. K. Varadan, Sci. Rep. 4, 1–8 (2014)
A. Shah, Y. Wang, H. Huang, L. Zhang, F. Xue, Y. Duan, X. Don, Z. Zhang, Compos. Struct. 131, 1132–1141 (2015)
H. Wu, G. Wu, L. Wang, Powder Technol. 269, 443–451 (2015)
H. Im, Y. Hwang, J.H. Moon, S.H. Lee, J. Kim, Compos. A 54, 159–165 (2013)
A. Agrawal, A. Satapathy, Int. J. Therm. Sci. 89, 203–209 (2015)
M.R. Zakaria, H.Md.. Akil, M.H.A. Kudus, S.S.Md. Saleh, Compos. A 66, 109–116 (2014)
C.C. Teng, C.C.M. Maa, K.C. Chiou, T.M. Lee, Compos. B 43, 265–271 (2012)
Y. Yao, X. Zeng, K. Guo, R. Sun, J.B. Xu, Compos. A 69, 49–55 (2015)
J.H. Lee, K.Y. Rhee, S.J. Park, Compos. A 42, 478–482 (2011)
S. Chandrasekaran, C. Seidel, K. Schulte, Eur. Polym. J. 49, 3878–3888 (2013)
H. Chen, V.V. Ginzburg, J. Yang, Y. Yang, W. Liu, Y. Huang, L. Du, B. Chen, Prog. Polym. Sci. 59, 41–85 (2016)
T. Zhou, X. Wang, P. Cheng, T. Wang, D. Xiong, X. Wang, Exp. Polym. Lett. 7, 585–594 (2013)
S.Y. Mun, H.M Lim, H. Ahn, D.J. Lee, Macromol. Res. 22, 613–617 (2014)
H. Rahmani, S.H.M. Najafi, S.S. Matin, A. Ashori, Polym. Eng. Sci. 54, 2676–2682 (2014)
Y. Shi, X. Feng, H. Wang, X. Lu, J. Mater. Sci. 42, 8465–8469 (2007)
M.B. Kilfoil, R.A. Hesby, G.B. Pelleu, J. Prosthet. Dent. 50, 40–43 (1983)
B.K. Daniels, N.K. Harakas, Nat. Phys. Sci. 231, 41–42 (1971)
Ravikumar, M.S.S. Prasad, IJSRP 4, 1–7 (2014)
A. S.G. Kuzak, Shanmugam. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 73, 649–658 (1999)
K. Kim, J. Kim, Ceram. Intern. 40, 5181–5189 (2014)
B.J. Ash, L.S. Schadler, R.W. Siegel, Mat. Lett. 55, 83–87 (2002)
M. Xiong, G. Gu, B. You, L. Wu, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 90, 1923–1931 (2003)
Y. Sun, Z. Zhang, K.S. Moon, C.P. Wong, J. Polym. Sci. B 42, 3849–3858 (2004)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank USM for the PRGS (1001/PFIZIK/846074) funding, OSRAM Optosemiconductors (Malaysia) Sdn. Bhd. and OSRAM Optosemiconductors GmbH, Regensburg, Germany for characterization facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the co-authors have seen and agreed with the contents of the manuscript and there is no financial interest to report. We certify that the submission is the original work by us and is not under review in any other publication. We also would like to justify that we do not have any conflict of interest to declare.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Permal, A., Devarajan, M., Hung, H.L. et al. Improved thermal and mechanical properties of aluminium oxide filled epoxy composites by reinforcing milled carbon fiber by partial replacement method. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 28, 13487–13495 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-7188-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-7188-8