Abstract
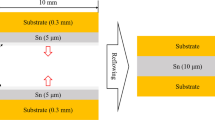
The interconnection lengths between the stacked chips in three-dimensional (3D) package are a few of microns, hence the solder joints for the stacked chips joining are mainly composed by intermetallic compounds (IMCs) after reflow processes. To evaluate the phase transformation of Cu–Sn IMCs in the small interconnection joints, the Cu/Sn/Cu structures were bonded with different bonding times at various temperatures in argon gas atmosphere in this study. Scanning electron microscope and energy-dispersive X-ray were used to observe the joint interfacial microstructures and electron back scattering diffraction was used to identify the grain orientations in the joints. Scalloped Cu6Sn5 grains were found to be initially formed on the Cu substrates at the early stage. A lot of small Cu6Sn5 grains formed on the surfaces of the big scallop Cu6Sn5 grains. Those small grains gradually grew up to merge into the big Cu6Sn5 grains. With longer reflow time, the Cu6Sn5 grains initiated at both side of Cu substrate continued to grow up and started to contact with each other. Meantime, the different Cu6Sn5 grains with different grain orientations have merged into some bigger grains. The Cu3Sn grains formed between Cu6Sn5 layers and Cu substrates have further developed at the expense of the depletion of Cu6Sn5. Most of columnar Cu3Sn grains were vertical to Cu substrate surface and their grain sizes were 1–5 μm. With 960 min at 300 °C, the pure Cu3Sn IMC joint has formed. The Cu3Sn grains in IMC joint had different grain orientations and a contact line was observed in the middle of the Cu3Sn IMC joint.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
C.T. Ko, K.N. Chen, Microelectron. Reliab. 50, 481 (2010)
H. Huebner, S. Penka, B. Barchmann, M. Eigner, W. Gruber, M. Nobis, S. Janka, G. Kristen, M. Schneegans, Microelectron. Eng. 83, 2155 (2006)
N.S. Bosco, F.W. Zok, Acta Mater. 52, 2965 (2004)
J.S. Kim, P.J. Wang, C.C. Lee, IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Technol. 31, 776 (2008)
C. Lee, A. Yu, L. Yan, H. Wang, J. He, Q. Zhang, J. Lau, Sens. Actuators A 154, 85 (2009)
J.F. Li, P.A. Agyakwa, C.M. Johnson, Acta Mater. 58, 3429 (2010)
J.F. Li, P.A. Agyakwa, C.M. Johnson, Acta Mater. 59, 1198 (2011)
S. Sommadossi, A.F. Guillermet, Intermetallics 15, 912 (2007)
T. Takahashi, S. Komatsu, T. Kono, Electrochem. Solid State 12, H263 (2009)
A.A. Wronkowska, A. Wronkowski, K. Kuklinski, M. Senski, L. Skowronski, Appl. Surf. Sci. 256, 4839 (2010)
D.Q. Yu, C. Lee, L.L. Yan, M.L. Thew, J.H. Lau, J. Alloy Compd. 485, 444 (2009)
M. Li, Z. Li, Y. Xiao, C. Wang, Appl. Phys. Lett. 102, 094104 (2013)
F. Niklaus, R.J. Kumar, J.J. McMahon, J. Yu, J.Q. Lu, T.S. Cale, R.J. Gutmann, J. Electrochem. Soc. 153, G291 (2006)
M.M.V. Taklo, P. Storas, K. Schjolberg-Henriksen, H.K. Hasting, H. Jakobsen, J. Micromech. Microeng. 14, 884 (2004)
K.N. Chen, C.S. Tan, A. Fan, R. Reif, Electrochem. Solid State 7, G14 (2004)
C.S. Tan, Microelectron. Eng. 87, 682 (2010)
Y.H. Cao, W.G. Ning, L. Luo, IEEE Trans. Electron. Packag. Manuf. 32, 125 (2009)
D.Q. Yu, C. Lee, L.L. Yan, W.K. Choi, A. Yu, J.H. Lau, Appl. Phys. Lett. 94, 034105 (2009)
H. Kato, S. Horikawa, K. Kageyama, Mater. Sci. Technol. 15, 851 (1999)
K.F. Dreyer, W.K. Neils, R.R. Chromik, D. Grosman, E.J. Cotts, Appl. Phys. Lett. 67, 2795 (1995)
H.K. Kim, K.N. Tu, Phys. Rev. B 53, 16027 (1996)
J.C. Gong, C.Q. Liu, P.P. Conway, V.V. Silberschmidt, Scripta Mater. 61, 682 (2009)
J.C. Gong, C.Q. Liu, P.P. Conway, V.V. Silberschmidt, Acta Mater. 56, 4291 (2008)
Acknowledgments
This work has been supported by the National Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51075103). Authors are grateful to the projects (HIT. NSRIF 2010120) supported by Natural Scientific Research Innovation Foundation in Harbin Institute of Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hang, C., Tian, Y., Zhang, R. et al. Phase transformation and grain orientation of Cu–Sn intermetallic compounds during low temperature bonding process. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 24, 3905–3913 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-013-1337-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-013-1337-5