Abstract
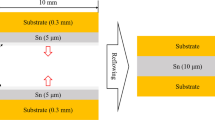
This paper investigates the influence of diffusion layer (solder layer) thickness (δ) on interface diffusion in both thermal aging and electro-thermal coupling aging. The different δ (δ = 60, 120 and 240 μm) of Cu/Sn–3.0Ag–0.5Cu (SAC305)/Cu butt solder joints are used. The results indicate that the geometrical size (solder layer thickness) of solder joint has significant effect on element diffusion behavior. The diffusion coefficient, time exponent, element concentrations and diffusion flux are greatly dependent upon δ. The effects of δ on the interface diffusion is different between thermal aging and electro-thermal coupling aging, due to driving force for diffusion is different. During thermal aging, concentration gradient is the main driving force of diffusion, and diffusion coefficient, time exponent and diffusion flux are relatively low for a thin solder layer. However, under electro-thermal coupling condition, the electron wind force provides the dominating driving force for diffusion, and diffusion coefficient and diffusion flux of thin δ are significantly larger than the thick ones. The Cu concentration of the area near interface is relatively high for a thin solder layer in both tests. Under the same experimental temperature, the effects of δ on the electro-thermal coupling aging are more obvious than thermal aging.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. He, G. Xu, F. Guo, J. Mater. Sci. 45(2), 334 (2010)
E.C.C. Yeh, W.J. Choi, K.N. Tu, P. Elenius, B. Haluk, J. Appl. Phys. Lett. 80(4), 580 (2002)
J.H. Ke, T.L. Yang, C.R. Kao, J. Acta. Mater. 59(6), 246 (2011)
J.H. Ke, H.Y. Chuang, W.L. Shih, C.R. Kao, J. Acta. Mater. 60(5), 2082 (2012)
Y.W. Lin, J.H. Ke, H.Y. Chuang, Y.S. Lai, C.R. Kao, J. Appl. Phys. 107(7), 073516 (2010)
Y. Yao, M. Leon, M.E. Keer, J. Appl. Phys. 105(6), 063710 (2009)
C.K. Wong, J.H.L. Pang, J.W. Tew, B.K. Lok, J. Microelectron. Reliab. 48(4), 611 (2008)
C.C. Chang, Y.W. Lin, Y.W. Wang, J. Alloys. Compd. 492(1–2, 4), 99 (2010)
W.K. Choi, S.K. Kang, D.Y. Shih, J. Electron. Mater. 31(11), 1283 (2002)
A. Ourdjini, M.A.A. Hanim, S.F.J. Koh, International electronic manufacturing technology (IEEE Inc, Petaling Jaya, 2006), p. 437
C.E. Ho, S.C. Yang, C.R. Kao, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 18(1), 147 (2007)
J.H. Lee, G.T. Lim, Y.B. 58th Park, Electronic components and technology conference (IEEE Inc, Lake Buena Vista, 2008), p. 2030
N. Tunca, G.W. Delamore, R.W. Smith, J. Metall. Trans. A 21(11), 2919 (1990)
G.T. Lim, Y.B. Park, J. Curr. Appl. Phys. 11(4), 115 (2011)
L. Xu, J.H.L. Pang, Electronic components and technology conference (IEEE Inc, San Diego, 2006), p. 1154
H.Y. Chuang, W.M. Chenl, W.L. Shih, Y.S. Lai, C.R. Kao, Electronic components and technology conference (IEEE, Lake Buena Vista, 2011), p. 1723
P.S. Ho, T. Kwok, J. Rep. Prog. Phys. 52(3), 301 (1989)
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (51075107; 51174069).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Sun, F., Liu, Y. et al. Geometrical size effect on the interface diffusion of micro solder joint in electro-thermal coupling aging. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 25, 3742–3746 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-014-2084-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-014-2084-y