Abstract
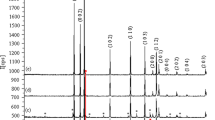
In this study, Tm2O3-doped ZnO powder system was synthesized in the stoichiometric range of 1–10 mol % by solid state method. Produced samples were characterized by XRD and monophase samples, which were indexed as hexagonal (wurtzite) structure, determined by using XRD data. The limit solubility of Tm2O3 in the ZnO lattice is determined to be 4 mol % (after heating at 1000 °C), and beyond 4 mol % the impurity phase was found as cubic-Tm2O3. For monophase Tm2O3–ZnO binary system (synthesized at 1000 °C), the lattice parameters a and c increased with Tm2O3 concentration. Electrical conductivity of undoped ZnO and monophase samples were measured using the four probe method. The electrical conductivity values of undoped ZnO and 4 mol % Tm2O3-doped ZnO samples (synthesized at 1000 °C) were found to be 8.7 × 10−7 and 3.1 × 10−6 Ω−1 cm−1, respectively, at 100 °C and 0.03 and 3.39 Ω−1 cm−1, respectively, at 1000 °C. Also, activation energy of monophase samples (synthesized at 1000 °C) was calculated. UV/Vis absorption and PL emission spectras of undoped and all doped ZnO samples were measured.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.A. Mereu, A. Mesaros, M. Vasilescu, M. Popa, M.S. Gabor, L. Ciontea, T. Petrisor, Ceram. Int. 39, 5535 (2013)
F. Fang, A.M.C. Ng, X.Y. Chen, A.B. Djurisic, Y.C. Zhong, K.S. Wong, P.W.K. Fong, H.F. Lui, C. Surya, W.K. Chan, Mater. Chem. Phys. 125, 813 (2011)
L. Wang, Y. Pu, W. Fang, J. Dai, C. Zheng, C. Mo, C. Xiong, Thin Solid Films 491, 323 (2005)
H. Colak, O. Turkoglu, Mater. High Temp. 29(4), 344 (2012)
H. Colak, O. Turkoglu, J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 27(10), 944 (2011)
S. Husain, L.A. Alkhtaby, E. Giorgetti, A. Zoppi, M.M. Miranda, J. Lumin. 145, 132 (2014)
Weast RC, Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 56. ed., CRC Press, (1975–1976)
S. Yilmaz, O. Turkoglu, I. Belenli, Mater. Chem. Phys. 112, 472 (2008)
J.B. Lee, H.J. Le, S.H. Seo, J.S. Park, Thin Solid Films 398–399, 641 (2001)
Y. Liu, L.E. Lao, Solid State Ionics 177, 159 (2006)
H. Colak, O. Turkoglu, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 23, 1750 (2012)
C.S. Prajapati, P.P. Sahay, Appl. Surf. Sci. 258, 2823 (2012)
C.H. Kwon, H.K. Hong, D.H. Yun, K. Lee, S.T. Kim, Y.H. Roh, B.H. Lee, Sensor. Actuat. B 24–25, 610 (1995)
P.P. Sahay, R.K. Nath, Sensor. Actuat. B 134, 654 (2008)
M.M. Rahman, M.K.R. Khan, M.R. Islam, M.A. Halim, M. Shahjahan, M.A. Hakim, D.K. Saha, J.U. Khan, J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 28(4), 329 (2012)
R.M. Mehra, P.C. Mathur, A.K. Kathuria, R. Shyam, Phys. Status Solidi A 41(2), 189 (1977)
A.V. Patil, C.G. Dighavkar, S.K. Sonawane, S.J. Patil, R.Y. Borse, J. Optoelectron. Biomed. Mater. 1(2), 226 (2009)
R. John, R. Rajakumari, Nano-Micro Lett. 4(2), 65 (2012)
D.D. Wang, J.H. Yang, L.L. Yang, Y.J. Zhang, J.H. Lang, M. Gao, Cryst. Res. Technol. 43, 1041 (2009)
L. Jinlan, D. Chaoyong, C. Ruirui, Opt. Commun. 326, 6 (2014)
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by Cankiri Karatekin University Dean of Science Faculty. The author is thankful to Mehmet Bozoklu who is a PhD student at Erciyes University Institute of Natural and Applied Sciences Department of Physics.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
ÇOLAK, H. Influence of Tm2O3 doping on structural and electrical properties of ZnO. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 26, 784–790 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-014-2464-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-014-2464-3