Abstract
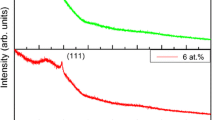
Various properties of MnS thin films deposited on glass substrate by a simple and novel nebulized spray technique are described in this work. The thickness of MnS thin film increases linearly with increase in molar ratio and substrate temperature. From the X-ray diffraction study, the impact of molar ratio and substrate temperature is well pronounced in the formation of well crystalline MnS thin films. The SEM images showed more grains formation and well defined compact nature composed of single type densely packed grains. The AFM images exhibited that all the films show homogenous surface with pinhole free in nature. The decrease in average transmittance of films with increasing substrate temperature and molar ratio are due to the influence of grain growth induced by the enhancement in crystalline behavior of the films. It is observed that the energy band gaps of MnS thin films are decreased with increasing substrate temperature and molar ratio. The intensity of emission peaks increased with increasing solution concentration and substrate temperature owing to the change in surface area to volume ratio of MnS micro/nano-structures with molar ratio. All the Raman peaks showed the vibrations of Mn–S bonds. The magnetic study confirmed the ferromagnetic behavior of MnS films at 5 K, whereas the film exhibits paramagnetic behavior at 300 K.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Sobhani, M. Salavati-Niasari, Superlattices Microstruct. 59, 1–12 (2013)
A. Sobhani, M. Salavati-Niasari, M. Sobhani, Mater. Sci. Semcond. Process. 16, 410 (2013)
M. Sobhani, M. Salavati-Niasari, S.M. Hosseinpour-Mashkani, J. Clust. Sci. 23, 1143 (2012)
D. Ghanbari, M. Salavati-Niasari, M. Sabet, J. Clust. Sci. 23, 1081 (2012)
H. Emadi, M. Salavati-Niasari, F. Davar, Polyhedron 31, 438 (2012)
P.G. Sheikhiabadi, F. Davar, M. Salavati-Niasari, Inorg. Chim. Acta 376, 271 (2011)
M. Shakouri-Arani, M. Salavati-Niasari, New J. Chem. 38, 1179 (2014)
P.G. Sheikhiabadi, M. Salavati-Niasari, F. Davar, Mater. Lett. 71, 168 (2012)
P.G. Sheikhiabadi, M. Salavati-Niasari, F. Davar, Superlattices Microstruct. 53, 76 (2013)
O. Goede, W. Heimbrodt, Phys. Stat. Sol. B 146 11 (1988)
H. Sato, T. Mihara, A. Furuta, Y. Ueda, H. Namatame, M. Taniguchi, J. Electron Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 78, 87 (1996)
D.R. Duffman, R.L. Wild, Phys. Rev. 156, 989 (1967)
R. Tappero, A. Lichanot, Chem. Phys 236, 97 (1998)
M. Okajima, T. Tohda, J. Cryst. Growth 117, 810 (1992)
S. Biswas, S. Kar, S. Chaudhuri, J. Cryst. Growth 284, 129 (2005)
T. Dedova, M. Krunks, I. Gromyko, V. Mikli, I. Sildos, K. Utt, T. Unt, Phys. Status Solidi A 211, 514 (2014)
Y. Ji-Beom, L.F. Alan, R.H. Bube, J. Appl. Phys. 68, 4694 (1990)
G.B. Williamson, R.C. Smallman, Phil. Mag 1, 34 (1956)
B. Lonnberg, T. Lundstrom, J. Mater. Sci. 29, 2993 (1994)
W. Qin, T. Nagase, Y. Umakoshi, J.A. Szpunar, J. Phys 23, 6217 (2007)
E. Ulutas, F. Guneri, G. Kirmizigul, F.Gode Altindemir, C. Gumus, Mater. Chem. Phys. 138, 817 (2013)
R. Tamrakar, M. Ramrakhiani, B.P. Chandra, Open Nanosci. J. 2, 12 (2008)
J. Tauc, R. Grigorovici, A. Vancu, Phys. Stat. Sol. 15, 627 (1966)
Y. Shi, F. Xue, C. Li, Q. Zhao, Z. Qu, Mater. Res. Bull. 46, 483 (2011)
D. Lokhande, K.M. Gadave, Turk. J. Phys. 18, 83 (1994)
K. Otto, A. Katerski, A. Mere, O. Volobujeva, M. Krunks, Thin Solid Films 519, 3055 (2011)
M.R.I. Chowdhury, J. Podder, A.B.M.O. Islam, Cryst. Res. Technol. 46, 267 (2011)
A. Changhua, K. Tang, X. Liu, F. Li, G. Zhou, Y. Qian, J. Cryst. Growth 252, 575 (2003)
R. Sivakumar, K. Punitha, C. Sanjeeviraja, R. Gopalakrishnan, Mater. Lett. 121, 141 (2014)
Y. Zhang, Z. Zhang, S. Wang, X. Ma, Y. Qian, Mater. Chem. Phys. 97, 365 (2006)
Z.F. Du, C.Z. Huang, Wang, X. Meng, G. Chen, J. Appl. Phys. 102, 113906 (2007)
D. Chen, H. Quan, X. Luo, S. Luo. Scr. Mater. 76, 1 (2014)
P. Vaquerio, M.P. Crosnier-Lopez, M.A.L. Quintela, J. Solid State Chem 126, 161 (1996)
Y. Yanmin, J. Jing, L. Liangchao, X. Yunlong, J. Rare Earths 25, 228 (2007)
M. Dekun, S. Huang, L. Zhang, Chem. Phys. Lett. 462, 96 (2008)
J. Cuda, T. Kohout, J. Filip, J. Tucek, A. Kosterov, J. Haloda, R. Skala, E. Santala, I. Medrik, R. Zboril, Am. Mineral. 98, 1550 (2013)
Acknowledgements
One of the authors M. Girish gratefully acknowledges the University Grants Commission (UGC), New Delhi, India for the financial support under UGC-BSR Research Fellowship Scheme. The authors would like to thank the UGC-DAE Consortium for Scientific Research, Indore Centre, India for providing the AFM and Raman facilities. In addition, R.S gratefully acknowledges the UGC, New Delhi, India for the financial support under Major Research Project (Ref.: F.No.42–818/2013(SR), dt.22.03.2013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Girish, M., Dhandayuthapani, T., Sivakumar, R. et al. Substrate temperature and molar ratio induced changes on the properties of nebulized spray deposited MnS films. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 28, 6741–6753 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-6370-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-6370-3