Abstract
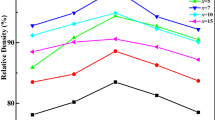
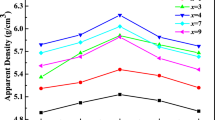
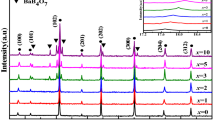
Ba(Zn1/3Nb2/3)O3–ZnNb2O6(BZNZ) composite ceramics were fabricated by conventional solid solution processing. After optimizing the composition, the effects of the sintering parameters, such as the heating rate, the soaking time, and the cooling rate on densities, microstructure, and microwave dielectric properties were investigated using orthogonal experimental design method. The results show that with increasing the content of Ba(Zn1/3Nb2/3)O3, the ε r increases, while the Q × f value increases first, then decreases, and τ f shifts to the negative value. The BZNZ ceramics with composition of 0.3Ba(Zn1/3Nb2/3)O3–0.7ZnNb2O6 show the optimal dielectric properties. The results of orthogonal experimental design show that sintering parameters play an important role in the microstructure and dielectric properties. The ceramics show obvious duplex-grain structure. The importance sequence of the sintering parameters is: cooling rate > heating rate > soaking time. The sintering parameters were optimized, with 0.3Ba(Zn1/3Nb2/3)O3–0.7ZnNb2O6 ceramic sintered at a heating rate of 2 °C/min, soaking time of 8 h, and cooling in the air. Samples have the excellent dielectric properties: εr = 32.75, Q × f = 34,100, and τ f = −10.2 ppm/°C.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Freer, F. Azough, Microstructural engineering of microwave dielectric ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 28, 1433–1441 (2008)
K. Wakino, T. Nishikawa, Y. Ishikawa, H. Tamura, Dielectric resonator materials and their applications for mobile communication system. Br. Ceram. Trans. 89(2), 39–43 (1990)
C. Xiujian, Z. Zhenyu, Z. Wendong, Z. Jiwei, Microstructures and dielectric properties of Ba0.5Sr0.5TiO3–Zn2TiO4 composite ceramics with low sintering temperature for tunable device applications. Mater. Des. 31, 3703–3707 (2010)
E.A. Nenasheva, S.S. Redozubov, N.F. Kartenko, I.M. Gaidamak, Microwave dielectric properties and structure of ZnO–Nb2O5–TiO2 ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 31, 1097–1102 (2011)
H. Yamada, T. Okawa, Y. Tohdo, H. Ohsato, Microwave dielectric properties of BaxLa4Ti3+xO12+3x (x = 0.0–1.0) ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 26, 2059–2062 (2006)
C.P. Robert, The synthesis, properties, and applications of columbite niobates (M2Nb2O6): a critical review. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 92(3), 563–577 (2009)
A.K. Lamrath, T. Sherin, T.S. Mailadil, Tailoring the microwave dielectric properties of MgNb2O6 and Mg4Nb2O9 ceramics. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 4(4), 359–366 (2007)
S. Wu, J. Luo, Mg-substituted ZnNb2O6–TiO2 composite ceramics for RF/microwaves ceramic capacitors. J. Alloy. Compd. 509, 8126–8129 (2011)
D.W. Kim, K.H. Ko, K.S. Hong, Influence of copperoxide additions to zinc niobate microwave ceramics on sintering temperature and dielectric properties. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 84(6), 1286–1290 (2001)
C.L. Huang, R.J. Lin, J.J. Wang, Effect of B2O3 additives on sintering and microwave dielectric behaviors of CuO-Doped ZnNb2O6 ceramics. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 41(1), 758–762 (2002)
Q.L. Zhang, H. Yang, Low-temperature firing and microwave dielectric properties of ZnO–Nb2O5–TiO2–SnO2 versmics with CuO–V2O5. Mater. Res. Bull. 40(11), 1891–1898 (2005)
F. Gao, J. Liu, R. Hong, Z. Li, C. Tian, Microstructure and dielectric properties of low temperature sintered ZnNb2O6 microwave ceramics. Ceram. Int. 35(7), 2687–2692 (2009)
Sebastian M.T. Dielectric Materials for Wireless Communication, (Elsevier B. V. publisher, 2008)
K. Dongwan, B.H. Hee, S.H. Kug, Structural transition and microwave dielectric properties of ZnNb2O6–TiO2 sintered at low temperatures. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 41, 1465–1469 (2002)
R.V. Manoj, M.T. Sebastian, Effect of dopants on microwave dielectric properties of Ba(Zn1/3Nb2/3)O3 ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 27, 2827–2833 (2007)
A. Mergen, E. Korkmaz, Effect of In, Ce and Bi dopings on sintering and dielectric properties of Ba(Zn1/3Nb2/3)O3 ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 31, 2649–2655 (2011)
N.J. Damaskos, B.J. Kelsall, Measuring dielectric constants of low loss materials using a broadband cavity technique. Microw. J. 38, 140–148 (1995)
A. Cheolwoo, J. Hyunjung, N. Sahn, P. Hyunmin, L. Hwackjoo, Effect of micro-structure on the microwave dielectric prosperties of Ba(Co1/3Nb2/3)O3 and (1 − x)Ba(Co1/3Nb2/3)O3–xBa(Zn1/3Nb2/3)O3 ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 23(4), 2473–2478 (2003)
S. Feng, Influence of BaZrO3, MnCO3 additives on dielectric properties and microstructure of Ba(Zn1/3Nb2/3)O3 ceramics and Ba(Zn1/3Nb2/3)O3–Sr(Zn1/3Nb2/3)O3 solid solutions. Inorg. Mater. 46, 85–90 (2010)
H.K. Yoon, K.J. Beom, S.K. Woo, Effect of BaSnO3 on the microwave dielectric properties of Ba2Ti9O20. J. Mater. Res. 11(8), 1996–2001 (1996)
K. Wakino, Recent development of dielectric resonator materials and filters in Japan. Ferroelectrics 91(1), 69–86 (1989)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Aviation Science Foundation of China, Industrial Technology Research Foundation of Shaanxi Province, and Basic Research Foundation of Northwestern Polytechnical University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Z., Gao, F., Hu, G. et al. Effect of sintering parameters on the microstructure and microwave dielectric properties of Ba(Zn1/3Nb2/3)O3–ZnNb2O6 Ceramics. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 25, 5020–5026 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-014-2266-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-014-2266-7