Abstract
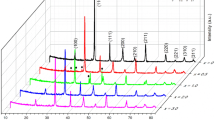
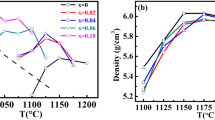
Lead-free 0.912Ba0.97TiO3–0.088(Bi0.5Na0.5)TiO3–xTa2O5 (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.005) ceramics with positive temperature coefficient of resistivity (PTCR) were prepared by solid reaction sintering of high-purity metal oxides and carbonates reagents. The doping effect of Ta5+ ions on the microstructure and electrical properties of the samples was investigated. X-ray diffraction analysis indicated that all the samples were of a single tetragonal perovskite structure with the calculated c/a value first increased and then decreased with increasing x. The Raman shift at 305 cm−1 became strong firstly and then declined, and the broad band at 722 cm−1 narrowed initially and then broadened with the increase in Ta5+ content. The Curie temperature raised first and then decreased, presenting the highest value up to 170 °C for the samples with x = 0.001. Moreover, after the incorporation of Ta5+ ions, the PTCR (defined by the resistivity jump with the ratio of maximum to minimum ones) decreased first and then increased, presenting the best PTCR performance for the samples with x = 0.005. And with increasing x, the room temperature resistivity decreased first and then increased, displaying the lowest room temperature resistivity for the samples with x = 0.003.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Shimada, K. Touji, Y. Katsuyama, H. Takeda, T. Shiosaki, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 27, 3877 (2007)
L.F. Chen, T.Y. Tseng, IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Manuf. Technol. A 19, 423 (1996)
H. Takeda, T. Shimada, Y. Katsuyama, T. Shiosaki, J. Electroceram. 22, 263 (2009)
W.R. Huo, Y.F. Qu, Sens. Actuators A 128, 265 (2006)
Q.B. Yuan, Y.P. Pu, J.F. Wei, J. Electroceram. 30, 98 (2013)
Y.P. Pu, J.F. Wei, Y.Q. Mao, J.F. Wang, J. Alloy. Compd. 498, L5 (2010)
M.M. Yang, Z.J. Peng, C.B. Wang, X.L. Fu, Ceram. Int. 42, 17792 (2016)
H.D. Wu, Y.P. Pu, Z. Wang, K. Chen, Mater. Lett. 76, 222 (2012)
H. Hakeda, Y. Hoshi, T.K. Kinoshita, T. Shishido, T. Nishida, T. Shiosaki, Ceram. Int. 34, 2073 (2008)
J.F. Wei, Y.P. Pu, Y.Q. Mao, G.D. Wu, J. Mater. Sci. 22, 551 (2010)
H.L. Li, J.N. Kang, F. Guo, Y.F. Qu, D.A. Yang, Ceram. Int. 39, 7589 (2013)
C.M. Valot, N. Floquet, J.C. Niepce, Key Eng. Mater. 132–136, 1127 (1997)
C. Ma, X. Tan, E. Dul’kin, M. Roth, J. Appl. Phys. 8, 04105 (2010)
C. Ma, X. Tan, Solid State Commun. 150, 1497 (2010)
Q.B. Yuan, Y.P. Pu, Ceram. Int. 39, 3507 (2013)
J.J. Zhao, Y.P. Pu, P.P. Zhang, L. Cheng, S.J. Li, L. Feng, Ceram. Int. 41, 4735 (2015)
A. Scalabrin, A.S. Chaves, D.S. Shin, S.P.S. Porto, Phys. Status Solidi 79, 731 (1977)
L.H. Robins, D.L. Kaiser, L.D. Rotter, P.K. Schenck, J. Appl. Phys. 76, 74 (1994)
F. Zhang, X.W. Zhu, Q. Xu, W.Z. Jiang, X. Zhou, Ferroelectrics 404, 213 (2010)
E. Brzozowski, M.S. Castro, C.R. Foschini, B. Stojanovic, Ceram. Int. 28, 773 (2002)
M.L. Liu, D.A. Yang, Y.F. Qu, J. Alloy. Compd. 508, 559 (2010)
J.Q. Qi, Z.L. Gui, Y.L. Wang, Q. Zhu, Y.J. Wu, L.T. Li, Ceram. Int. 28, 141 (2002)
Z.C. Li, H. Zhang, X. Zou, B. Bergman, Mater. Sci. Eng. B 116, 34 (2005)
M.L. Liu, D.A. Yang, Y.F. Qu, J. Alloy. Compd. 496, 449 (2010)
G.A. Smolenskii, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 28, 26 (1970)
Y.P. Pu, H.D. Wu, J.F. Wei, Sens. Actuators A 173, 158 (2012)
B. Li, Inorganic Dielectric Material, 1st edn. (National Defence Industry Press, Beijing, 1980), p. 263
Y.P. Pu, H.D. Wu, J.F. Wei, B. Wang. J. Mater. Sci. 22, 1479 (2011)
S.L. Leng, G.R. Li, L.Y. Zheng, W. Shi, Y. Zhu, J. Mater. Sci. 24, 431 (2013)
H.T. Langhammer, D. Makovec, Y.P. Pu, H.P. Abicht, M. Drofenik, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 26, 2899 (2006)
D.C. Sinclair, A.R. West, J. Appl. Phys. 66, 3850 (1989)
D.C. Sinclair, A.R. West, J. Mater. Sci. 29, 6061 (1994)
J.Q. Qi, Z.L. Gui, Y.J. Wu, L.T. Li, Sens. Actuators A 93, 84 (2001)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 11674035, 61274015, and 11274052), and Excellent Adviser Foundation in China University of Geosciences from the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, M., Wang, C., Peng, Z. et al. Doping effect of Ta5+ ions on microstructure and electrical properties of BaTiO3–(Bi0.5Na0.5)TiO3 ceramics with positive temperature coefficient of resistivity. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 28, 10589–10595 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-6833-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-6833-6