Abstract
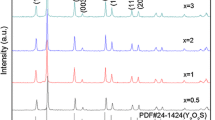
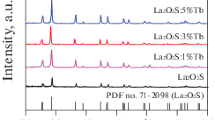
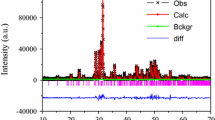
Y2O3:Eu3+ hollow nanofibers were prepared by calcination of the electrospun PVP/[Y(NO3)3 + Eu(NO3)3] composite nanofibers, and then Y2O2S:Eu3+ hollow nanofibers were successfully synthesized by sulfurization of the as-obtained Y2O3:Eu3+ hollow nanofibers via a double-crucible method using sulfur powders as sulfur source. The samples were investigated in detail by X-ray diffractometry (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, and fluorescence spectroscopy. XRD analysis shows that the Y2O2S:Eu3+ hollow nanofibers are pure hexagonal phase with the space group of P\( \bar{3} \) m1. SEM observation indicates that as-prepared Y2O2S:Eu3+ nanofibers are obvious hollow-centered structure with the mean outer diameter of 184 ± 26 nm. Under the excitation of 260-nm ultraviolet light, the Y2O2S:Eu3+ hollow nanofibers exhibit red emissions of predominant emission peaks at 628 and 618 nm originated from 5D0 → 7F2 energy levels transitions of Eu3+ ions. The luminescent intensity of Y2O2S:Eu3+ hollow nanofibers is remarkably increased with the increase of doping concentration of Eu3+ ions and reaches a maximum at 3 mol % of Eu3+ ions. The emitting colors of the samples are located in the red region in CIE chromaticity coordinates diagram. The possible formation mechanism of Y2O2S:Eu3+ hollow nanofibers is also proposed. This preparation technique could be applied to prepare other rare earth oxysulfide hollow nanofibers.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Yang, Y.L. Hou, Rare Met. 32(2), 105–112 (2013)
J.B. Lian, X.D. Sun, J.G. Li, X.D. Li, Opt. Mater. 33(4), 596–600 (2011)
J. Thomas, N. Hans, R. Cees, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 37(22), 3084–3103 (1998)
Y. Tian, W.H. Cao, X.X. Luo, Y. Fu, J. Alloy. Compd. 433(1–2), 313–317 (2007)
M. Nazarov, J. Moldavian, Phys. Sci. 12, 102–118 (2013)
R. Martín-Rodríguez, S. Fischer, A. Ivaturi, B. Froehlich, K.W. Krämer, J.C. Goldschmidt, B.S. Richards, Meijerink Andries. Chem. Mater. 25(9), 1912–1921 (2013)
P.D. Han, X.G. Huang, Q.T. Zhang, Adv. Mater. Res. 197, 558–562 (2011)
Y.J. Li, M.W. Wang, L.D. Zhang, D. Gao, S.X. Liu, Int. J. Min. Met. Mater. 20(10), 972–977 (2013)
O.Y. Manashirov, A.N. Georgobiani, V.B. Gutan, E.M. Zvereva, A.N. Lobanov, Inorg. Mater. 48(7), 721–726 (2012)
T.W. Chou, S. Mylswamy, R.S. Liu, S.Z. Chuang, Solid State Commun. 136(4), 205–209 (2005)
T.A. Trottier, H.C. Swart, S.L. Jones, J.S. Sebastian, P.H. Holloway, J. Soc. Inf. Disp. 4(4), 351–355 (1996)
D. Liu, P. Huang, L. Wang, G.W. Jiang, Ceram. Int. 40, 117–122 (2014)
H. Chen, Y.C. Zhang, C. Chen, Z.L. Wang, N. Yao, Appl. Mech. Mater. 513, 138–142 (2014)
L. Lu, Z.L. Wang, Adv. Mater. Res. 571, 129–132 (2012)
L. Lu, Z.L. Wang, Y.D. Li, C.Y. Li, Y. Li, Y.Z. Du, Adv. Mater. Res. 774, 1001–1005 (2013)
J. Thirumalai, R. Chandramohan, S. Valanarasu, T.A. Vijayan, S. Ezhilvizhian, Micro. Nano Lett. 6(8), 614–618 (2011)
P. Huang, F. Yang, L. Wang, X. Lei, Ceram. Int. 39(5), 5615–5621 (2013)
C.E. Cui, H. Liu, P. Huang, L. Wang, J. Lumin. 149, 196–199 (2014)
X.B. Han, X.G. Li, G.H. Peng, Z.H. Liang, X. Wang, Adv. Mater. Res. 652, 669–672 (2013)
P.F. Ai, Y.L. Liu, L.Y. Xiao, H.J. Wang, J.X. Meng, Sci. Technol. Adv. Mat. 11(3), 1–5 (2010)
Y. Fu, W.H. Cao, Y. Peng, X.X. Luo, M.M. Xing, J. Mater. Sci. 45(23), 6556–6561 (2010)
P.D. Han, L. Zhang, L.X. Wang, Q.T. Zhang, J. Rare Earth 29(9), 849–854 (2011)
X. Yan, G.R. Fern, R. Withnall, J. Silver, Nanoscale 5(3), 1091–1096 (2013)
J.W. Zhang, N.H. Tan, Y.L. Liu, S.Q. Man, Chin. J. Inorg. Chem. 26(2), 229–232 (2010)
J. Zhang, C. Sun-Woo, S.S. Kim, J. Solid State Chem. 184(11), 3008–3013 (2011)
J.X. Wang, X.T. Dong, Q.Z. Cui, G.X. Liu, W.S. Yu, J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 11(3), 2514–2519 (2011)
D.Q. Shao, J.X. Wang, X.T. Dong, W.S. Yu, G.X. Liu, F.F. Zhang, L.M. Wang, J. Mater. Sci.-Mater. Electron. 24, 4263–4269 (2013)
Q.Z. Cui, X.T. Dong, J.X. Wang, M. Li, J. Rare Earth 26(5), 664–669 (2008)
D. Li, X.T. Dong, W.S. Yu, J.X. Wang, G.X. Liu, J. Mater. Sci.-Mater. Electron. 24, 3041–3048 (2013)
Q.L. Ma, J.X. Wang, X.T. Dong, W.S. Yu, G.X. Liu, J. Xu, J. Mater. Chem. 22(29), 14438–14442 (2012)
F. Bi, X.T. Dong, J.X. Wang, G.X. Liu, J. Mater. Sci.-Mater. Electron. (2014). doi:10.1007/s10854-014-2158-x
Q.L. Ma, W.S. Yu, X.T. Dong, J.X. Wang, G.X. Liu, Nanoscale 6, 2945–2952 (2014)
S.J. Sheng, Q.L. Ma, X.T. Dong, N. Lv, J.X. Wang, W.S. Yu, G.X. Liu, J. Mater. Sci.-Mater. Electron. 25, 2279–2286 (2014)
B. Mirosław, S. Karol, M. Sebastian, G. Marek, Opt. Mater. 36(10), 1616–1621 (2014)
A.A. Kader, M.M. Elkholy, J. Mater. Sci.-Mater. Electron. 1(2), 95–99 (1990)
G. Blasse, Phys. Lett. A 28(6), 444–445 (1968)
H.R. Che, X.T. Dong, L. Liu, J.X. Wang, Chin. Rare Earths 29(6), 11–16 (2008)
Y. Hou, X.T. Dong, J.X. Wang, G.X. Liu, L.H. Li, Chem. J. Chin. U. 32(2), 225–230 (2011)
W.W. Ma, X.T. Dong, J.X. Wang, W.S. Yu, G.X. Liu, J. Mater. Sci. 48(6), 2557–2565 (2013)
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC 50972020, 51072026), Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education (20102216110002, 20112216120003), the Science and Technology Development Planning Project of Jilin Province (Grant Nos. 20130101001JC, 20070402), the Science and Technology Research Project of the Education Department of Jilin Province during the eleventh five-year plan period(Under Grant No. 2010JYT01), Key Research Project of Science and Technology of Ministry of Education of China (Grant No. 207026).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, L., Pan, M., Lv, Y. et al. Fabrication of Y2O2S:Eu3+ hollow nanofibers by sulfurization of Y2O3:Eu3+ hollow nanofibers. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 26, 677–684 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-014-2449-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-014-2449-2