Abstract
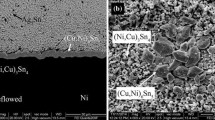
The intermetallic compound (IMC) growth behavior of Sn–3.5Ag–3.5Bi/Cu joint was investigated with a change in the solder melt structure during soldering and 180 °C isothermal aging. The results show that when the solders undergo liqiud–liquid structure transition (LLST), the IMC of the joint is thinner and more evenly distributed during soldering. The interface IMC is also thinner, and the quantity of Ag3Sn as well as Cu6Sn5 in the solder is relatively lower. However, the IMCs are more bulky after long-time aging at 180 °C. When the solders do not undergo LLST, microcracks form in the solder. Kirkendall voids are more abundant and interconnected after long, high-temperature aging. This finding indicates better joint reliability after than before LLST. The growth rate constants of the interface IMC for the two kinds of joints are calculated to be 1.94 × 10−12 and 9.71 × 10−13. The correlation of IMC growth behavior and melt state is analyzed from the viewpoints of LLST and atom diffusion.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Kang, A. Sarkhel, Lead (Pb)-free solders for electronic packaging. J. Electron. Mater. 23, 701–707 (1994)
P.T. Vianco, D.R. Frear, Issues in the replacement of lead-bearing solders. JOM 45, 14–19 (1993)
M. Abtew, G. Selvaduray, Lead-free solders in microelectronics. Mater. Sci. Eng. 27, 95–141 (2000)
K.J. Puttlitz, G.T. Galyon, Impact of the ROHS directive on high-performance electronic systems Part II: key reliability issues preventing the implementation of lead-free solders. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electr. 18(1–3), 347–365 (2007)
I.E. Anderson, Development of Sn–Ag–Cu and Sn–Ag–Cu–X alloys for Pb-free electronic solder applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electr. 18(1–3), 55–76 (2007)
C.W. Hwang, K. Suganuma, Joint reliability and high temperature stability of Sn–Ag–Bi lead-free solder with Cu and Sn–Pb/Ni/Cu substrates. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 373, 187–194 (2004)
K. Zeng, K.N. Tu, Six cases of reliability study of Pb-free solder joints in electronic packaging technology. Mater. Sci. Eng., R 38, 55–105 (2002)
K. Suganuma, Advances in lead-free electronics soldering. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 5, 55–64 (2001)
C.W. Hwang, J.G. Lee, K. Suganuma, H. Mori, Interfacial microstructure between Sn–3Ag–xBi alloy and Cu substrate with or without electrolytic Ni plating. J. Electron. Mater. 32, 52–62 (2003)
M.L. Huang, C.M.L. Wu, J.K.L. Lai, Y.C. Chan, Microstructural evolution of a lead-free solder alloy Sn–Bi–Ag–Cu prepared by mechanical alloying during thermal shock and aging. J. Electron. Mater. 29, 1021–1026 (2000)
C.P. Wu, J. Shen, C.F. Peng, Effects of trace amounts of rare earth additions on the microstructures and interfacial reactions of Sn57Bi1Ag/Cu solder joints. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 23, 14–21 (2012)
P. McMillan, Phase transitions: jumping between liquid states. Nature 403, 151–154 (2000)
J.N. Glosli, F.H. Ree, Liquid–liquid phase transformation in carbon. Phys. Rev. Lett. 82, 4659–4662 (1999)
Y. Katayama, T. Mizutani, W. Utsumi, O. Shimomura, M. Yamakata, K. Funakoshi, A first-order liquid–liquid phase transition in phosphorus. Nature 403, 170–173 (2000)
J. Chen, F.Q. Zu, X.F. Li, G.H. Ding, H.S. Chen, L. Zou, Influence of a liquid structural change on the solidification of the alloy CuSn30. Met. Mate. Int. 14, 569–574 (2008)
X.F. Li, F.Q. Zu, H.F. Ding, J. Yu, L.J. Liu, Anomalous change of electrical resistivity with temperature in liquid Pb–Sn alloys. Phys. B 358, 126–131 (2005)
F.Q. Zu, J. Chen, X.F. Li, L.N. Mao, Y.C. Liu, A new viewpoint to the mechanism for the effects of melt overheating on solidification of Pb–Bi alloys. J. Mater. Res. 24, 2378–2384 (2009)
X.F. Li, H.S. Chen, F.Q. Zu, Z.H. Chen, Q.Q. Sun, L.L. Guo, Kinetics of liquid structure transition of Sn- (40 wt%)Bi Melt. Chin. Phys. Lett. 25, 317–320 (2008)
F.Q. Zu, Z.G. Zhu, L.J. Guo, X.B. Qin, H. Yang, W.J. Shan, Observation of an anomalous discontinuous liquid-structure change with temperature. Phys. Rev. Lett. 89, 125505 (2002)
W.M. Wang, X.F. Bian, J.Y. Qin, S.I. Syliusarenko, The atomic-structure changes in Al-16 pct Si alloy above the liquidus. Met. Mater. Trans. A 31, 2163–2168 (2000)
Q.D. Qin, Y.G. Zhao, Y.H. Liang, W. Zhou, Effects of melt superheating treatment on microstructure of Mg2Si/Al–Si–Cu composite. J. Alloys Comp. 399, 106–109 (2005)
C.L. Xu, Q.C. Jiang, Morphologies of primary silicon in hypereutectic Al–Si alloys with melt overheating temperature and cooling rate. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 437, 451–455 (2006)
X.Y. Li, F.Q. Zu, W.L. Gao, X. Cui, L.F. Wang, G.H. Ding, Effects of the melt state on the microstructure of a Sn–3.5 %Ag solder at different cooling rates. Appl. Surf. Sci. 258, 5677–5682 (2012)
X.Y. Li, F.Q. Zu, Z.Y. Huang, X. Cui , Z.Z. Wang, Electrical resistivity of Sn–3.5Ag–xBi solder melts, Phase Transitions, doi:10.1080/01411594.2011.618755
X.Y. Li, F.Q. Zu, W. Wu, X.F. Zhang, D.S. Feng Liquid-liquid structure transition in Sn-3.5Ag–3.5Bi melts, Phase Transitions, doi:10.1080/01411594.2012.671321
J. Chen, F.Q. Zu, Y. Xi, X.F. Li, Effects of different types of liquid structure transition on solidification of CuSn80 Alloy. T. Nonferr. Metal. Soc. 17-S1, 71–75 (2007). in Chinese
C.W. Hwang, J.G. Lee, K. Suganuma, H. Mori, Interfacial microstructure between Sn–3Ag–xBi alloy and Cu substrate with or without electrolytic Ni plating. J. Electron. Mater. 32, 52–62 (2003)
W. Yang, R.W. Messler, Microstructure evolution of eutectic Sn–Ag solder joints. J. Electron. Mater. 23, 765–772 (1994)
C.K. Alex, Y.C. Chan, Aging studies of Cu–Sn intermetallic compounds in annealed surface mount solder joints. Elect. Comp. Technol. Conf. 5, 1164–1171 (1996)
W.J. Tomlinson, H.G. Rhodes, Kinetics of intermetallic compound growth between nickel, electroless, Ni–P, electroless Ni–B and tin at 453 to 493 K. J. Mater. Sci. 22, 1769–1772 (1987)
D. Gur, M. Bamberger, Reactive isothermal solidification in the Ni–Sn system. Acta Mater. 46, 4917–4923 (1998)
C.Y. Lee, K.L. Lin, The interaction kinetics and compound formation between electroless Ni–P and solder. Thin Solid Films 249, 201–206 (1994)
J.W. Yoon, C.B. Lee, S.B. Jung, Growth of an intermetallic compound layer with Sn–3.5Ag–5Bi on Cu and Ni–P/Cu during Aging Treatment. J. Electron. Mater. 32, 1195–1202 (2003)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 50571033), and by the Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province (No. 070414178), and HFUT Research and Development Funds (No. 2009HGXJ0090).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Zu, F., Huang, Z. et al. Correlation of intermetallic compound growth behavior and melt state of Sn–3.5Ag–3.5Bi/Cu joint during soldering and isothermal aging. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 24, 1231–1237 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-012-0912-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-012-0912-5