Abstract
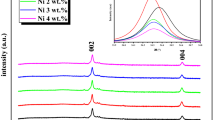
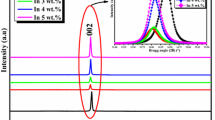
In the present study, tin doped ZnO thin films (ZnO:Sn) at different contents (0–3 wt%) were deposited onto glass substrates by RF magnetron sputtering using a powder compacted target at room temperature. The effect of Sn concentration on the structural, optical and electrical properties of the ZnO:Sn thin films were investigated. The X-ray diffraction analysis shows that the pure ZnO thin film exhibits a strong intensity of the (002) peak indicating a preferential orientation along the c-axis. For Sn doped ZnO thin films, there is a change in the orientation from the (002) plane to the (101) one. The undoped ZnO thin films have transmittance 85% in the visible range and slightly increased for 0.5 wt% of Sn, while it get decreased with further increasing the Sn doping concentration. The optical band gap energy get increased with increasing the doping concentration. Moreover, the electrical conductivity and conduction mechanism are also studied by impedance spectroscopy in the frequency range of 1KHz–13 MHz at various temperatures (633–743 K). The AC conductivity in ZnO thin films increased with angular frequency. The frequency exponent S decreases with increasing temperature. Such behavior suggests that the correlated barrier hopping (CBH) model may be suitable to explain the conduction mechanism in ZnO thin films. The activation energy values calculated from angular frequency and DC conductivity are in good agreement confirming that the conduction mechanism is thermally activated by hopping between localized states.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.B. Baxter, E.S. Aydil, Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 90, 607–622 (2006)
S.T. Shishiyanu, T.S. Shishiyanu, O.I. Lupan, Sens. Actuators B 107, 379–386 (2005)
T. Ootsuka, Z. Liu, M. Osamura, Y. Fukuzawa, R. Kuroda, Y. Suzuki, N. Otogawa, T. Mise, S. Wang, Y. Hoshino, Y. Nakayama, H. Tanoue, Y. Makita, Thin Solid Films 476, 30–34 (2005)
F. Ye, X. Cai, F. Dai, D. Zhang, P. Fan, L. Liu, Physica B 407, 64–67 (2012)
A. Iqbal, A. Mahmood, T. Muhammad Khan, E. Ahmed, Prog. Nat. Sci. 23(1), 64–69 (2013)
V. Ganesh, I.S. Yahia, S. AlFaify, M. Shkir, J. Phys. Chem. Solid 100, 115–125 (2017)
S. Ameen, M.S. Akhtar, H.-K. Seo, Y.S. Kim, S.H. Shim, Chem. Eng. J. 187, 351–356 (2012)
P. Chrysicopoulou, D. Davazoglou, C. Trapalis, G. Kordas, Thin Solid Films 323, 188 (1998)
M. Takeuchi, T. Itoh, H. Nagasaka, Thin Solid Films 51, 83 (1978)
K.S. Yeung, Y.W. Lam, Thin Solid Films 109, 169 (1983)
C. Manoharan, G. Pavithra, S. Dhanapandian, P. Dhamodharan, Spectrochim. Acta A 149, 793–799 (2015)
A. Mhamdi, B. Ouni, A. Amlouk, K. Boubaker, M. Amlouk, J. Alloys Compd. 582, 810–822 (2014)
B.E. Warren, X-ray Diffraction. (Dover Publications, New York, 1990)
O.S. Heavens, Optical Properties of Thin Solid Films. (Butterworths, London, 1950)
R. Swanepoel, J. Phys. E 16, 1214 (1983)
S. Lemlikchi, S. Abdelli-Messaci, S. Lafane, T. Kerdja, A. Guittoum, M. Saad, Appl. Surf. Sci. 256, 5650–5655 (2010)
T.S. Moss, Proc. Phys. Soc. B 67, 775–782 (1954)
M. Caglar, S. Ilican, Y. Caglar, F. Yakuphanoglu, J. Mater. Sci. 19, 704 (2008)
R.T. Chen, D. Robinson, Appl. Phys. Lett. 60, 1541 (1992)
N. Chahmal, T. Souier, A. Mokri, M. Bououdina, M.S. Aida, M. Ghers, J. Alloys Compd. 593, 148–153 (2014)
T. Nagata, T. Shimura, A. Ashida, N. Fujimura, TaichiroIto. J. Cryst. Growth 237–239, 533–537 (2002)
B. Khalfallah, F. Chaabouni, G. Schmerber, A. Dinia, M. Abaab, J. Mater. Sci. (2016). doi: 10.1007/s10854-016-5494-1
P.N. Butcher, P.L. Morys, J. Phys. C 6, 2147 (1973)
L.J. Meng, Y.M. Adritsck, M.P. Dos Santos, Vacuum 45, 19 (1994)
A. Ghosh, Phys. Rev. B 42, 5665–5676 (1990)
J. Han, M. Shen, W. Cao, Appl. Phys. Lett. 82, 67 (2003)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Andolsi, Y., Chaabouni, F. & Abaab, M. Sn doping effects on properties of ZnO thin films deposited by RF magnetron sputtering using a powder target. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 28, 8347–8358 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-6551-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-6551-0