Abstract
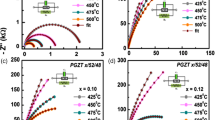
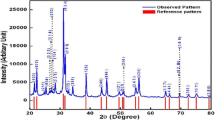
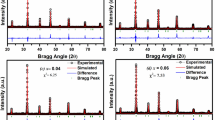
The gadolinium (Gd)-modified lead zirconate titanate (i.e., Pb1−xGdx (Zr0.65Ti0.35)1−x/4O3; x = 0, 0.07, 0.10 and 0.12) ceramics have been synthesized using a high-temperature (~1,100 °C) solid-state reaction route. Preliminary X-ray structural studies show the formation of single-phase compounds in the tetragonal crystal system. Scanning electron micrographs of the surface of pellet samples show uniform distribution of grains of different shape and size with few voids. It is interesting to observe the significant effect of Gd-substitution on the nature, size, and distribution of grains, and the density of samples. Detailed analysis of dielectric properties of the materials indicates that the materials are non-relaxor but have diffused ferroelectric phase transition. The temperature and frequency dependence of conductivity follows Jonscher’s universal power law.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Bruno, A. Poggialini, G. Felice, Design and calibration of a piezoelectric actuator for interferometric applications. Opt. Lasers Eng. 45, 1148 (2007)
A. Hirt, Printing with ferroelectric ceramics. Ferroelectrics 201, 1 (1997)
S.G. Porter, Materials for pyroelectric detectors. Mater. Des. 8, 120 (1978)
P. Muralt, Recent progress in materials issues for piezoelectric MEMS. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 91, 1385 (2008)
K. Carl, K. Geisen, Dielectric and optical properties of quasi-ferroelectric PLZT ceramic. Proc. IEEE 63, 967 (1973)
G.H. Heartling, C.E. Land, Hot-pressed (Pb, La)(Zr,Ti)O3 ferroelectric ceramics for electrooptic applications. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 54, 1 (1971)
S. Dutta, R.N.P. Choudhary, P.K. Sinha, Impedance spectroscopic studies on Fe3+ ion modified PLZT ceramics. Ceram. Int. 33, 13 (2007)
Eric Bocher, Benoit Guiffard, Laurent Lebrun, Daniel Guyomar, Effects of Zr/Ti ratio on structural, dielectric and piezoelectric properties of Mn- and (Mn, F)-doped lead zirconate titanate ceramics. Ceram Int. 32, 479 (2006)
S.K.S. Parasar, R.N.P. Choudhary, B.S. Murty, Electrical properties of Gd-doped PZT nanoceramic synthesized by high energy ball milling. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 110, 58 (2004)
C.E. Land, P. Thatcher, G.H. Haertling, Electro-optic ceramics, in Advances in Materials and Device Research, vol. 4, ed. by R. Wolfe (Academic, New York, 1974), pp. 137–233
H. Liu, H. Toraya, Study on new tetragonal phase of Nb–doped lead titanate zirconate by synchrotron X-ray powder diffraction. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 60, 729 (1999)
S.K. Sinha, R.N.P. Choudhary, S.N. Choudhary, Phase transition in Pb(Mn1/4Cd1/4W1/2)O3 ceramics. Mater. Chem. Phys. 78, 432 (2002)
E. Wu, POWD, An Interactive Powder Diffraction Data Interpretation, Indexing Programme, version 2.2, School of Physical Science, Flinder University of South Australia Bedford Park, SA, Australia
K.H. Härdtl, D. Hennings, Distribution of A-site and B-site vacancies in (Pb, La) (Ti, Zr) O3 ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 55, 230 (1972)
H.P. Klug, L.E. Alexander, X-ray Diffraction Procedures for Polycrystalline and Amorphous Materials (Wiley-Interscience, New York, 1974)
M.E. Lines, A.M. Glass, Principles and Applications of Ferroelectrics and Related Materials, Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1977
S.L. Swartz, T.R. Shrout, Fabrication of perovskite lead magnesium niobate. Mater. Res. Bull. 17, 1245 (1982)
C. Kittel, Introduction to Solid State Physics, Wiley, UK
I. Chen, P. Li, Y. wang, Structural origin of relaxor pervoskites. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 57, 1525 (1966)
S.M. Pilgrim, A.E. Sutherland, S.R. Winzer, Diffuseness as a useful parameter for relaxor ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 73, 3122 (1990)
G.H. Heartling, Ferroelectric ceramics: History and technology. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 84, 797 (1999)
C.G.F. Strenger, A.J. Burggraff, Study of phase transitions and properties of tetragonal (Pb, La) (Zr, Ti) O3 ceramics—I: phase diagram and β-phase. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 41, 25 (1980)
B.A. Boukamp, M.T.N. Pham, D.H.A. Blank, H.J.M. Bouwmeester, Ionic and electronic conductivity in lead-zirconate-titanate (PZT). Sol State Ionics 170, 239 (2004)
O. Raymond, R. Font, N. Suarez-Almodovar, J. Portelles, J.M. Siqueiros, Frequency-temperature response of ferroelectromagnetic Pb (Fe1/2Nb1/2)O3 ceramics obtained by different precursors. Part 1 structural and thermo-electrical characterization. J. Appl. Phys. 97, 084107 (2005)
J. Portelles, N.S. Almodovar, J. Fuentes, O. Raymond, J. Heiras, J.M. Siqueiros, AC conductivity in Gd doped Pb(Zr0.53Ti0.57)O3 ceramics. J. Appl. Phys. 104, 073511 (2008)
V.M. Fridkin, Ferroelectric Semiconductors (Consultant Bureau, New York, 1980)
A.K. Jonscher, The universal dielectric responses. Nature 267, 673 (1977)
K. Funke, Jump relaxation in solid electrolytes. Prog. Solid State Chem. 22, 111 (1993)
Z. Lu, J.P. Bonnet, J. Ravez, P. Hagenmuller, Correlation between low frequency dielectric dispersion (LFDD) and impedance relaxation in ferroelectric ceramic Pb2KNb4TaO15. Solid State lon. 57, 235 (1992)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Panigrahi, S.C., Das, P.R., Parida, B.N. et al. Effect of Gd-substitution on dielectric and transport properties of lead zirconate titanate ceramics. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 24, 3275–3283 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-013-1243-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-013-1243-x