Abstract
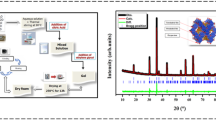
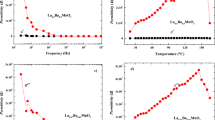
Anhydrous polycrystalline sodium molybdate (Na2MoO4) ceramics has been prepared by a solid-state reaction technique. The formation of the compound in cubic system is confirmed by a preliminary structural analysis using X-ray diffraction data. Energy dispersive spectrum analysis of Na2MoO4 has confirmed its chemical formula and composition. Spectroscopic studies of the compound have been carried by a vibration spectroscopy (Raman/FTIR) in order to understand its molecular structure at microscopic level. The complex impedance spectroscopy technique has been used to study the electrical properties of the material as a function of frequency (102–106 Hz) at different temperatures (23–450 °C), and also to investigate the fundamental mechanism involved in the material. Impedance analysis also indicates that below 300 °C, the material electrical conduction is related to the grain volume. Above 300 °C, the contribution of grain boundary is clearly evident. The electrical processes in the material are found to be temperature-dependent, and due to relaxation phenomena in it. A frequency dependent maximum of the imaginary electrical impedance is found to obey an Arrhenius law with activation energy of 1.07 eV. The frequency dependence of electrical conductivity spectra does follow the universal power law.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Mathews, D. Krishnamurthy, T. Gnanasekaran, J Nucl Mater. 247, 280 (1997)
K.C. Emregül, A.A. Aksüt, Corros Sci. 45, 2415 (2003)
M. Fujimoto, Physics of Structural Phase Transitions (Springer, New York, 2005)
S. Sharma, R.N.P. Choudhary, S.R. Shanigrahi, Mat Letts. 40, 134 (1999)
J. Liu, J. Ma, B. Lin, Y. Ren, X. Jiang, J. Tao, X. Zhu, Ceram Inter. 34, 1557 (2008)
S. Mukherjee, M. Chakraborty, A.K. Panda, S.C. Bhattacharya, S.P. Moulik, Colloids and surfaces A. Physicochem Eng Aspects 388, 1 (2011)
Y. Ding, N. Hou, N. Chen, Y. Xia, Rare Met. 25, 316 (2006)
K. Gesi, J Phys Soc Jpn. 53, 3850 (1984)
S.N. Choudhary, R.N.P. Choudhary, Mat Letts. 34, 411 (1998)
A.H. Yahaya, A.K. Arof, Mat Sc Eng B. 34, 7 (1995)
O.P. Barinova, S.V. Kirsanova, Glass Ceram. 65, 362 (2008)
Wu E. POWD: An interactive powder diffraction data interpretation and indexing programme, Ver 2.5, School of Physical Science, Flinders University of South Australia, Bedford Park, SA 5042, Australia
P. Scherrer, Gottin Nachricht. 2, 98 (1918)
M. Seleborg, Acta Chimica Scandinavica. 21, 499 (1967)
C. Luz Lima, G.D. Saraiva, P.T.C. Freire, M. Maczka, W. Paraguassu, F.F. de Sousa, J. Mendes Filho, J Raman Spectrosc. 42, 799 (2011)
G.D. Saraiva, W. Paraguassu, M. Maczka, P.T.C. Freire, J.A. Lima Jr, C.W.A. Paschoal, J. Mendes Filho, A.G. Souza Filho, J Raman Spectrosc 39, 937 (2008)
M. Balkanski, R.F. Wallis, E. Haro, Phys Rev B 28, 1928 (1983)
R.H. Busey, O.L. Keller, J Chem Phys. 41, 215 (1964)
M.R. Johan, T.K. Han, A.K. Arof, Ionics 16, 323 (2010)
A. Rulmont, M. Almou, Spectrochim Acta 45A(5), 603 (1989)
M.E. Poloznikova, O.I. Kondratov, V.V. Fomichev, Zh Neorg Khim. 33(10), 2526 (1988)
A.J. Marchi, E.J. Lede, F.G. Requejo, M. Renteria, S. Irusta, E.A. Lombardo, E.E. Miro, Catal Lett. 48(1–2), 47 (1997)
C. Bharti, A. Dutta, T.P. Sinha, Mat Res Bull. 43, 1246 (2008)
S.K. Bera, S.K. Barik, R.N.P. Choudhary, P.K. Bajpai, Bull Mater Sci. 35(1), 47 (2011)
S. Chatterjee, P.K. Mahapatra, R.N.P. Choudhary, A.K. Thakur, Phy Stat Sol a. 201(3), 588 (2004)
J.R. Macdonald, Impedance Spectroscopy Emphasizing Solid Materials and Systems (Wiley, New York, 1987)
A.K. Jonscher, Nature 264, 673 (1977)
Acknowledgments
The work was carried out at the Ferroelectric Laboratory, Department of Physics and Meteorology and Central Research Facility of IIT Kharagpur. The facilities availed at IIT Kharagpur and discussions among the research group are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chatterjee, S., Barik, S.K. & Choudhary, R.N.P. Studies of structural, spectroscopic and electrical properties of sodium molybdate ceramics. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 24, 3359–3364 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-013-1255-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-013-1255-6