Abstract
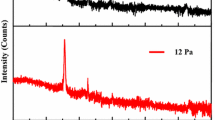
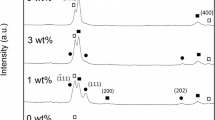
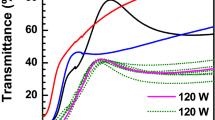
Copper oxide films were prepared by RF reactive magnetron sputtering at different percentages of oxygen pressure in a Ar:O2 reactive gas mixture at room temperature. The structural and optical properties of CuO films were investigated by a field emission scanning electron microscope, Raman spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction and UV–Visible spectrophotometer. The structure of the deposited film changed from a mixture of Cu2O + CuO phases to a pure CuO phase with an increase in oxygen percentage. In addition the crystallite size increased from 12 to 24 nm as the oxygen pressure percentage increased. The optical transmittance significantly increased with the increase of the oxygen pressure percentage and the optical band gap of the film increased from 1.33 to 1.41 eV. The film prepared with 30 and 40 % oxygen pressure showed (002) crystallographic orientation. The I–V characteristic of p-CuO/n-Si heterojunction diode was also found to be dependent on the oxygen pressure percentage.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. Gao, X.-J. Liu, J.-S. Zhang, M.-Z. Song, N. Li, J Appl Phys 111(8), 084507 (2012)
N.D. Hoa, S.Y. An, N.Q. Dung, N. Van Quy, D. Kim, Sens Actuators, B 146(1), 239 (2010)
S. Wang, C. Hsiao, S. Chang, K. Lam, K. Wen, S. Hung, S. Young, B. Huang, Sens Actuators, A 171(2), 207 (2011)
S.-L. Cheng, M.-F. Chen, Nanoscale Res Lett 7(1), 1 (2012)
P. Samarasekara, N. Kumara, N.J. Yapa, Phys Condens Matter 18(8), 2417 (2006)
P. Chand, A. Gaur, A. Kumar, Superlattices Microstruct 60, 129 (2013)
M. Abaker, A. Umar, S. Baskoutas, S. Kim, S. Hwang, J Phys D Appl Phys 44(15), 155405 (2011)
N. Serin, A. Yildiz, E. Çam, Ş. Uzun, T. Serin, Superlattices Microstruct 52(4), 759 (2012)
V. Dhanasekaran, T. Mahalingam, R. Chandramohan, J.-K. Rhee, J. Chu, Thin Solid Films 520(21), 6608 (2012)
J.H. Lee, K.H. Jeong, W.H. Cho, W.J. Ho, H.J. Yang, C.S. Kim, J.G. Lee, Met Mater Int 17(6), 917 (2011)
S. Berg, T. Nyberg, Thin Solid Films 476(2), 215 (2005)
G. Beensh-Marchwicka, L. Kròl-Stȩpniewska, M. Słaby, Thin Solid Films 88(1), 33 (1982)
A. Ogwu, E. Bouquerel, O. Ademosu, S. Moh, E. Crossan, F. Placido, J Phys D Appl Phys 38(2), 266 (2005)
E. Darezereshki, F. Bakhtiari, J Min Metall Sect B 47(1), 73 (2011)
J.F. Xu, W. Ji, Z.X. Shen, W.S. Li, S.H. Tang, X.R. Ye, D.Z. Jia, X.Q. Xin, J Raman Spectrosc 30(5), 413 (1999)
D. Schroder, R.N. Thomas, J.C. Swartz, IEEE J Solid-State Circ 13(1), 180 (1978)
J. Tauc, A. Menth, J Non-Cryst Solids 8–10, 569 (1972)
M. Nolan, S.D. Elliott, Phys Chem Chem Phys 8(45), 5350 (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elfadill, N.G., Hashim, M.R., Chahrour, K.M. et al. The influence of oxygen pressure on the growth of CuO nanostructures prepared by RF reactive magnetron sputtering. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 25, 262–266 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-013-1581-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-013-1581-8