Abstract
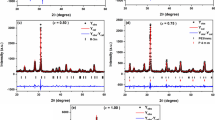
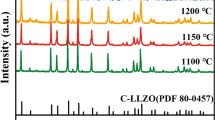
The effects of Ti-doping on the decomposition behavior, crystal structure, sintering behavior and dielectric properties have been investigated for the Ti-doped BiFeO3 ceramics derived from molten salt method. XRD reveals the almost pure phase BiFeO3 is synthesized in the Ti-doped BiFeO3 powders. And the particle size of Ti-doped BiFeO3 powers obviously decreases with the increase of Ti content. However, the sintering temperature elevates significantly after Ti-doping. The DC resistivity can enhance by up to four orders of magnitude (from 104 to 108 Ωm) with only 5 at% Ti doping. But the dielectric constant is suppressed from 104 to 102, and dielectric loss obviously reduces with a small amount of Ti doping. The variation of dielectric properties has been discussed from the decomposition of BiFeO3 phase. The Ti-doping can effectively suppress the decomposition reaction in Ti-doped BiFeO3 ceramics.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. Eerenstein, N.D. Mathur, J.F. Scott, Nature 442, 759 (2006)
M. Fiebig, T. Lottermoser, D. Frohlich, A.V. Goltsev, R.V. Pisarev, Nature 419, 818 (2002)
G. Catalan, J.F. Scott, Adv. Mater. 21, 2463 (2009)
Zheng XH, Chen PJ, Ma N, Ma ZH (2011) J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. doi:10.1007/s10854-011-0533-4
J. Wang, J.B. Neaton, H. Zheng, Science 299, 1719 (2003)
Y.P. Wang, L. Zhou, M.F. Zhang, X.Y. Chen, J.M. Liu, Z.G. Liu, Appl. Phys. Lett. 84, 1731 (2004)
Y. Wang, C.W. Nan, Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 052903 (2006)
M.I. Morozov, N.A. Lomanova, V.V. Gusarov, Russ. J. Gen. Chem. 73, 1676 (2003)
A. Maitre, M. Francois, J.C. Gachon, J. Phase Equilibria. Diffusion 25, 59 (2004)
S.M. Selbach, M.A. Einarsrud, T. Grande, Chem. Mater. 21, 169 (2009)
M.M. Kumar, V.R. Palkar, K. Srinivas, V. Suryanarayana, Appl. Phys. Lett. 76, 2764 (2000)
M. Kumar, K.L. Yadav, J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 18, L503 (2006)
C. Lepoittevin, S. Malo, N. Barrier, N. Nguyen, G.V. Tendeloo, M. Hervieu, J. Solid State Chem. 181, 2601 (2008)
J. Schiemer, R. Withers, L. Noren, Y. Liu, L. Bourgeois, G. Stewart, Chem. Mater. 21, 4223 (2009)
Y. Wang, G. Xu, Ceram. Inter. 35, 1285 (2009)
J.H. Xu, H. Ke, D.C. Jia, W. Wang, Y. Zhou, J. Alloys Comp. 472, 473 (2009)
L. Zhang, X.F. Cao, Y.L. Ma, X.T. Chen, Z.L. Xue, J. Solid State Chem. 181, 1761 (2010)
J. Chen, X.R. Xing, A. Watson, W. Wang, R.B. Yu, J.X. Deng, L. Yan, C. Sun, X.B. Chen, Chem. Mater. 19, 3598 (2007)
X. He, L. Gao, Ceram. Inter. 35, 975 (2009)
K.L. Yadav, J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 11, 2682 (2011)
M. Valant, A.K. Axelsson, N. Alford, Chem. Mater. 19, 5431 (2007)
X.H. Zheng, C. Zhang, B.L. Liang, D.P. Tang, X. Huang, X.L. Liu, J. Alloys Compd. 505, L10 (2010)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University of Fujian Province (XSJRC2007-16) and Fuzhou University Science Foundation (2010-XQ-01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, X.H., Ma, Z.H., Chen, P.J. et al. Decomposition behavior and dielectric properties of Ti-doped BiFeO3 ceramics derived from molten salt method. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 23, 1533–1537 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-012-0624-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-012-0624-x