Abstract
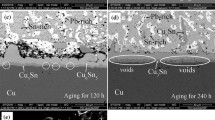
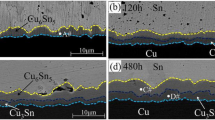
The massive spalling of CuZn IMC was mainly affected by the Zn concentration. Only when the Zn concentration was about 0.67 wt% in the solder sample during liquid-state aging, this behavior could occur. Comparing with the Sn–58Bi–0.7Zn bulk solder sample, the massive spalling phenomenon was more likely to appear in small solder ball sample. The related IMCs transformation was explained by the Cu–Sn–Zn isotherm with the diffusion path concept for the different addition of Zn in the solder sample during liquid-state aging. The average concentration distribution of Sn between the CuZn and Cu6(Sn, Zn)5 IMC layer also affected this behavior. When the aging temperature was just higher than the liquidus temperature of Sn–58Bi–0.7Zn bulk solder, the massive spalling phenomenon appeared. Trace amounts of Bi atoms in the Sn-rich layer between the CuZn and Cu6(Sn, Zn)5 could lead to lattice distortion, which delayed the occurrence of this behavior. Thermodynamic analysis showed that this kind of spalling behavior was partly attributed to the reduction of free energy at the CuZn/Cu6(Sn, Zn)5 interface due to the change of Sn concentration.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
C.E. Ho, Y.L. Lin, C.R. Kao, Chem. Mater. 14, 949–951 (2002)
C.E. Ho, R.Y. Tsai, Y.L. Lin, C.R. Kao, J. Electron. Mater. 31, 584–590 (2002)
C.E. Ho, Y.W. Lin, S.C. Yang, C.R. Kao, D.S. Jiang, J. Electron. Mater. 35, 1017–1024 (2006)
S.C. Yang, C.E. Ho, C.W. Chang, C.R. Kao, J. Appl. Phys. 101, 084911(1)–084911(6) (2007)
Y.H. Wu, C.Y. Yu, C.Y. Ho, J.G. Duh, Mater. Lett. 105, 40–42 (2013)
J.H. Hong, H.Y. Lee, A.T. Wu, J. Alloy. Compd. 580, 195–200 (2013)
W.M. Chen, S.C. Yang, M.H. Tsai, C.R. Kao, Scripta Mater. 63, 47–49 (2010)
M.H. Tsai, W.M. Chen, M.Y. Tsai, C.R. Kao, J. Alloy. Compd. 504, 341–344 (2010)
J.W. Jang, L.N. Ramanathan, J.K. Lin, D.R. Frear, J. Appl. Phys. 95, 8286–8289 (2004)
M.H. Tsai, Y.W. Lin, H.Y. Chuang, C.R. Kao, J. Mater. Res. 24, 3407–3411 (2009)
C.C. Chang, H.Y. Chung, Y.S. Lai, C.R. Kao, J. Electron. Mater. 39, 2662–2668 (2010)
S.C. Yang, C.E. Ho, C.W. Chang, C.R. Kao, J. Mater. Res. 21, 2436–2439 (2006)
S.C. Yang, Y.W. Wang, C.C. Chang, C.R. Kao, J. Electron. Mater. 37, 1591–1597 (2008)
H.R. Kotadia, A. Panneerselvam, O. Mokhtari, M.A. Green, S.H. Mannan, J. Appl. Phys. 111, 074902(1)–074902(6) (2012)
C.E. Ho, S.C. Yang, C.R. Kao, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 18, 155–174 (2007)
X. Wang, Y.C. Liu, Z.M. Gao, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 22, 14–19 (2011)
H.R. Kotadia, O. Mokhtari, M. Bottrill, M.P. Clode, M.A. Green, S.H. Mannan, J. Electron. Mater. 39, 2720–2731 (2010)
J.Y. Wang, C.F. Lin, C.M. Chen, J. Electron. Mater. 41, 3303–3308 (2012)
H.R. Kotadia, O. Mokhtari, M.P. Clode, M.A. Green, S.H. Mannan, J. Alloy. Compd. 511, 176–188 (2012)
P.Y. Chia, A.S.M.A. Haseeb, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 24, 3423–3429 (2013)
A.A. El-Daly, Y. Swilem, M.H. Makled, M.G. El-Shaarawy, A.M. Abdraboh, J. Alloy. Compd. 484, 134–142 (2009)
C.Y. Chou, S.W. Chen, Acta Mater. 54, 2393–2400 (2006)
M. He, V.L. Acoff, J. Electron. Mater. 37, 288–299 (2008)
M. Date, T. Shoji, M. Fujiyoshi, K. Sato, K.N. Tu, Scripta Mater. 51, 641–645 (2004)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51074112).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, D., Wu, P. Effects of Zn concentration on the aging reactions and IMC massive spalling phenomenon in the Sn–58Bi–xZn/Cu system. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 26, 1338–1346 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-014-2544-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-014-2544-4