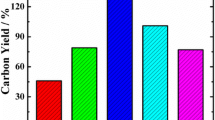
Abstract
Structural transformation of carbon black (CB) into nanotubes and nano-onion like structures in the presence of bimetallic catalysts (Fe and Ni) is reported and the influence of the substrate (alumina and stainless steel) in the structural transformation is studied. In addition, the importance of a specific weight ratio of CB to catalyst in the transformation of amorphous CB into graphitic nanostructures is verified. The experiments were carried out at 1,000 °C in a horizontal tube furnace under N2 atmosphere. The samples were characterized by transmission electron microscopy, high-resolution transmission electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, Raman spectroscopy and also thermomagnetic analysis (Curie-temperature determinations) were done to assess thermally induced magnetic phase changes. All the characterization techniques showed the resulting structures were influenced by the substrate and weight ratio for CB to catalysts. However, there was no significant difference in the magnetic performance of the resulting structures obtained on different substrates.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Iijima, Nature 354, 56 (1991)
D.S. Bethune, C.H. Klang, M.S. de Vries et al., Nature 363, 605 (1993)
R. Ehlich, L.P. Biro, I.V. Hertel, Synth. Met. 103, 2486 (1999)
F. Kokai, I. Nozaki, T. Okada, A. Koshio, T. Kuzumaki, Carbon 49, 1173 (2011)
J.L. Li, L.J. Wang, G.Z. Bai, W. Jiang, Scripta Mater. 54, 93 (2006)
P. Mahanandia, P.N. Vishwakarma, K.K. Nanda et al., Mater. Res. Bull. 41, 2311 (2006)
B.S. Martin, B.K.T. Kenneth, G.L. Rodrigo, W.I. Milne, B.H. David, M. Meyyappan, Pure Appl. Chem. 78, 1117 (2006)
R. Sen, S. Suzuki, H. Kataura, Y. Achiba, Chem. Phys. Lett. 349, 383 (2001). doi:10.1016/s0009-2614(01)01208-8
M.M. Shaijumon, S. Ramaprabhu, Chem. Phys. Lett. 374, 513 (2003). doi:10.1016/s0009-2614(03)00741-3
D. Tang, L. Sun, J. Zhou, W. Zhou, S. Xie, Carbon 43, 2812 (2005). doi:10.1016/j.carbon.2005.05.034
Y.-H. Wang, S.-C. Chiu, K.-M. Lin, Y.-Y. Li, Carbon 42, 2535 (2004). doi:10.1016/j.carbon.2004.05.028
S. Wei, W.P. Kang, J.L. Davidson, J.H. Huang, Diam. Relat. Mater. 15, 1828 (2006). doi:10.1016/j.diamond.2006.09.010
T.S. Wong, C.T. Wang, K.H. Chen, L.C. Chen, K.J. Ma, Diam. Relat. Mater. 10, 1810 (2001). doi:10.1016/s0925-9635(01)00454-x
N.M. Rodriguez, J. Mater. Res. 8, 3233 (1993)
C.P. Deck, K. Vecchio, Carbon 44, 267 (2006). doi:10.1016/j.carbon.2005.07.023
W. Shen, F.E. Huggins, N. Shah et al., Appl. Catal. A 351, 102 (2008). doi:10.1016/j.apcata.2008.09.004
G. Luo, Z. Li, F. Wei, L. Xiang, X. Deng, Y. Jin, Phys. B 323, 314 (2002). doi:10.1016/s0921-4526(02)01039-6
T. Tsoufis, P. Xidas, L. Jankovic et al., Diam. Relat. Mater. 16, 155 (2007). doi:10.1016/j.diamond.2006.04.014
W. Qian, T. Liu, Z. Wang et al., Carbon 41, 2487 (2003)
S.P. Doherty, R.P.H. Chang, Appl. Phys. Lett. 81, 2466 (2002)
S. Kishinevsky, S.I. Nikitenko, D.M. Pickup, E.R.H. van-Eck, A. Gedanken, Chem. Mater. 14, 4498 (2002)
D.B. Buchholz, S.P. Doherty, R.P.H. Chang, Carbon 41, 1625 (2003). doi:10.1016/s0008-6223(03)00110-6
Z.-G. Chen, F. Li, W.-C. Ren et al., Nanotechnology 17, 3100 (2006)
J.B. Donnet, H. Oulanti, T. Le Huu, Diam. Relat. Mater. 17, 1506 (2008). doi:10.1016/j.diamond.2008.01.001
W. Lian, H. Song, X. Chen et al., Carbon 46, 525 (2008)
A. Govindaraj, C.N.R. Rao, Pure Appl. Chem. 74, 1571 (2002)
C.N.R. Rao, A. Govindaraj, Acc. Chem. Res. 35, 998 (2002)
A. Leela Mohana Reddy, S. Ramaprabhu, Nanoscale Res. Lett. 3, 76 (2008)
A. Leela Mohana Reddy, M.M. Shaijumon, S. Ramaprabhu, Nanotechnology 17, 5299 (2006)
A. Bianco, K. Kostarelos, M. Prato, Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 9, 674 (2005). doi:10.1016/j.cbpa.2005.10.005
D.-C. Li, L. Dai, S. Huang, A.W.H. Mau, Z.L. Wang, Chem. Phys. Lett. 316, 349 (2000). doi:10.1016/s0009-2614(99)01334-2
P.M. Ajayan, S. Iijima, Nature 361, 333 (1993)
P.J.F. Harris, Carbon nanotube science (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2009)
R.L. Vander Wal, T.M. Ticich, V.E. Curtis, Carbon 39, 2277 (2001). doi:10.1016/s0008-6223(01)00047-1
P.A. Marsh, A. Voet, T.J. Mullens, L.D. Price, Carbon 9, 797 (1971). doi:10.1016/0008-6223(71)90013-3
J.W. Ward, B.Q. Wei, P.M. Ajayan, Chem. Phys. Lett. 376, 717 (2003). doi:10.1016/s0009-2614(03)01067-4
R. Lv, A. Cao, F. Kang et al., J. Phys. Chem. C 111, 11475 (2007)
G. Ovejero, J.L. Sotelo, M.D. Romero et al., Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 45, 2206 (2006)
H. Wu, C. Qian, Y. Cao et al., J. Phys. Chem. Solids 71, 290 (2010)
L. Liu, Y. Qin, Z.-X. Guo, D. Zhu, Carbon 41, 331 (2003). doi:10.1016/s0008-6223(02)00286-5
H. Hiura, T.W. Ebbesen, K. Tanigaki, H. Takahashi, Chem. Phys. Lett. 202, 509 (1993)
J. Sengupta, C. Jacob, J. Nanopart. Res. 12, 457 (2010)
M.A. Pimenta, G. Dresselhaus, M.S. Dresselhaus, L.G. Cancado, A. Jorio, R. Saito, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 9, 1276 (2007)
M.A. van Zuilen, D. Fliegel, R. Wirth et al., Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 83, 252 (2012). doi:10.1016/j.gca.2011.12.030
G. Cacciamani, A. Dinsdale, M. Palumbo, A. Pasturel, Intermetallics 18, 1148 (2010). doi:10.1016/j.intermet.2010.02.026
W.-H. Chiang, R.M. Sankaran, Carbon 50, 1044 (2012). doi:10.1016/j.carbon.2011.10.008
E.F. Kukovitsky, S.G. L’Vov, N.A. Sainov, V.A. Shustov, L.A. Chernozatonskii, Chem. Phys. Lett. 355, 497 (2002)
Acknowledgments
The work was partially funded by NFR and Carbontech Holding AS. The authors would like to thank Boobalan Kasilingam, School of advanced studies, VIT, India for his assistance in obtaining XRD results.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Asokan, V., Velauthapillai, D., Løvlie, R. et al. Effect of substrate and catalyst on the transformation of carbon black into nanotubes. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 24, 3231–3239 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-013-1233-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-013-1233-z