Abstract
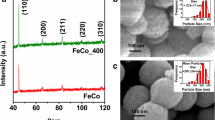
Magnetic FeCo alloy nanoparticles have been synthesized by reduction of FeSO4 and CoCl2 with hydrazine in concentrated alkaline media via a hydrothermal route. The size could be controlled by synthetic conditions such as reaction time and temperature, respectively. The obtained samples were characterized by XRD, SEM, TEM, and VSM techniques. Magnetic investigations show the ferromagnetic behavior with saturation magnetization higher than 148.2 emu/g and maximum coercivity up to 411.0 Oe at room temperature. The present method is simple, inexpensive, surfactant-free, and may stimulate technological interests. Such FeCo alloy nanoparticles may have potential applications in biomedical field and magnetic storage devices.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Kuhrt, L. Schultz, J. Appl. Phys. 73, 6588–6590 (1993)
G. Reiss, A. Hutten, Nat. Mater. 4, 725–726 (2005)
M. Arruebo, R. Fernández-Pacheco, M.R. Ibarra, J. Santamaría, Nano Today 2, 22–32 (2007)
W.S. Seo, J.H. Lee, X. Sun, Y. Suzuki, D. Mann, Z. Liu et al., Nat. Mater. 5, 971–976 (2006)
C. Kuhrt, L. Schultz, J. Appl. Phys. 73, 6588–6590 (1993)
Elbaile L, Crespo RD, Vega V, Garcia JA. J Nanomater 2012; 198453
N.V. Myung, D.Y. Park, D.E. Urgiles, T. George, Electrochim. Acta 49, 4397–4404 (2004)
G.S. Chaubey, C. Barcena, N. Poudyal, C. Rong, J. Gao, S. Sun et al., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129, 7214–7215 (2007)
Z.X. Yu, N. Zhang, Z.P. Yao, X.J. Han, Z.H. Jiang, J Mater Chem A 1, 12462–12470 (2013)
X.W. Wei, K.L. Wu, G.X. Zhu, Y.J. Liu, W. Shi, X.Z. Li et al., J Alloys Compd 539, 21–25 (2012)
Y. Yang, C.L. Xu, Y.X. Xia, T. Wang, F.S. Li, J Alloys Compd 493, 549–552 (2010)
X.W. Wei, G.X. Zhu, Y.J. Liu, Y.H. Ni, Y. Song, Z. Xu, Chem. Mater. 20, 6248–6253 (2008)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Shanxi Scholarship Council of China, and High-level Scientific Research Foundation for the Introduction of Talent through North University of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, C., Wang, Y., Chen, H. et al. Facile and controlled synthesis of FeCo nanoparticles via a hydrothermal method. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 25, 1965–1969 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-014-1830-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-014-1830-5