Abstract
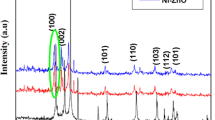
Nowadays, tremendous increase in environmental issue is an alarming threat to the ecosystem. Influence of pH is the major concern for the application of ZnO nanoparticles. These nanoparticles with different tuning defects were prepared by simple combustion method using Zn nitrate as precursor and glucose as fuel and oxidizer. This paper reports the effect of four different pH values 5, 7, 9 and 11 to synthesize ZnO nanoparticles namely PZ1-PZ4. Prepared samples were characterized by several techniques including XRD, FESEM, FTIR, UV Vis, PL, LCR and Raman spectroscopy. These detailed characterization study confirmed that the prepared ZnO nanoparticles are possessing well crystalline and hexagonal wurtzite structure. Interestingly, it was observed that influence of pH greatly effects on morphological and electrical properties. The average grain size is in the range of 40–80nm. Raman spectroscopy exhibited a sharp and strong mode near 487 cm−1 which further confirmed the well crystalline and hexagonal wurtzite structure. Furthermore, ZnO as photocatalyst exhibited photocatalytic degradation towards direct red (DR-31) dye. From the photocatalytic experiment it was observed that degradation percentage increases with increasing pH value up to 9 and thereafter percentage degradation was decreased. Thus an ideal pH value of prepared nanoparticles is pH-9 exhibiting almost completes degradation only in 75 min under UV irradiation. Kinetic studied revealed that all the samples follows first order rate constant and for pH-9 rate constant is 0.04075 min−1.












Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
15 February 2018
The original version of this article unfortunately contained an error in affiliation of the authors. The updated affiliation has been corrected with this erratum.
References
Y. Sha, I. Mathew, Q. Cui, M. Clay, F. Gao, X.J. Zhang, Z. Gu, Rapid degradation of azo dye methyl orange using hollow cobalt nanoparticles, Chemosphere 144, 1530–1535 (2016). doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.10.040
M. Hussain, H. Sun, S. Karim, A. Nisar, M. Khan, H. Munawar, I. Mashkoor, Noble metal nanoparticle-functionalized ZnO nanoflowers for photocatalytic degradation of RhB dye and electrochemical sensing of hydrogen peroxide. J. Nanoparticle Res. (2016). doi:10.1007/s11051-016-3397-y.
S. Bhatia, N. Verma, R.K. Bedi, Optical application of Er-doped ZnO nanoparticles for photodegradation of direct red – 31 dye. Opt. Mater. (Amst). 62, 392–398 (2016). doi:10.1016/j.optmat.2016.10.013.
S. Ito, T.N. Murakami, P. Comte, P. Liska, C. Grätzel, M.K. Nazeeruddin, M. Grätzel, Fabrication of thin film dye sensitized solar cells with solar to electric power conversion efficiency over 10%. Thin Solid Films. 516, 4613–4619 (2008). doi:10.1016/j.tsf.2007.05.090
T. Zhang, R. Liang, L. Dong, J. Wang, J. Xu, C. Pan, Wavelength tunable infrared light emitting diode based on ordered ZnO nanowire / Si 1−x Ge x alloy heterojunction. Nano Res. (2015). doi:10.1007/s12274-015-0774-2.
A.S. Kazemi, R. Afzalzadeh, M. Abadyan, ZnO nanoparticles as ethanol gas sensors and the effective parameters on their performance. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 29, 393–400 (2013). doi:10.1016/j.jmst.2013.03.009.
M.I.N. Zhang, J. Yang, S. Dai, P. He, Z. Zhang, Effect of Au deposition on photocatalytic activity of ZnO nanoparticles for co oxidation. Surf. Rev. Lett. 12, 749–752 (2005)
S. Bhatia, R.K. Bedi, Morphological, electrical and optical properties of zinc oxide films grown on different substrates by spray pyrolysis technique. Nanostruct. Thin Film III 7766, 776610-776610 (2010). doi:10.1117/12.863878.
R. Bel-hadj-tahar, A.B. Mohamed, Sol-gel processed indium-doped zinc oxide thin films and their electrical and optical properties, New J. Glas. Ceram. 4, 55–65 (2014). doi:10.4236/njgc.2014.44008.
H. Bahadur, A.K. Srivastava, R.K. Sharma, S. Chandra, Morphologies of sol-gel derived thin films of zno using different precursor materials and their nanostructures. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2, 469–475 (2007). doi:10.1007/s11671-007-9089-x
K. Sivakumar, V.S. Kumar, N. Muthukumarasamy, M. Thambidurai, T.S. Senthil, Influence of pH on ZnO nanocrystalline thin films prepared by sol–gel. Bull. Mater. Sci. 35, 327–331 (2012)
A. El Manouni, F.J. Manjon, M. Perales, M. Mollar, B. Mari Soucase, M.C. Lopez, J.R. Ramos Barrado, Effect of thermal annealing on ZnO:Al thin films grown by spray pyrolysis. Superlattices Microstruct. 42, 134–139 (2007). doi:10.1016/j.spmi.2007.04.005.
N. Srinatha, Y.S. No, V.B. Kamble, S. Chakravarty, N. Suriyamurthy, B. Angadi, A.M. Umarji, W.K. Choi, Effect of RF power on the structural, optical and gas sensing properties of RF-sputtered Al doped ZnO thin films. RSC Adv. 6, 9779–9788 (2016). Doi:10.1039/C5RA22795J.
S. Rajendiran, A.K. Rossall, A. Gibson, E. Wagenaars, Modelling of laser ablation and reactive oxygen plasmas for pulsed laser deposition of zinc oxide. Surf. Coatings Technol. 260, 417–423 (2014). Doi:10.1016/j.surfcoat.2014.06.062.
J. Zhang, L. Sun, J. Yin, H. Su, C. Liao, Control of ZnO morphology via a simple solution route control of ZnO morphology via a simple solution route. Chem. Mater. 14, 4172–4177 (2002). Doi:10.1021/cm020077h.
Y. Li, L. Xu, X. Li, X. Shen, A. Wang, Effect of aging time of ZnO sol on the structural and optical properties of ZnO thin films prepared by sol-gel method, Appl. Surf. Sci. 256 4543–4547 (2010). Doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2010.02.044
G.A. Kumar, M.V.R. Reddy, K.N. Reddy, Effect of annealing on ZnO thin films grown on quartz substrate by RF magnetron sputtering. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 365, 12031 (2012). doi:10.1088/1742-6596/365/1/012031
J. Morales, J. Solis, W.L. Estrada, Doping effects on the response of thin film ZnO gas sensor to ethanol vapour. Superf. Y Vacio. 9, 245–247 (1999).
I. Kazeminezhad, A. Sadollahkhani, Influence of pH on the photocatalytic activity of ZnO nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. (2016). doi:10.1007/s10854-016-4284-0.
R. Ikono, P.R. Akwalia, W.B. Siswanto Wahyu, A. Sukarto, N.T. Rochman, Effect of PH variation on particle size and purity of nano zinc oxide synthesized by Sol-Gel method, (2012) 10–14.
H. Sutanto, S. Wibowo, I. Nurhasanah, E. Hidayanto, H. Hadiyanto, Ag doped ZnO thin films synthesized by spray coating technique for methylene blue photodegradation under UV irradiation. Int. J. Chem. Eng. 2016, 6 (2016)
P. Pradhan, J.C. Alonso, M. Bizarro, Photocatalytic performance of ZnO: Al films under different light sources. Int. J. Photoenergy 2012 (2012). doi:10.1155/2012/780462
R. Kumar, A. Umar, G. Kumar, M.S. Akhtar, Y. Wang, S.H. Kim, Ce-doped ZnO nanoparticles for efficient photocatalytic degradation of direct red-23 dye. Ceram. Int. 41, 7773–7782 (2015). Doi:10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.02.110.
S.B. Rana, A. Singh, S. Singh, Characterization and optical studies of pure and Sb doped ZnO nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanoelectron. Mater. 6, 45–57 (2013).
S. Bhatia, N. Verma, R.K. Bedi, Effect of aging time on Gas sensing properties and photocatalytic efficiency of dye on In-Sn co-doped ZnO nanoparticles. Mater. Res. Bull (2016). Doi:10.1016/j.materresbull.2016.12.011
M.J. Chithra, M.S.K. Pushpanathan, Effect of pH on crystal size and photoluminescence property of ZnO nanoparticles prepared by chemical precipitation method. Acta Metall. Sin. (2015). Doi:10.1007/s40195-015-0218-8.
K.L. Foo, M. Kashif, U. Hashim, M.E. Ali, Fabrication and characterization of ZnO thin films by sol-gel spin coating method for the determination of phosphate buffer saline concentration. Curr. Nanosci. 9, 288–292 (2013). Doi:10.2174/1573413711309020020.
T.A.J.M. Khan, T. Bibi, B. Hussain, Synthesis and optical study of heat-treated ZnO nanopowder for optoelectronic applications. Bull. Mater. Sci. 38, 1851–1858 (2015).
C. Jayachandraiah, K.S. Kumar, G. Krishnaiah, N.M. Rao, Influence of Dy dopant on structural and photoluminescence of Dy-doped ZnO nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 623, 248–254 (2015). doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2014.10.067
D.S. Dhawale, D.P. Dubal, A.M. More, T.P. Gujar, C.D. Lokhande, Room temperature liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) sensor. Sens. Actuat. B Chem. 147, 488–494 (2010). doi:10.1016/j.snb.2010.02.063
C. Jayachandraiah, G. Krishnaiah, Erbium induced raman studies and dielectric properties of Er-doped ZnO nanoparticles, Adv. Mater. Lett. Adv. Mater. Lett. 6, 743–748 (2015). doi:10.5185/amlett.2015.5801
S. Bhatia, N. Verma, A. Mahajan, R.K. Bedi, Characterization of ZnO films based sensors prepared by different techniques, Appl. Mech. Mater. 772 (2015) 50–54. doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.772.50
N. Sobana, K. Thirumalai, Kinetics of solar light assisted degradation of direct red 23 on activated carbon-loaded zinc oxide and influence of operational parameters, Can. Chem. Trans. 4, 77–89 (2016). doi:10.13179/canchemtrans.2016.04.01.0258.
Acknowledgements
Authors are grateful to U.G.C, New Delhi for providing financial assistance for carrying out project (F.No. 42–770/2013). Thanks due to the IKGPTU Kapurthala, Director, R.S.I.C, Panjab University Chandigarh, for providing SEM and XRD facility.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
A correction to this article is available online at https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-8759-z.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Verma, N., Bhatia, S. & Bedi, R.K. Role of pH on electrical, optical and photocatalytic properties of ZnO based nanoparticles. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 28, 9788–9797 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-6732-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-6732-x