Abstract
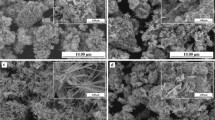
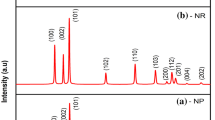
ZnO nanostructures have been synthesized in a controlled manner by varying the pH of the precursor solution using hydrothermal technique. The morphological changes of the prepared ZnO nanostructures have been investigated in the range of pH 5–10. Radial hexagonal rod-like shape is formed at lower pH values of 5 and 6 whereas, flower-like shape is obtained for higher pH values of 9 and 10. Flake-like structure is observed at moderate pH of 8. The prepared ZnO nanostructures have been characterized using X-ray diffraction technique (XRD), energy dispersive X-ray analysis, scanning electron microscope and FTIR spectroscopy. XRD results show that the prepared ZnO nanostructures exhibit hexagonal wurtzite structure. The growth mechanism suggests that the supersaturation of the precursor results in various nucleation habits, which induce the formation of ZnO nanostructures with different morphologies. UV–Vis spectroscopy and photoluminescence were applied to study the optical properties. The photoluminescence spectrum demonstrated two emission bands, a near band edge emission in the UV region and a strong deep band emission in the visible region. The change in pH from 5 to 10 results in band gap variations of 3.47–3.97 eV and blue-shift in the peak emission of visible PL from 560 to 460 nm.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Yu, L. Hong-Bing, L. Lei, L. Jin-Chai, W. Yun, F. Qiang, Phys. E 41, 729 (2009)
M.H. Kim, Y.H. Cho, H. Lee, S.I. Kim, S.R. Ryu, D.Y. Kim, T.W. Kang, K.S. Chung, Nano Lett. 4, 1059 (2004)
W. Zhang-lin, J. Mater. Chem. 15, 1021 (2005)
W. Zhong-lin, J. Mater. Today 7, 26 (2004)
W.C. Shih, M.S. Wu, J. Cryst. Growth 137, 319 (1994)
Y. Sun, G.M. Fuge, M.N.R. Ashfold, Chem. Phys. Lett. 396, 21 (2004)
Y.W. Heo, V. Varadarajan, M. Kaufman, K. Kim, D.P. Norton, Appl. Phys. Lett. 81, 3046 (2002)
J.Q. Hu, X.L. Ma, Z.Y. Xie, N.B. Wong, C.S. Lee, S.T. Lee, Chem. Phys. Lett. 344, 97 (2001)
J.J. Wu, S.C. Liu, Adv. Mater. 14, 215 (2002)
B. Illy, B.A. Shollock, J.L. MacManus-Driscoll, M.P. Ryan, Nanotechnology 16, 320 (2005)
S.A. Studenkin, N. Golego, M. Cocivera, J. Appl. Phys. 83, 2104 (1998)
M. Ohyama, H. Kozuka, T. Yoko, Thin Solid Films 306, 78 (1997)
D. Vernardou, G. Kenanakis, S. Couris, A.C. Manikas, G.A. Voyiatzis, M.E. Pemble, E. Koudoumas, N. Katsarakis, J. Cryst. Growth 308, 105 (2007)
N. Rajeswari Yogamalar, R. Srinivasan, A. Chandra Bose, Opt. Mater. 31, 1570 (2009)
O. Lupan, L. Chowa, G. Chai, B. Roldan, A. Naitabdi, A. Schulte, H. Heinrich, Mater. Sci. Eng. B 145, 57 (2007)
L.E. Greene, M. Law, J. Goldberger, F. Kim, J.C. Johnson, Y.F. Zhang, R.J. Saykally, P. Yang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 42, 3031 (2003)
S.J. Henley, M.N.R. Ashfold, D.P. Nicholls, P. Wheatley, D. Cherns, Appl. Phys. A 79, 1169 (2004)
Y. Tong, Y. Liu, L. Dong, D. Zhao, J. Zhang, Y. Lu, D. Shen, X. Fan, J. Phys. Chem. B 110, 20263 (2006)
U. Pal, P. Santiago, J. Phys. Chem. B 109, 32 (2005)
X. Gao, X. Li, W. Yu, J. Phys. Chem. B 109, 1155 (2005)
S. Maensiri, C. Masingboon, V. Promarak, S. Seraphin, Opt. Mat. 29, 1700 (2007)
H. Wei, Y. Wu, N. Lun, C. Hu, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 80, 393 (2005)
E. Ziegler, A. Heinrich, H. Oppermann, G. Stover, Phys. Status Solidif. A 66, 635 (1981)
F. Xu, Y. Lu, Y. Xie, Y. Liu, J. Phys. Chem. C 113, 3 (2009)
M. Ghosh, A.K. Raychaudhuri, Nanotechnology 19, 445704 (2008)
C.Y. Jiang, X.W. Sun, G.Q. Lo, D.L. Kwong, J.X. Wang, Appl. Phys. Lett. 90, 263501 (2007)
H.-S. Goh, R. Adnan, M.A. Farrukh, Turk. J. Chem. 35, 375 (2011)
W. Yang, Q. Li, S. Gao, J.K. Shang, Nanoscale Res. Lett. 6, 491 (2011)
G.-C. Yi, C. Wang, W. Park II, Semicond. Sci. Technol. 20, S22 (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sambath, K., Saroja, M., Venkatachalam, M. et al. Morphology controlled synthesis of ZnO nanostructures by varying pH. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 23, 431–436 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-011-0507-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-011-0507-6