Abstract
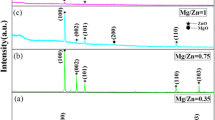
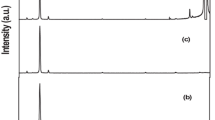
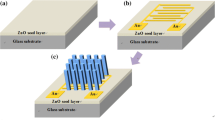
This study successfully synthesized the first core–shell ZnO/Mg doped ZnO (ZnO:Mg) nanorod arrays on p-silicon (100) substrates using the simple hydrothermal method. The vertically aligned synthesized ZnO nanorod arrays served as a template for the growth of 1.75 atomic% Mg doped ZnO. The morphological, structural, and optical features of the nanorod arrays were characterized using microscopic and spectroscopic techniques. The FESEM micrographs showed that diameter of the core is approximately 50 nm encapsulated by shell with thickness of about 30 nm. The low-resolution transmission electron microscopy images showed distinctive morphologies of the core and shell layers. Raman spectroscopy measurements provided structural evidence for the formation of a core–shell ZnO/ZnO:Mg nanorod arrays. The photoluminescence spectra of the core–shell ZnO/ZnO:Mg exhibited an intense sharp peak near-band-edge emission with splitting at 376 and 384 nm, with very weak and negligible defect emission at around 520 nm. Increase in the intensity ratio of the IUV/IVIS emission by three confirmed the relatively enhanced optical properties compared with that of core (ZnO) nanorod arrays.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Miao, H. Zhang, Y. Zhu, Y. Yang, Q. Li, J. Li, Epitaxial growth of ZnO nanorods on electrospun ZnO nanofibers by hydrothermal method. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 23(10), 1887–1890 (2012)
S. Singh, G.R. Dillip, S. Vyas, et al., Fabrication and characterization of hydrothermally grown MgZnO nanorod films for Schottky diode applications. Microsyst. Technol. 10, 1–8 (2015)
J.J. Hassan, M.A. Mahdi, S.J. Kasim, N.M. Ahmed, H. Abu Hassan, Z. Hassan, High sensitivity and fast response and recovery times in a ZnO nanorod array/p-Si self-powered ultraviolet detector. Appl. Phys. Lett. 101(26), 2013–2016 (2012)
J.J. Hassan, M.A. Mahdi, Y. Yusof et al., Fabrication of ZnO nanorod/p-GaN high-brightness UV LED by microwave-assisted chemical bath deposition with Zn(OH)2-PVA nanocomposites as seed layer. Opt. Mater. (Amst.) 35(5), 1035–1041 (2013)
C.Y. Liu, H.Y. Xu, J.G. Ma et al., Electrically pumped near-ultraviolet lasing from ZnO/MgO core/shell nanowires. Appl. Phys. Lett. 99(6), 2012–2015 (2011)
S. Xu, Z.L. Wang, One-dimensional ZnO nanostructures: solution growth and functional properties. Nano Res. 4(11), 1013–1098 (2011)
D.N. Montenegro, A. Souissi, C. Martínez-Tomás, V. Muñoz-Sanjosé, V. Sallet, Morphology transitions in ZnO nanorods grown by MOCVD. J. Cryst. Growth 359(1), 122–128 (2012)
H.S. Al-Salman, M.J. Abdullah, RF sputtering enhanced the morphology and photoluminescence of multi-oriented ZnO nanostructure produced by chemical vapor deposition. J. Alloys Compd. 547, 132–137 (2013)
M. Asghar, K. Mahmood, I.T. Ferguson et al., Investigation of VO–Zni native donor complex in MBE grown bulk ZnO. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 28(10), 105019 (2013)
J.W. Lee, B.U. Ye, D.-Y. Kim et al., ZnO nanowire-based antireflective coatings with double-nanotextured surfaces. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 6(3), 1375–1379 (2014)
R. Shabannia, Vertically aligned ZnO nanorods on porous silicon substrates: effect of growth time. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 25(2), 95–100 (2015)
F. Zhou, W. Jing, J. Shi, Z. Jiang, Y. Cheng, K. Gao, Effects of etching parameters on ZnO nanotubes evolved from hydrothermally synthesized ZnO nanorods. Ceram. Int. 42(4), 4788–4796 (2016)
A. Di Mauro, M. Zimbone, M.E. Fragalà, G. Impellizzeri, Synthesis of ZnO nanofibers by the electrospinning process. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 42, 8–11 (2015)
X. Wei, R. Zhao, M. Shao, X. Xu, J. Huang, Fabrication and properties of ZnO/GaN heterostructure nanocolumnar thin film on Si (111) substrate. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 8(1), 112 (2013)
G. Yao, Y. Tang, Y. Fu et al., Fabrication of high-quality ZnCdO epilayers and ZnO/ZnCdO heterojunction on sapphire substrates by pulsed laser deposition. Appl. Surf. Sci. 326, 271–275 (2015)
J.P. Mathew, G. Varghese, J. Mathew, Effect of doping concentration and annealing temperature on the structural and optical properties of Zn1−xCuxO films. SOP Trans. Nano-Technol. 1(3), 1–11 (2014)
N. Guo, Y.L. Wang, X.Q. Wei, Y.X. Yu, M. Ding, X.J. Xu, Effects of Mg-contents and substrate parameters on structure and optical properties of Mg-doped ZnO nanorods fabricated by hydrothermal method. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 36, 1–8 (2016)
M.H. Habibi, E. Askari, Fabrication and spectral properties of zinc zirconate nanorod composites by sol–gel method for optical applications: effect of chloride and oxychloride precursors and sintering temperature on band gap. Synth. React. Inorg. Met. Org. Nano-Met. Chem. 45(2), 281–285 (2015)
Y. Zhang, B. Zhang, Photoluminescence performance enhancement of ZnO/MgO heterostructured nanowires and their applications in ultraviolet laser diodes. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 17(21), 13813–13820 (2015)
G.P. Li, R. Chen, D.L. Guo et al., Nanoscale semiconductor-insulator-metal core/shell heterostructures: facile synthesis and light emission. Nanoscale 3(8), 3170–3177 (2011)
K.S. Babu, A.R. Reddy, K.V. Reddy, Green emission from ZnO–MgO nanocomposite due to Mg diffusion at the interface. J. Lumin. 158, 306–312 (2015)
P. Shimpi, Y. Ding, E. Suarez, J. Ayers, P.X. Gao, Annealing induced nanostructure and photoluminescence property evolution in solution-processed Mg-alloyed ZnO nanowires. Appl. Phys. Lett. 97(10), 3–5 (2010)
M. Caglar, Y. Caglar, S. Ilican, Investigation of the effect of Mg doping for improvements of optical and electrical properties. Phys. B Condens. Matter 485, 6–13 (2016)
X. Fang, X. Wang, D. Zhao et al., Electroluminescence of ZnO nanorods/ZnMgO films/p-SiC structure heterojunction LED. Phys. E Low-dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 59, 93–97 (2014)
J. Ji, W. Zhang, H. Zhang et al., High density Si/ZnO core/shell nanowire arrays for photoelectrochemical water splitting. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 24(9), 3474–3480 (2013)
Z. Zhang, Y. Hu, F. Qin, Y. Ding, DC sputtering assisted nano-branched core–shell TiO2/ZnO electrodes for application in dye-sensitized solar cells. Appl. Surf. Sci. 376, 10–15 (2016)
A. Rivera, A. Mazady, M. Anwar, Co-axial core–shell ZnMgO/ZnO NWs. Solid State Electron. 104, 126–130 (2015)
G. Grinblat, F. Bern, J. Barzola-Quiquia, M. Tirado, D. Comedi, P. Esquinazi, Luminescence and electrical properties of single ZnO/MgO core/shell nanowires. Appl. Phys. Lett. 104(10), 1–6 (2014)
J.G. Song, J. Park, J. Yoon et al., Plasma enhanced atomic layer deposition of magnesium oxide as a passivation layer for enhanced photoluminescence of ZnO nanowires. J. Lumin. 145, 307–311 (2014)
W. Liu, Y. Liang, H. Xu et al., Heteroepitaxial growth and spatially resolved cathodoluminescence of ZnO/MgZnO coaxial nanorod arrays. J. Phys. Chem. C 114, 16148–16152 (2010)
A.M. Selman, Z. Hassan, M. Husham, Structural and photoluminescence studies of rutile TiO2 nanorods prepared by chemical bath deposition method on Si substrates at different pH values. Measurement 56, 155–162 (2014)
J.J. Hassan, Z. Hassan, H. Abu-Hassan, High-quality vertically aligned ZnO nanorods synthesized by microwave-assisted CBD with ZnO-PVA complex seed layer on Si substrates. J. Alloys Compd. 509(23), 6711–6719 (2011)
D. Polsongkram, P. Chamninok, S. Pukird et al., Effect of synthesis conditions on the growth of ZnO nanorods via hydrothermal method. Phys. B Condens. Matter 403, 3713–3717 (2008)
J. Yang, Y. Wang, J. Kong, M. Yu, H. Jin, Synthesis of Mg-doped hierarchical ZnO nanostructures via hydrothermal method and their optical properties. J. Alloys Compd. 657, 261–267 (2016)
X.Q. Meng, H. Peng, Y.Q. Gai, J. Li, Influence of ZnS and MgO shell on the photoluminescence properties of ZnO core/shell nanowires. J. Phys. Chem. C 114(3), 1467–1471 (2010)
K.V.A. Renitta, Enhanced H2 sensing performance presented by Mg doped ZnO films fabricated with a novel ITO seed layer. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 26, 3458–3465 (2015)
P. Shimpi, P.-X. Gao, D.G. Goberman, Y. Ding, Low temperature synthesis and characterization of MgO/ZnO composite nanowire arrays. Nanotechnology 20, 125608 (2009)
S. Sharma, C. Periasamy, A study on the electrical characteristic of n-ZnO/p-Si heterojunction diode prepared by vacuum coating technique. Superlattices Microstruct. 73, 12–21 (2014)
H. Benzarouk, A. Drici, M. Mekhnache et al., Effect of different dopant elements (Al, Mg and Ni) on microstructural, optical and electrochemical properties of ZnO thin films deposited by spray pyrolysis (SP). Superlattices Microstruct. 52(3), 594–604 (2012)
S. Wei, J. Lian, H. Wu, Annealing effect on the photoluminescence properties of ZnO nanorod array prepared by a PLD-assistant wet chemical method. Mater. Charact. 61(11), 1239–1244 (2010)
R. Shabannia, H.A. Hassan, Growth and characterization of aligned ZnO nanorods synthesized on porous silicon. Mater. Lett. 98, 135–137 (2013)
N. Guo, X.Q. Wei, R.R. Zhao, X.J. Xu, Preparation and optical properties of Mg-doped ZnO nanorods. Appl. Surf. Sci. 317, 400–404 (2014)
H. Chen, J. Ding, W. Guo, F. Shi, Y. Li, Violet-blue-green emission and shift in Mg-doped ZnO films with different ratios of oxygen to argon gas flow. Appl. Surf. Sci. 258(24), 9913–9917 (2012)
P. Kumar, H.K. Malik, A. Ghosh, R. Thangavel, K. Asokan, Bandgap tuning in highly c-axis oriented Zn1-xMgxO thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 102, 8–13 (2013)
S. Sharma, R. Vyas, N. Sharma et al., Highly efficient green light harvesting from Mg doped ZnO nanoparticles: Structural and optical studies. J. Alloys Compd. 552, 208–212 (2013)
R.T. Ginting, C.C. Yap, M. Yahaya, M.M. Salleh, Improvement of inverted type organic solar cells performance by incorporating Mg dopant into hydrothermally grown ZnO nanorod arrays. J. Alloys Compd. 585, 696–702 (2014)
K. Vijayalakshmi, A. Renitta, K. Karthick, Growth of high quality ZnO: Mg films on ITO coated glass substrates for enhanced H2 sensing (spray). Ceram. Int. 40(4), 6171–6177 (2014)
R. Shabannia, H. Abu-Hassan, Vertically aligned ZnO nanorods synthesized using chemical bath deposition method on seed-layer ZnO/polyethylene naphthalate (PEN) substrates. Mater. Lett. 90, 156–158 (2013)
R. Shabannia, H.A. Hassan, Growth and characterization of vertically aligned ZnO nanorods grown on porous silicon: effect of precursor concentration. Superlattices Microstruct. 62, 242–250 (2013)
J.H. Gu, L. Long, Z. Lu, Z.Y. Zhong, Optical, electrical and structural properties of aluminum-doped nano-zinc oxide thin films deposited by magnetron sputtering. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 26(2), 734–741 (2014)
O.F. Farhat, M.M. Halim, M.J. Abdullah, M.K.M. Ali, N.K. Allam, Morphological and structural characterization of single-crystal ZnO nanorod arrays on flexible and non-flexible substrates. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 6, 720–725 (2015)
Y. Wang, X. Zhao, L. Duan et al., Structure, luminescence and photocatalytic activity of Mg-doped ZnO nanoparticles prepared by auto combustion method. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 29, 372–379 (2015)
Y. Li, C. Wan, C. Chang, Y. Huang, W. Tsai, Annealing effect on the photoluminescence characteristics of ZnO-nanowires and the improved optoelectronic characteristics of p-NiO/n-ZnO nanowire UV detectors. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 54(6S1), 06FG05 (2015)
S.D. Senol, O. Ozturk, C. Terzioğlu, Effect of boron doping on the structural, optical and electrical properties of ZnO nanoparticles produced by the hydrothermal method 384 nm. Ceram. Int. 41(9), 11194–11201 (2015)
K. Huang, Z. Tang, L. Zhang et al., Preparation and characterization of Mg-doped ZnO thin films by sol–gel method (384 nm). Appl. Surf. Sci. 258(8), 3710–3713 (2012)
W. Zeng, X. Yang, M. Shang, X. Xu, W. Yang, H. Hou, Fabrication of Mg-doped ZnO nanofibers with high purities and tailored band gaps. Ceram. Int. 42(8), 10021–10029 (2016)
R. Yousefi, F.J. Sheini, M.R. Muhamad, M.A. More, Characterization and field emission properties of ZnMgO nanowires fabricated by thermal evaporation process. Solid State Sci. 12(7), 1088–1093 (2010)
P. Kumar, A. Singh, D. Pathak, L. Hromadko, T. Wagner, Structural and optical properties of sol–gel processed ZnCdMgO nanostructured films as transparent conductor. Adv. Mater. Lett. 5(10), 587–592 (2014)
K. Karthick, K. Vijayalakshmi, Influence of Mg doping on the properties of ZnO films prepared on c-cut sapphire by sputtering. Superlattices Microstruct. 67, 172–180 (2014)
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Universiti Sains Malaysia under RU Top-Down Grant (1001/CINOR/870019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Azzez, S.A., Hassan, Z. & Hassan, J.J. Identification and characteristics of core–shell ZnO/ZnO:Mg nanorods synthesized by hydrothermal method. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 27, 12618–12626 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-5394-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-5394-4